本文为自学记录,部分内容转载于
python3网络爬虫实战
知乎专栏:写点python
如有侵权,请联系删除。
语法
1、选取节点
XPath 使用路径表达式在 XML 文档中选取节点。节点是通过沿着路径或者 step 来选取的。
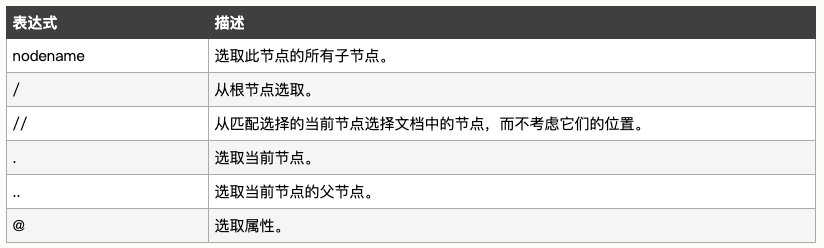
实例解释
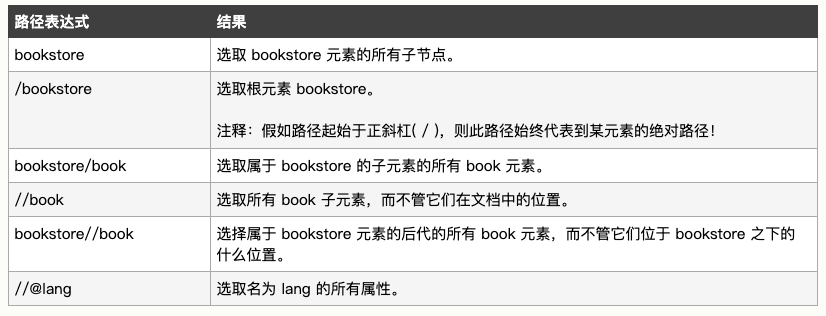
2、谓语
谓语用来查找某个特定的节点或者包含某个指定的值的节点。
谓语被嵌在方括号中。
text =''' <bookstore> <book> <title lang="eng">Harry Potter</title> <price>29.99</price> </book> <book> <title lang="eng">Learning XML</title> <price>39.95</price> </book> </bookstore> ''' from lxml import etree # 初始化,构造xpath解析对象 html = etree.HTML(text) # 修正HTML代码,结果为bytes类型,还需要转化为str类型 # html = etree.tostring(html,encoding='utf-8') result = html.xpath('//@lang') print(result)
结果:
['eng', 'eng']
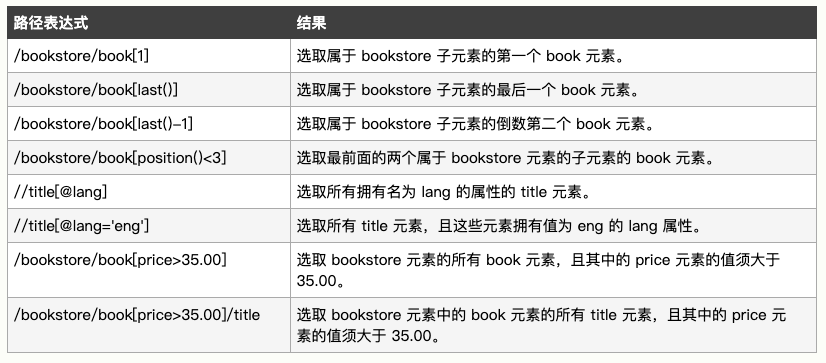
3、选取未知节点

4、选取若干路径

实例
from lxml import etree myPage = '''<html> <title>TITLE</title> <body> <h1>我的博客</h1> <div>我的文章</div> <div id="photos"> <img src="pic1.jpeg"/><span id="pic1">PIC1 is beautiful!</span> <img src="pic2.jpeg"/><span id="pic2">PIC2 is beautiful!</span> <p><a href="http://www.example.com/more_pic.html">更多美图</a></p> <a href="http://www.baidu.com">去往百度</a> <a href="http://www.163.com">去往网易</a> <a href="http://www.sohu.com">去往搜狐</a> </div> <p class="myclassname">Hello, world!<br/>-- by Adam</p> <div class="foot">放在尾部的其他一些说明</div> </body> </html>''' html = etree.HTML(myPage) # 定位 div1 = html.xpath('//div') div2 = html.xpath('//div[@id]') div3 = html.xpath('//div[@class="foot"]') div4 = html.xpath('//div[@*]') div5 = html.xpath('//div[1]') div6 = html.xpath('//div[last()-1]') div7 = html.xpath('//div[position()<3]') div8 = html.xpath('//div|//h1') div9 = html.xpath('//div[not(@*)]') # 取文本text()区别html.xpath('string()') text1 = html.xpath('//div/text()') text2 = html.xpath('//div[@id]/text()') text3 = html.xpath('//div[@class="foot"]/text()') text4 = html.xpath('//div[@*]/text()') text5 = html.xpath('//div[1]/text()') text6 = html.xpath('//div[last()-1]/text()') text7 = html.xpath('//div[position()<3]/text()') text8 = html.xpath('//div/text()|//h1/text()') text9 = html.xpath('//div[not(@*)]/text()') # 取属性 value1 = html.xpath('//a/@href') value2 = html.xpath('//img/@src') value3 = html.xpath('div[2]/span/@id') # print(value1) # print(value2) # print(value3) # 定位(进阶) a_href = html.xpath('//div[position()<3]/a/@href') print(a_href) a_href = html.xpath('//div[position()<3]//a/@href') print(a_href)
实例2
在上一篇爬取猫眼TOP100里面,我们是用正则表达式去进行解析的,这里用xpath进行解析测试
from lxml import etree html = ''' <dd> <i class="board-index board-index-1">1</i> <a href="/films/1203" title="霸王别姬" class="image-link" data-act="boarditem-click" data-val="{movieId:1203}"> <img src="//s0.meituan.net/bs/?f=myfe/mywww:/image/loading_2.e3d934bf.png" alt="" class="poster-default" /> <img data-src="https://p1.meituan.net/movie/20803f59291c47e1e116c11963ce019e68711.jpg@160w_220h_1e_1c" alt="霸王别姬" class="board-img" /> </a> <div class="board-item-main"> <div class="board-item-content"> <div class="movie-item-info"> <p class="name"><a href="/films/1203" title="霸王别姬" data-act="boarditem-click" data-val="{movieId:1203}">霸王别姬</a></p> <p class="star"> 主演:张国荣,张丰毅,巩俐 </p> <p class="releasetime">上映时间:1993-01-01</p> </div> <div class="movie-item-number score-num"> <p class="score"><i class="integer">9.</i><i class="fraction">5</i></p> </div> </div> </div> </dd> ''' # 初始化 html = etree.HTML(html) # html = etree.tostring(html, encoding='utf-8') # print(html.decode('utf-8')) # print(type(html)) # print(html)
# 排名 index = html.xpath('//dd/i[@class="board-index board-index-1"]/text()') print(index)
# 图片 image = html.xpath('//dd/a/img/@data-src') print(image)
# 标题 title = html.xpath('//dd/div/div/div/p/a/text()') print(title)
# 演员 star = html.xpath('//dd/div/div/div/p[@class="star"]/text()') print(star)
# 上映时间 time = html.xpath('//dd/div/div/div/p[@class="releasetime"]/text()') print(time)
# 评分 sorce = html.xpath('//dd/div/div/div/p/i[@class="integer"]/text()') print(sorce) sorce2 = html.xpath('//dd/div/div/div/p/i[@class="fraction"]/text()') print(sorce2)
结果:
