数组基本知识
数组对于每一门编程语言来说都是重要的数据结构之一,当然不同语言对数组的实现及处理也不尽相同。
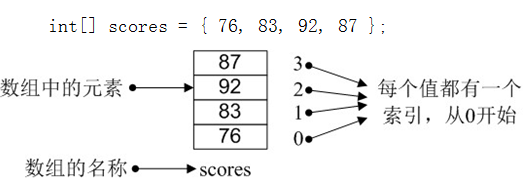
Java语言中提供的数组是用来存储固定大小的同类型元素。
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组,保存五名学生的成绩
int[] scores = { 78, 93, 97, 84, 63 };
// 输出数组中的第二个成绩
System.out.println("数组中的第2个成绩为:" + scores[1]);
}
}
数组的基本使用
1、 声明数组
语法: 数据类型[ ] 数组名;
或者 数据类型 数组名[ ];
其中,数组名可以是任意合法的变量名,如:

2、 分配空间
简单地说,就是指定数组中最多可存储多少个元素
语法: 数组名 = new 数据类型 [ 数组长度 ];
其中,数组长度就是数组中能存放元素的个数,如:

话说,我们也可以将上面的两个步骤合并,在声明数组的同时为它分配空间,如:
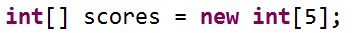
3、 赋值
分配空间后就可以向数组中放数据了,数组中元素都是通过下标来访问的,例如向 scores 数组中存放学生成绩

4、 处理数组中数据
我们可以对赋值后的数组进行操作和处理,如获取并输出数组中元素的值

在 Java 中还提供了另外一种直接创建数组的方式,它将声明数组、分配空间和赋值合并完成,如

它等价于:

使用循环操作 Java 中的数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个数组,保存五名学生的成绩
int[] scores = { 78, 93, 97, 84, 63 };
//for循环打印
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
System.out.print(scores[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//foreach打印
//foreach是for语句的特殊简化版本,在遍历数组、集合时, foreach更简单便捷。
//for(元素类型 变量:遍历对象){
//执行的代码
//}
for (int i : scores) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
执行结果
78 93 97 84 63
78 93 97 84 63
编程练习
package com.zhb;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[] { 61, 23, 4, 74, 13, 148, 20 };
int max = nums[0]; // 假定最大值为数组中的第一个元素
int min = nums[0]; // 假定最小值为数组中的第一个元素
double sum = 0;// 累加值
double avg = 0;// 平均值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 循环遍历数组中的元素
// 如果当前值大于max,则替换max的值
if(nums[i]> max){
max = nums[i];
}
// 如果当前值小于min,则替换min的值
if(nums[i]< min){
min = nums[i];
}
// 累加求和
sum+=nums[i];
}
// 求平均值
avg = sum/nums.length;
System.out.println("数组中的最大值:" + max);
System.out.println("数组中的最小值:" + min);
System.out.println("数组中的平均值:" + avg);
}
}
输出结果
数组中的最大值:148
数组中的最小值:4
数组中的平均值:49.0
使用 Arrays 类操作 Java 中的数组
Arrays 类是 Java 中提供的一个工具类,在 java.util 包中。该类中包含了一些方法用来直接操作数组,比如可直接实现数组的排序、搜索等.
package com.zhb;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串数组
String[] hobbys = { "sports", "game", "movie" };
// 使用Arrays类的sort()方法对数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(hobbys);
// 使用Arrays类的toString()方法将数组转换为字符串并输出
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(hobbys) );
}
}
执行结果
[game, movie, sports]
构建动态数组
其实,这里就是类似模拟实现ArrayList类的实现。这里只是简化了部分。主要是代码
首先我们先构建一个int类型的动态数组
- 这里默认容量为10和ArrayList一致,这也告诉我们ArrayList默认容量为10,其中阿里规约提到,使用集合时,要指定集合初始值大小
/**
* 动态int数组
*
* @author: curry
* @Date: 2018/8/2
*/
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
/**
* 构造函数。传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
*
* @param capacity
*/
public Array(int capacity) {
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
/**
* 无参构造函数,默认容量为10
*/
public Array() {
this(10);
}
/**
* 获取数组中的元素个数
*
* @return
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* 获取数组容量
*
* @return
*/
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length;
}
/**
* 返回数组是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 向数组最后添加元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void addLast(int e) {
add(size, e);
}
/**
* 向数组最后增加一个元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void addFirst(int e) {
add(0, e);
}
/**
* 向index位置增加元素e
*
* @param index
* @param e
*/
public void add(int index, int e) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
//判断容量是否超出
if (size == data.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Array is full");
}
//将index后面的值进行后移
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
data[i + 1] = data[i];
}
//赋值到index 位置
data[index] = e;
size++;
}
/**
* 获取index索引位置的值
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public int get(int index) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
return data[index];
}
public void set(int index, int e) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
data[index] = e;
}
/**
* 查找数组中的是否有元素
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(int e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i] == e) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 查找数组中元素e所在的索引
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public int find(int e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i] == e) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 删除索引为index的值
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public int remove(int index) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
int ret = data[index];
for (int i = index; i < size; i++) {
data[i] = data[i + 1];
}
size--;
return ret;
}
/**
* 删除第一个元素
*
* @return
*/
public int removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
/**
* 删除最后一个元素
*
* @return
*/
public int removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
/**
* 删除数组中的元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void removeElement(int e) {
int index = find(e);
if (index != -1) {
remove(index);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d
", size, data.length));
res.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
res.append(data[i]);
if (i != size - 1) {
res.append(", ");
}
}
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
}
修改上面的代码,加入泛型
- 注意:这里增加了resize方法,用于扩容,因为底层还是数组实现的,所以当数组的长度不够的时候,需要扩容,这里扩容为原先长度的2倍。ArrayList中为1.5倍
/**
* 使用泛型
*
* @author: curry
* @Date: 2018/8/2
*/
public class Array1<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
/**
* 构造函数。传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
*
* @param capacity
*/
public Array1(int capacity) {
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
/**
* 无参构造函数,默认容量为10
*/
public Array1() {
this(10);
}
/**
* 获取数组中的元素个数
*
* @return
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
/**
* 获取数组容量
*
* @return
*/
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length;
}
/**
* 返回数组是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 向数组最后添加元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
add(size, e);
}
/**
* 向数组最后增加一个元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0, e);
}
/**
* 向index位置增加元素e
*
* @param index
* @param e
*/
public void add(int index, E e) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
//判断容量是否超出
if (size == data.length) {
resize(2 * data.length);
}
//将index后面的值进行后移
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
data[i + 1] = data[i];
}
//赋值到index 位置
data[index] = e;
size++;
}
/**
* 获取index索引位置的值
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E get(int index) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
return data[index];
}
public void set(int index, E e) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
data[index] = e;
}
/**
* 查找数组中的是否有元素
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 查找数组中元素e所在的索引
*
* @param e
* @return
*/
public int find(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 删除索引为index的值
*
* @param index
* @return
*/
public E remove(int index) {
// 判断index 是否合法
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is error");
}
E ret = data[index];
for (int i = index; i < size; i++) {
data[i] = data[i + 1];
}
size--;
data[size] = null;
return ret;
}
/**
* 删除第一个元素
*
* @return
*/
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
/**
* 删除最后一个元素
*
* @return
*/
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
/**
* 删除数组中的元素
*
* @param e
*/
public void removeElement(E e) {
int index = find(e);
if (index != -1) {
remove(index);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d
", size, data.length));
res.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
res.append(data[i]);
if (i != size - 1) {
res.append(", ");
}
}
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
/**
* 扩容
*
* @param newCapacity
*/
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
newData[i] = data[i];
}
data = newData;
}
}
其实,这里写的动态数组,也是在实现一个简单的ArrayList类。