stream
Java8新特性Stream流,那Stream表达式到底是什么呢,为什么可以使你的代码更加整洁而且对集合的操作效率也会大大提高?
一、概述
1、什么是Stream
Stream是一种可供流式操作的数据视图有些类似数据库中视图的概念,它不改变源数据集合如果对其改变的操作它会返回一个新的数据集合
总的来说它有三大特性:在之后我们会对着详细说明
1、stream不存储数据
2、stream不改变源数据
3、stream的延迟执行特性
2、Stream的优点
1、代码简洁,函数式编程写出的代码简洁且意图明确,使用stream接口让你从此告别for循环
2、多核友好,Java函数式编程使得编写并行程序从未如此简单,你需要的全部就是调用一下parallel()方法
3、Stream API常用方法
| Stream操作分类 | ||
| 中间操作(Intermediate operations) | 无状态(Stateless) |
unordered() filter() map() mapToInt() mapToLong() mapToDouble() flatMap() flatMapToInt() flatMapToLong() flatMapToDouble() peek() |
| 有状态(Stateful) | distinct() sorted() sorted() limit() skip() | |
| 结束操作(Terminal operations) | 非短路操作 |
forEach() forEachOrdered() toArray() reduce() collect() max() min() count() |
| 短路操作(short-circuiting) | anyMatch() allMatch() noneMatch() findFirst() findAny() | |
Stream上的所有操作分为两类:中间操作和结束操作,中间操作只是一种标记,只有结束操作才会触发实际计算。
中间操作又分为无状态和有状态的:
无状态中间操作是指元素的处理不受前面元素的影响,而有状态的中间操作必须等到所有元素处理之后才知道最终结果,比如排序是有状态操作,在读取所有元素之前并不能确定排序结果。
结束操作又分为短路操作和非短路操作:
短路操作是指不用处理全部结果就可以返回结果,比如找到第一个满足条件的元素,之所以要进行如此精细的划分,是因为底层对每一种情况的处理方式不同
常用中间件
filter:过滤流,过滤流中的元素,返回一个符合条件的Stream
map:转换流,将一种类型的转换为另外一种流。(mapToInt、mapToLong、mapToDouble返回int、long、double基本类型对应的Stream)
flatMap:简单的说,就是一个或多个流合并成一个新的流( flatMapToInt、 flatMapToLong、flatMapToDouble返回对应的IntStream、LongStream、DoubleStream流)
distinct:返回去重的Stream
sorted:返回一个排序的Stream
peek:主要用来查看流中元素的数据状态
limit:返回前n个元素数据组成的Stream.属于短路操作
skip:返回第n个元素后面数据组成的Stream
结束操作
forEach:循环操作Stream中数据
toArray:返回流中元素对应的数组对象
reduce:聚合操作,用来做统计
collect:聚合操作,封装目标数据
min、max、count:聚合操作,最小值,最大值,总数量
anyMatch:短路操作,有一个符合条件返回true
allMatch:所有数据都符合条件返回true
noneMatch:所有数据都不符合条件返回true
findFirst:短路操作,获取第一个元素
findAny:短路操作,获取任一元素
forEachOrdered:暗元素顺序执行循环操作
二、各种案例说明
首先写一个实体类对象
public class Person { private Integer id; private String name; private String sex; private Integer age; //提供get、set和满参构造函数 }
1、map中间件相关例子
public class TestMap { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Person> persionList = new ArrayList<Person>(); persionList.add(new Person(1, "张三", "男", 38)); persionList.add(new Person(2, "小小", "女", 2)); persionList.add(new Person(3, "李四", "男", 65)); persionList.add(new Person(4, "王五", "女", 20)); persionList.add(new Person(5, "赵六", "男", 38)); persionList.add(new Person(6, "大大", "男", 65)); //只取出该集合所有姓名组成一个新集合 List<String> nameList = persionList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(nameList.toString()); //只取出该集合中所有id组成一个新的集合 List<Integer> idList = persionList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getId).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(idList.toString()); //list转map key值为id,value为person对象 Map<Integer, Person> personMap = persionList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getId, person -> person)); System.out.println(personMap.toString()); //list转map,key值为id,value为name Map<String, Integer> nameMap = persionList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Person::getAge)); System.out.println(nameMap.toString()); //进行map集合存放,key为age值,value为person对象,它会把相同age的对象放到一个集合中 Map<Integer, List<Person>> ageMap = persionList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge)); System.out.println(ageMap.toString()); //获取最小年龄 Integer ageMin = persionList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).min().getAsInt(); System.out.println("最小年龄"+ageMin); //获取最大年龄 Integer ageMax = persionList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).max().getAsInt(); System.out.println("最大年龄"+ageMax); //年龄属性求和 Integer sum = persionList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getAge).sum(); System.out.println("年龄总和为:"+sum);
运行结果:
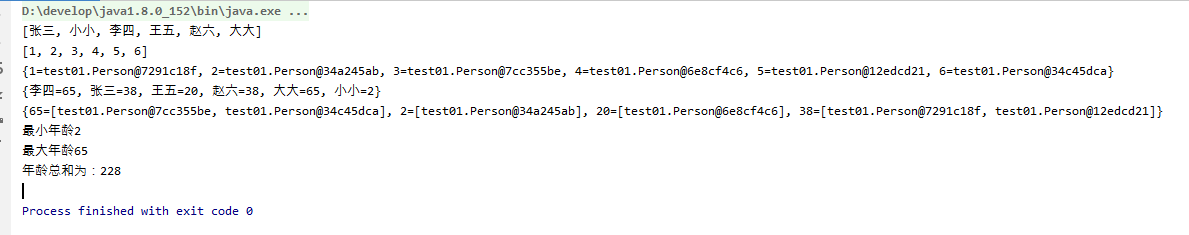
是不是之前要好几层的for循环解决的问题,通过Stream只要一行代码就可以解决了。
这里要注意,如果你list转map的key如果不唯一,会报错,所以如果你不确定你的key是否唯一,可以改成如下:
Map<Integer,String> map=persionList.stream().collect( Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge,Person::getName,(key1,key2)->key1) );
2、filter相关例子:
public class TestFilter { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Person> persionList = new ArrayList<Person>(); persionList.add(new Person(1, "张三", "男", 8)); persionList.add(new Person(2, "小小", "女", 2)); persionList.add(new Person(3, "李四", "男", 25)); persionList.add(new Person(4, "王五", "女", 8)); persionList.add(new Person(5, "赵六", "女", 25)); persionList.add(new Person(6, "大大", "男", 65)); //1、查找年龄大于20岁的人数 long age=persionList.stream().filter(p->p.getAge()>20).count(); System.out.println(age); //2、查找年龄大于20岁,性别为男的人数 List<Person> ageList=persionList.stream().filter(p->p.getAge()>20).filter(p->"男".equals(p.getSex())).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(ageList.size()); } /* *运行结果: * 3 * 2 */ }
3、sorted相关例子
对于数组举例
public class TestSort { String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"}; /** * 按照字符长度排序 */ @Test public void testSorted1_(){ Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println); //输出:a、bc、abc、abcd } /** * 倒序 * reversed(),java8泛型推导的问题,所以如果comparing里面是非方法引用的lambda表达式就没办法直接使用reversed() * Comparator.reverseOrder():也是用于翻转顺序,用于比较对象(Stream里面的类型必须是可比较的) * Comparator. naturalOrder():返回一个自然排序比较器,用于比较对象(Stream里面的类型必须是可比较的) */ @Test public void testSorted2_(){ Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println); //输出:abcd、abc、bc、a Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).forEach(System.out::println); //输出:bc、abcd、abc、a Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.naturalOrder()).forEach(System.out::println); //输出:a、abc、abcd、bc } /** * 先按照首字母排序 * 之后按照String的长度排序 */ @Test public void testSorted3_(){ Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(this::com1).thenComparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println); } //输出:a、abc、abcd、bc public char com1(String x){ return x.charAt(0); } }
对于集合举例
public class TestSort { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Person> persionList = new ArrayList<Person>(); persionList.add(new Person(1, "张三", "男", 8)); persionList.add(new Person(2, "小小", "女", 2)); persionList.add(new Person(3, "李四", "男", 25)); persionList.add(new Person(4, "王五", "女", 8)); persionList.add(new Person(5, "赵六", "女", 25)); persionList.add(new Person(6, "大大", "男", 65)); //1、找到年龄最小的岁数 Collections.sort(persionList, (x, y) -> x.getAge().compareTo(y.getAge())); Integer age = persionList.get(0).getAge(); System.out.println("年龄最小的有:" + age); //输出:年龄最小的有:2 //2、找到年龄最小的姓名 String name = persionList.stream() .sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x.getAge())) .findFirst() .get().getName(); System.out.println("年龄最小的姓名:" + name); //输出:年龄最小的姓名:小小 } }