Spring 是什么?:
一个开源的分层的轻量级框架
(轻量级:与EJB对比,依赖的资源少,消耗的资源少)
分层 web: service: dao:
Spring的核心是:
控制反转(IoC)
切面编程(AOP)
Spring的优点:
1.方便解耦,简化开发(高内聚低耦合)
Spring就是一歌工厂,可以将所有的对象和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理,
2.AOP编程支持
3.方便食物的测试
4.方便集成各种优秀的框架
5.降低JavaEE api的使用难度
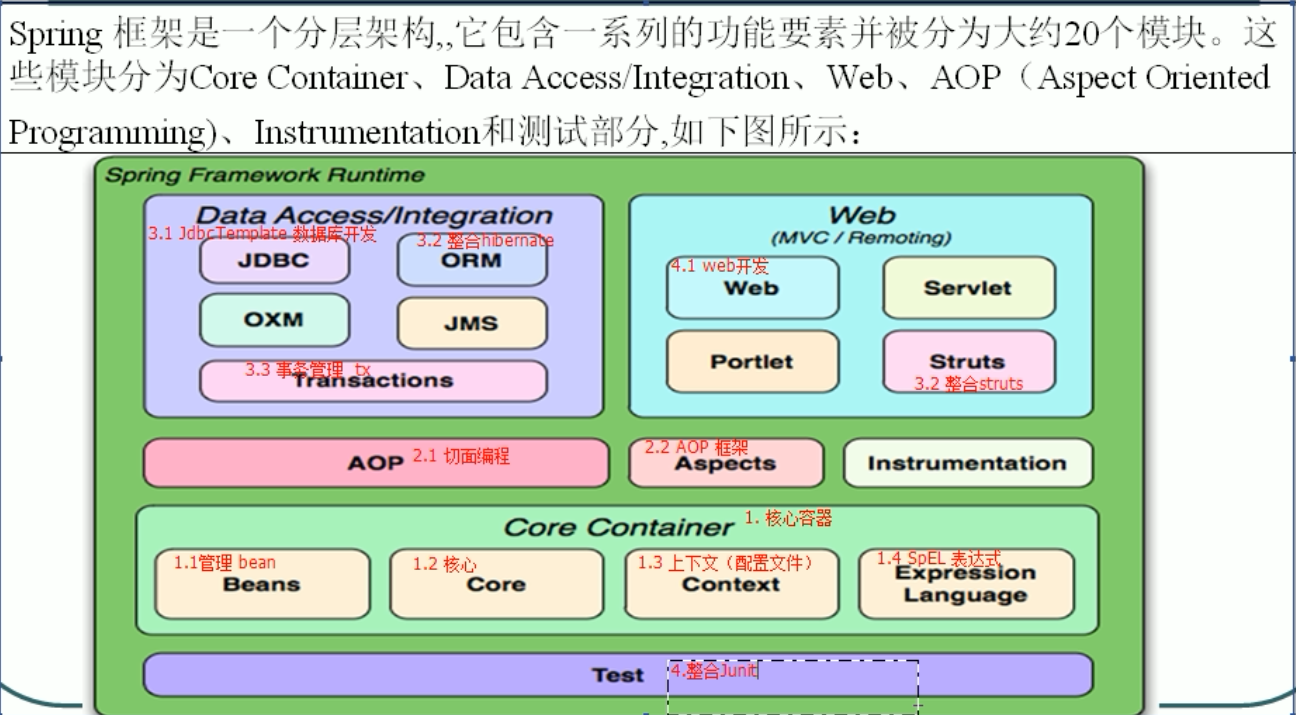
核心容器:beans core contest expression
2 入门案例:
2.1 导入jar包
4+1:4个核心(beans core contest expression) 一个依赖(commons-logging...jar)
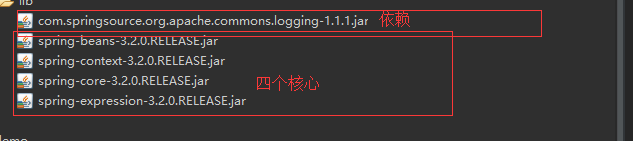
2.2配置文件
位置:一般在classPath下(src)
名称:任意 开发中一般是applicationContext.xml
内容:添加(schema)约束
约束文件的位置:
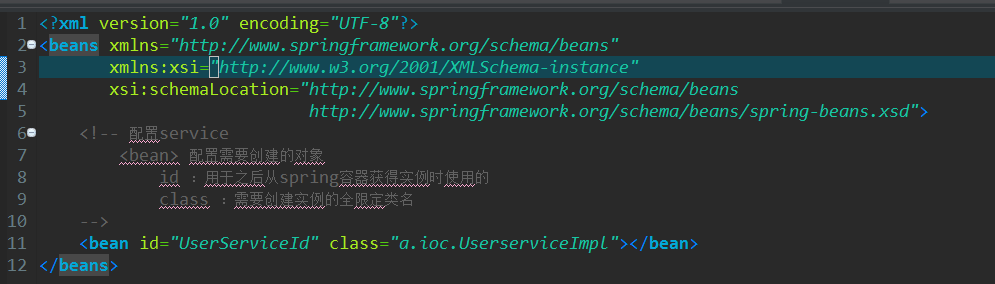
配置文件
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 6 <!-- 配置service 7 <bean> 配置需要创建的对象 8 id :用于之后从spring容器获得实例时使用的 9 class :需要创建实例的全限定类名 10 --> 11 <bean id="UserServiceId" class="a.ioc.UserserviceImpl"></bean> 12 </beans>
实现类
package a.ioc; public class UserserviceImpl implements Uservice { @Override public void addUser() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("this is add" + "User"); } }
service
package a.ioc; public interface Uservice { public void addUser(); }
测试类
package a.ioc; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestIoc { @Test public void demo01(){ //之前开发 Uservice userService=new UserserviceImpl(); userService.addUser(); } @Test public void demo02(){ //从Spring 容器中获得 //1获得容器 String xmlPath="a/ioc/beans.xml"; ApplicationContext application =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); //获取内容--不需要自己去new 都是从容器中获取 Uservice Uservice =(a.ioc.Uservice) application.getBean("UserServiceId"); Uservice.addUser(); } }