数据准备
1 %matplotlib notebook 2 import numpy as np 3 import pandas as pd 4 import seaborn as sn 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer 7 8 # Breast cancer dataset 9 cancer = load_breast_cancer() 10 (X_cancer, y_cancer) = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y = True) 11 12 # Our sample fruits dataset 13 fruits = pd.read_table('fruit_data_with_colors.txt') 14 X_fruits = fruits[['mass','width','height', 'color_score']] 15 y_fruits = fruits[['fruit_label']] - 1
降维和流形学习
PCA
使用PCA查找乳腺癌数据集的前两个主要组成部分
1 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 2 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA 3 from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer 4 5 cancer = load_breast_cancer() 6 (X_cancer, y_cancer) = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y = True) 7 8 # Before applying PCA, each feature should be centered (zero mean) and with unit variance 9 X_normalized = StandardScaler().fit(X_cancer).transform(X_cancer) 10 #n_components设置主成分个数 11 pca = PCA(n_components = 2).fit(X_normalized) 12 13 X_pca = pca.transform(X_normalized) 14 print(X_cancer.shape, X_pca.shape)
(569, 30) (569, 2)
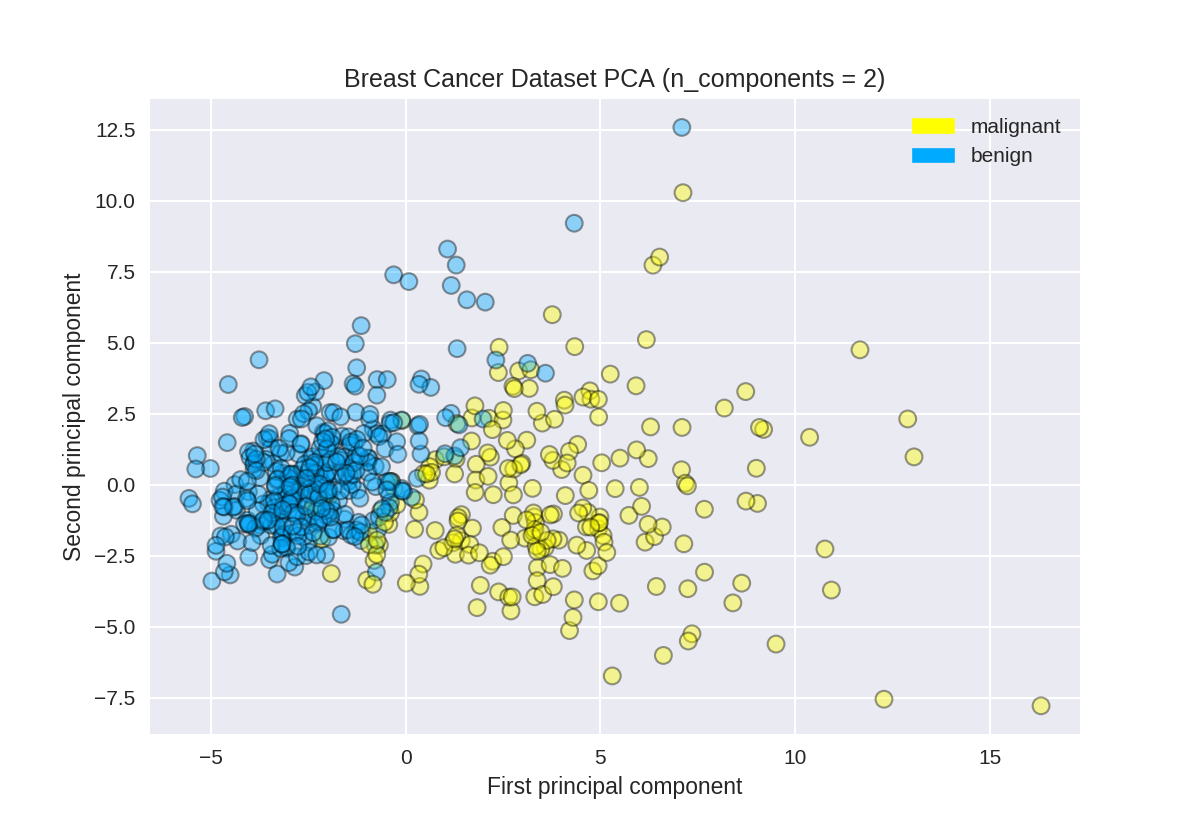
绘制乳腺癌数据集的PCA转换版本
1 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 2 plot_labelled_scatter(X_pca, y_cancer, ['malignant', 'benign']) 3 4 plt.xlabel('First principal component') 5 plt.ylabel('Second principal component') 6 plt.title('Breast Cancer Dataset PCA (n_components = 2)');
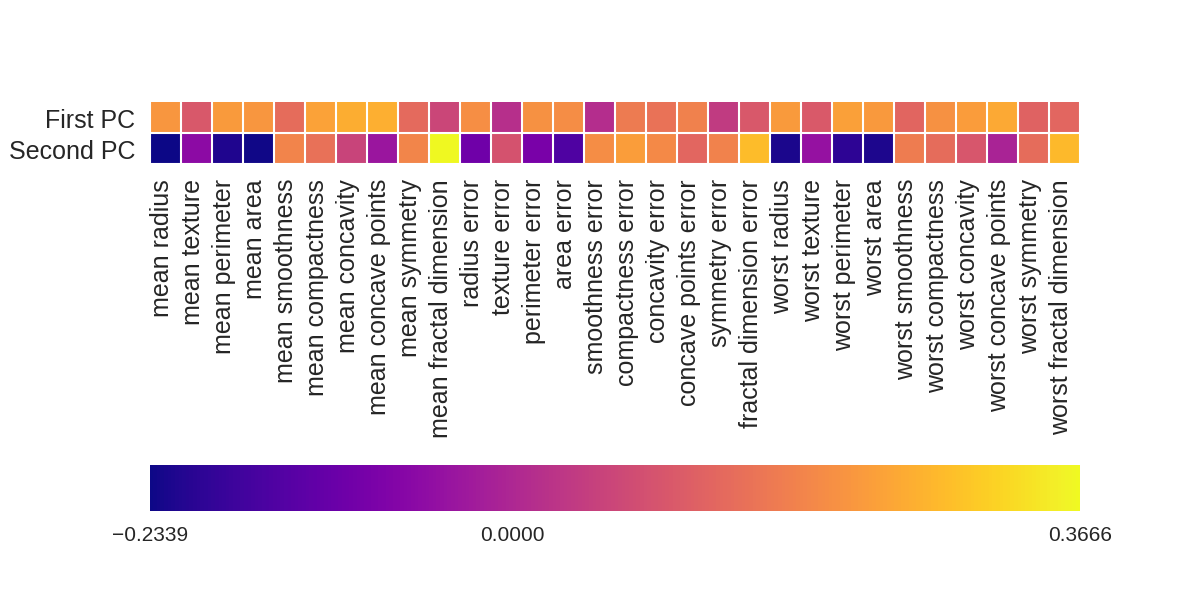
画出各个因素对两个主成分的影响大小
1 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4)) 2 plt.imshow(pca.components_, interpolation = 'none', cmap = 'plasma') 3 feature_names = list(cancer.feature_names) 4 5 plt.gca().set_xticks(np.arange(-.5, len(feature_names))); 6 plt.gca().set_yticks(np.arange(0.5, 2)); 7 plt.gca().set_xticklabels(feature_names, rotation=90, ha='left', fontsize=12); 8 plt.gca().set_yticklabels(['First PC', 'Second PC'], va='bottom', fontsize=12); 9 10 plt.colorbar(orientation='horizontal', ticks=[pca.components_.min(), 0, 11 pca.components_.max()], pad=0.65);
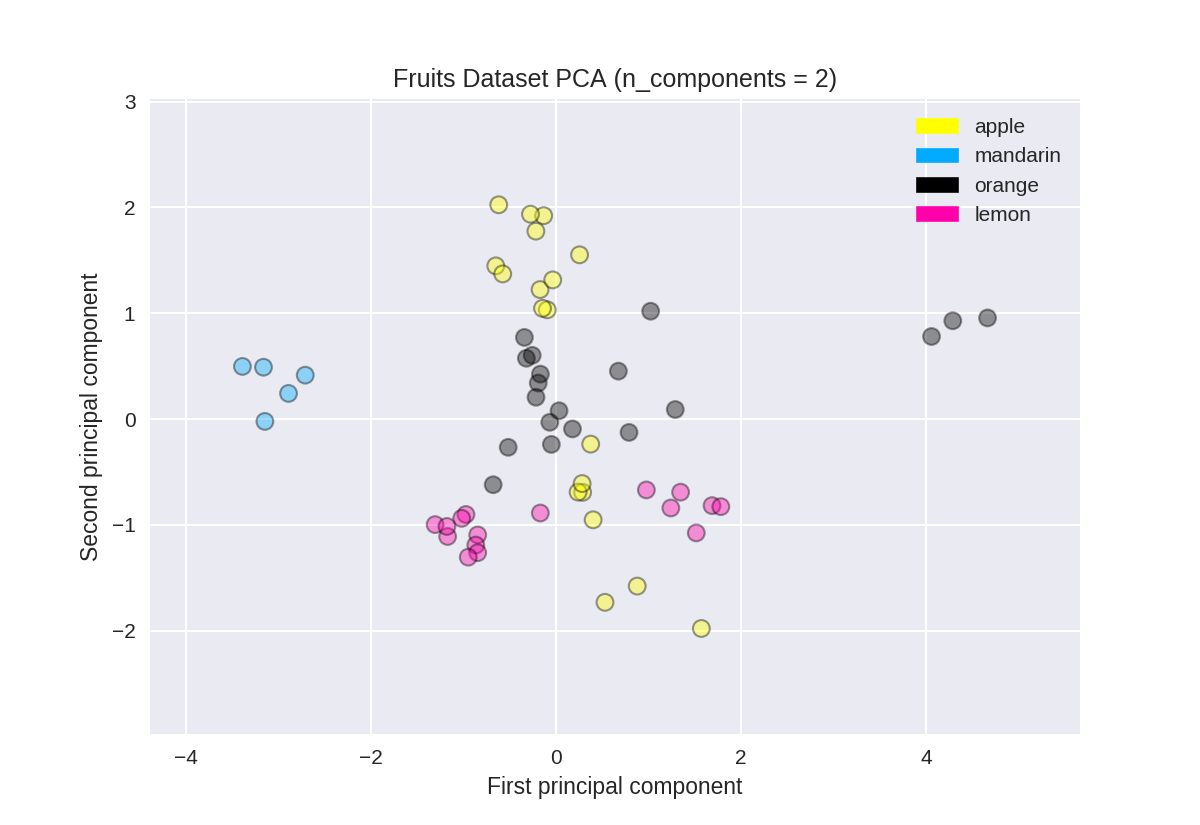
PCA用于水果数据集(用于比较)
1 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 2 from sklearn.decomposition import PCA 3 4 # each feature should be centered (zero mean) and with unit variance 5 X_normalized = StandardScaler().fit(X_fruits).transform(X_fruits) 6 7 pca = PCA(n_components = 2).fit(X_normalized) 8 X_pca = pca.transform(X_normalized) 9 10 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 11 plot_labelled_scatter(X_pca, y_fruits, ['apple','mandarin','orange','lemon']) 12 13 plt.xlabel('First principal component') 14 plt.ylabel('Second principal component') 15 plt.title('Fruits Dataset PCA (n_components = 2)');
多种学习方法
水果数据集上的多维缩放(MDS)
1 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 2 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 3 from sklearn.manifold import MDS 4 5 # each feature should be centered (zero mean) and with unit variance 6 X_fruits_normalized = StandardScaler().fit(X_fruits).transform(X_fruits) 7 8 mds = MDS(n_components = 2) 9 10 X_fruits_mds = mds.fit_transform(X_fruits_normalized) 11 12 plot_labelled_scatter(X_fruits_mds, y_fruits, ['apple', 'mandarin', 'orange', 'lemon']) 13 plt.xlabel('First MDS feature') 14 plt.ylabel('Second MDS feature') 15 plt.title('Fruit sample dataset MDS');
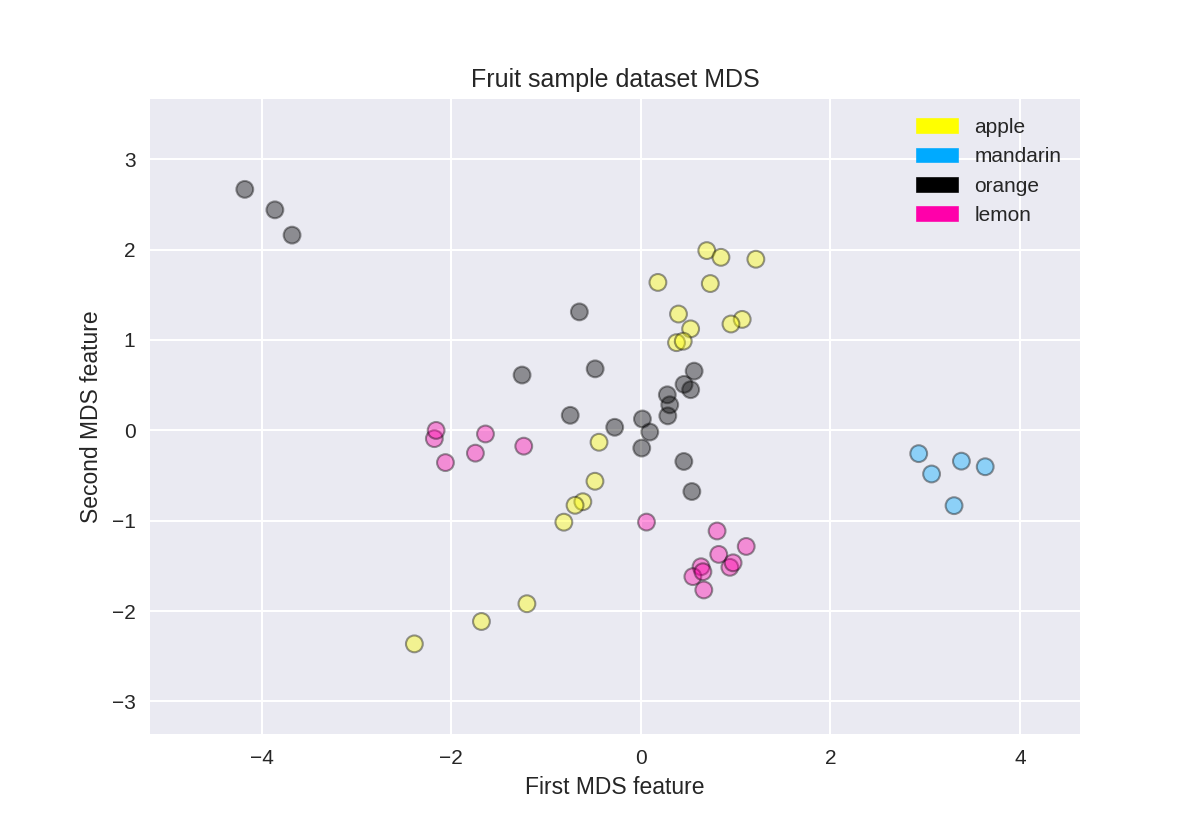
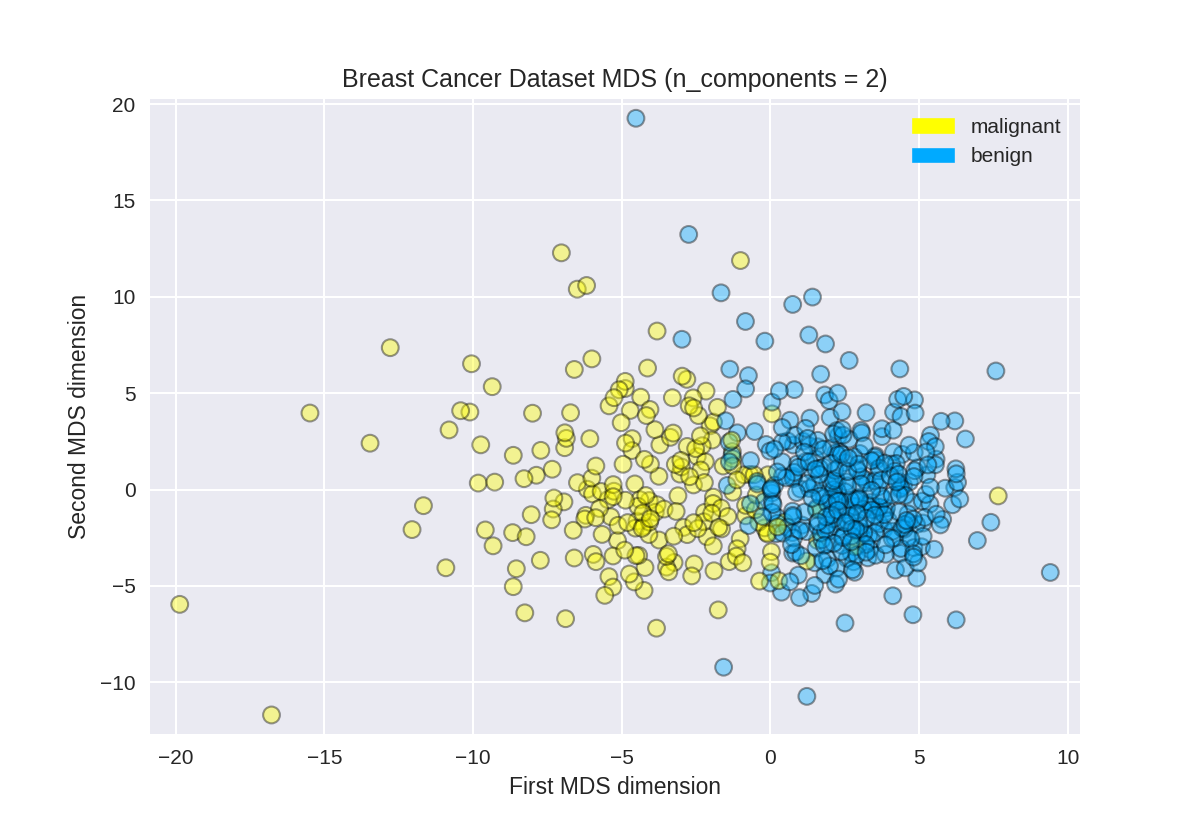
乳腺癌上的多维缩放
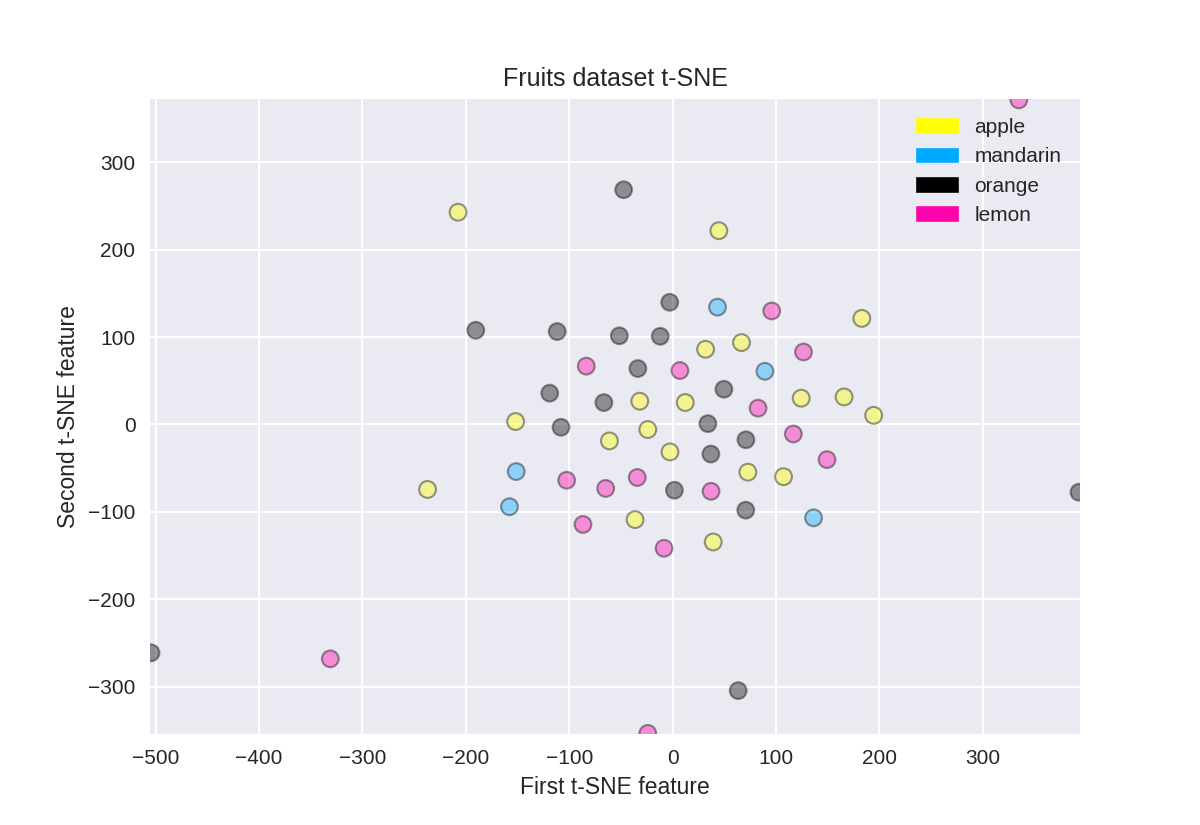
t-SNE on the fruit dataset
(结果不是很好)
1 from sklearn.manifold import TSNE 2 3 tsne = TSNE(random_state = 0) 4 5 X_tsne = tsne.fit_transform(X_fruits_normalized) 6 7 plot_labelled_scatter(X_tsne, y_fruits, 8 ['apple', 'mandarin', 'orange', 'lemon']) 9 plt.xlabel('First t-SNE feature') 10 plt.ylabel('Second t-SNE feature') 11 plt.title('Fruits dataset t-SNE');
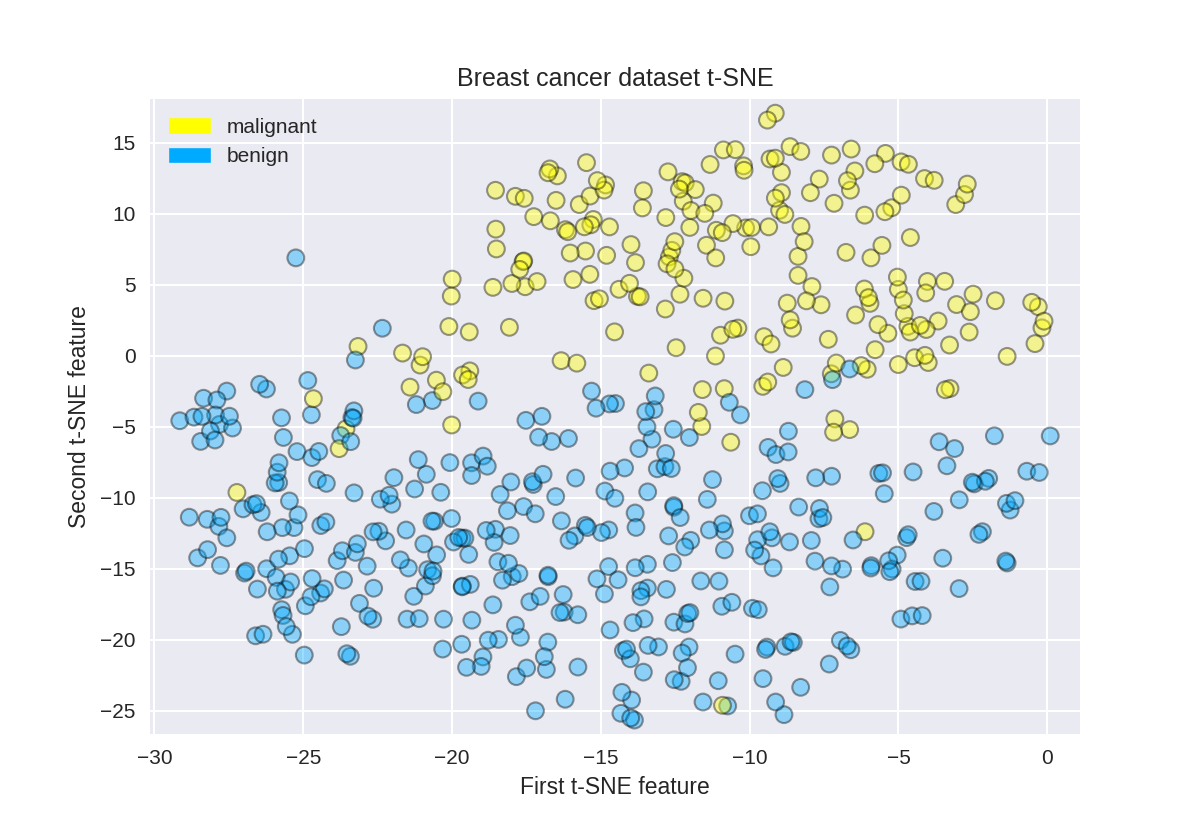
t-SNE on the breast cancer dataset
1 tsne = TSNE(random_state = 0) 2 3 X_tsne = tsne.fit_transform(X_normalized) 4 5 plot_labelled_scatter(X_tsne, y_cancer, 6 ['malignant', 'benign']) 7 plt.xlabel('First t-SNE feature') 8 plt.ylabel('Second t-SNE feature') 9 plt.title('Breast cancer dataset t-SNE');
聚类算法
k-means
#分成三个聚类中心
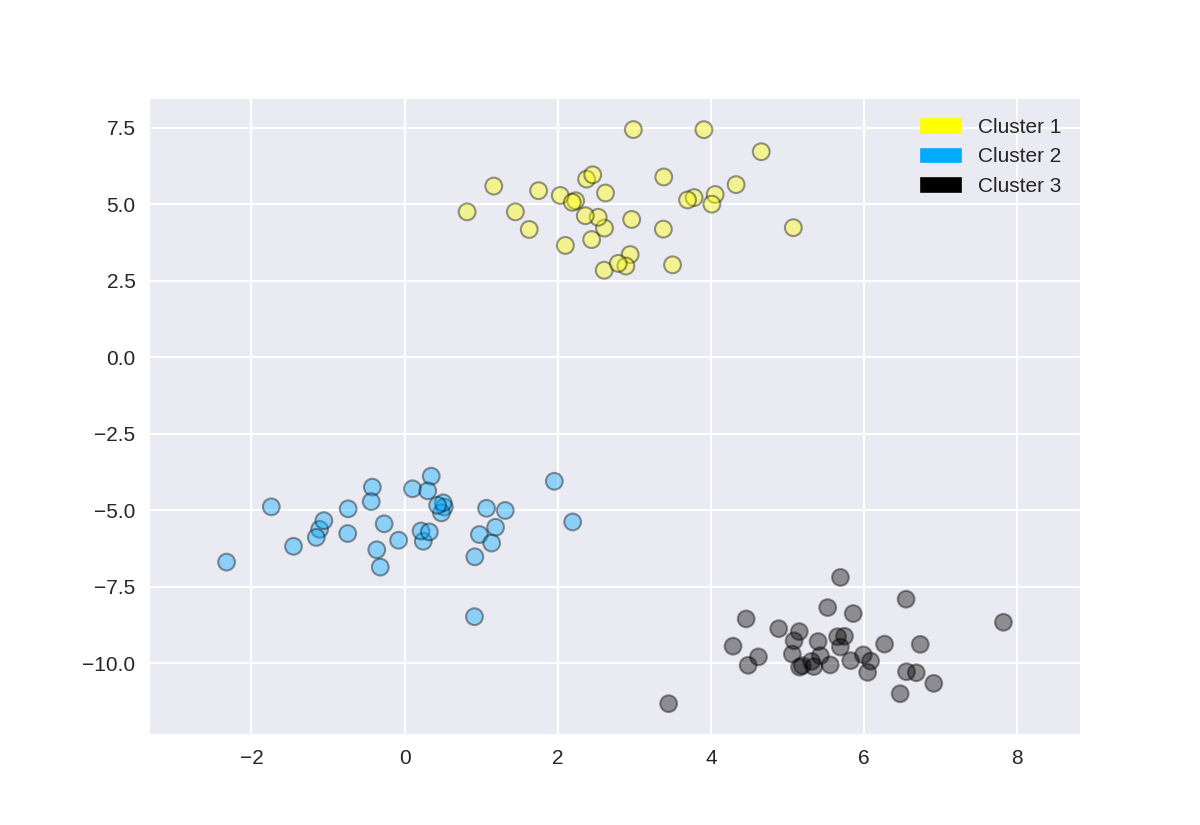
1 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs 2 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans 3 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 4 5 X, y = make_blobs(random_state = 10) 6 7 kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 3) 8 kmeans.fit(X) 9 10 plot_labelled_scatter(X, kmeans.labels_, ['Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2', 'Cluster 3'])

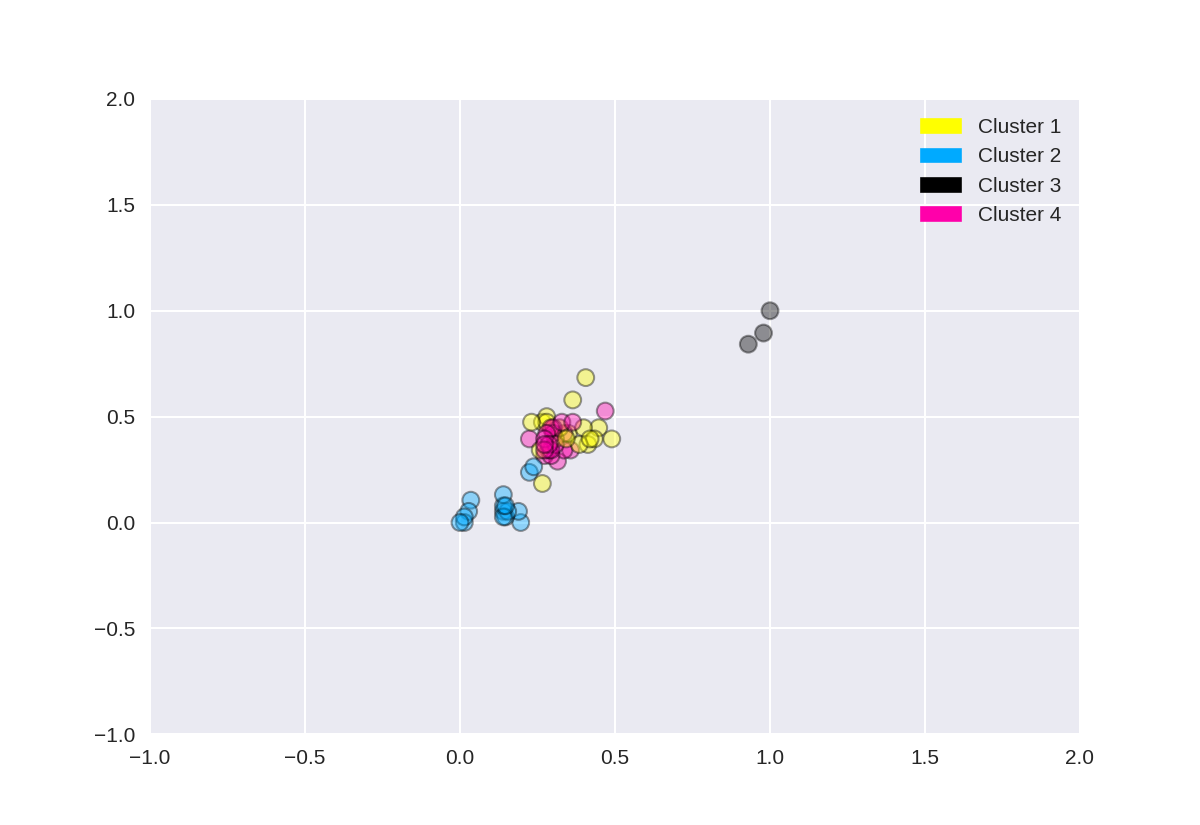
#分成4个聚类中心
1 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs 2 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans 3 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 4 from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler 5 6 fruits = pd.read_table('fruit_data_with_colors.txt') 7 X_fruits = fruits[['mass','width','height', 'color_score']].as_matrix() 8 y_fruits = fruits[['fruit_label']] - 1 9 10 X_fruits_normalized = MinMaxScaler().fit(X_fruits).transform(X_fruits) 11 12 kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 4, random_state = 0) 13 kmeans.fit(X_fruits_normalized) 14 15 plot_labelled_scatter(X_fruits_normalized, kmeans.labels_, 16 ['Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2', 'Cluster 3', 'Cluster 4'])
Agglomerative clustering
1 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs 2 from sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering 3 from adspy_shared_utilities import plot_labelled_scatter 4 5 X, y = make_blobs(random_state = 10) 6 7 cls = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters = 3) 8 cls_assignment = cls.fit_predict(X) 9 10 plot_labelled_scatter(X, cls_assignment, 11 ['Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2', 'Cluster 3'])
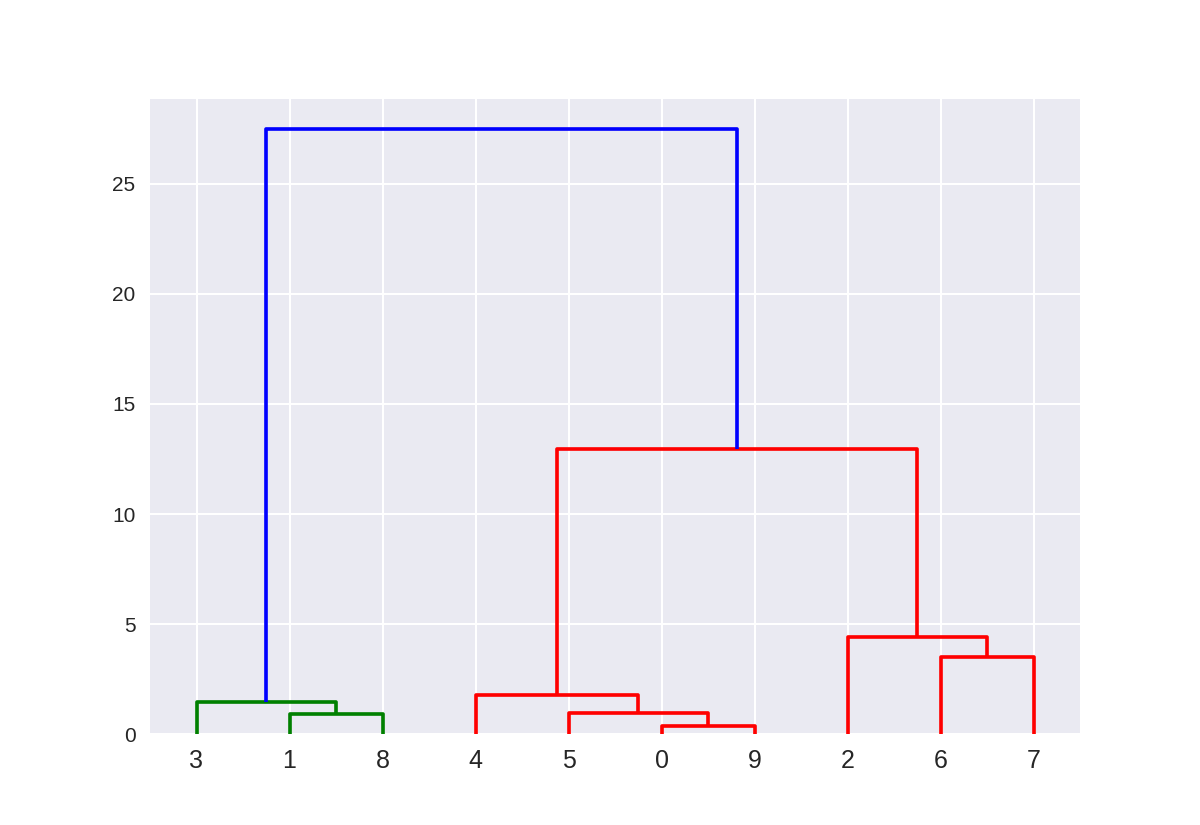
创建树状图(使用scipy)
此树形图是基于上一步中使用make_blobs创建的数据集,但为了清楚起见,本示例仅选择了10个样本,如下所示:
1 X, y = make_blobs(random_state = 10, n_samples = 10) 2 plot_labelled_scatter(X, y, 3 ['Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2', 'Cluster 3']) 4 print(X)
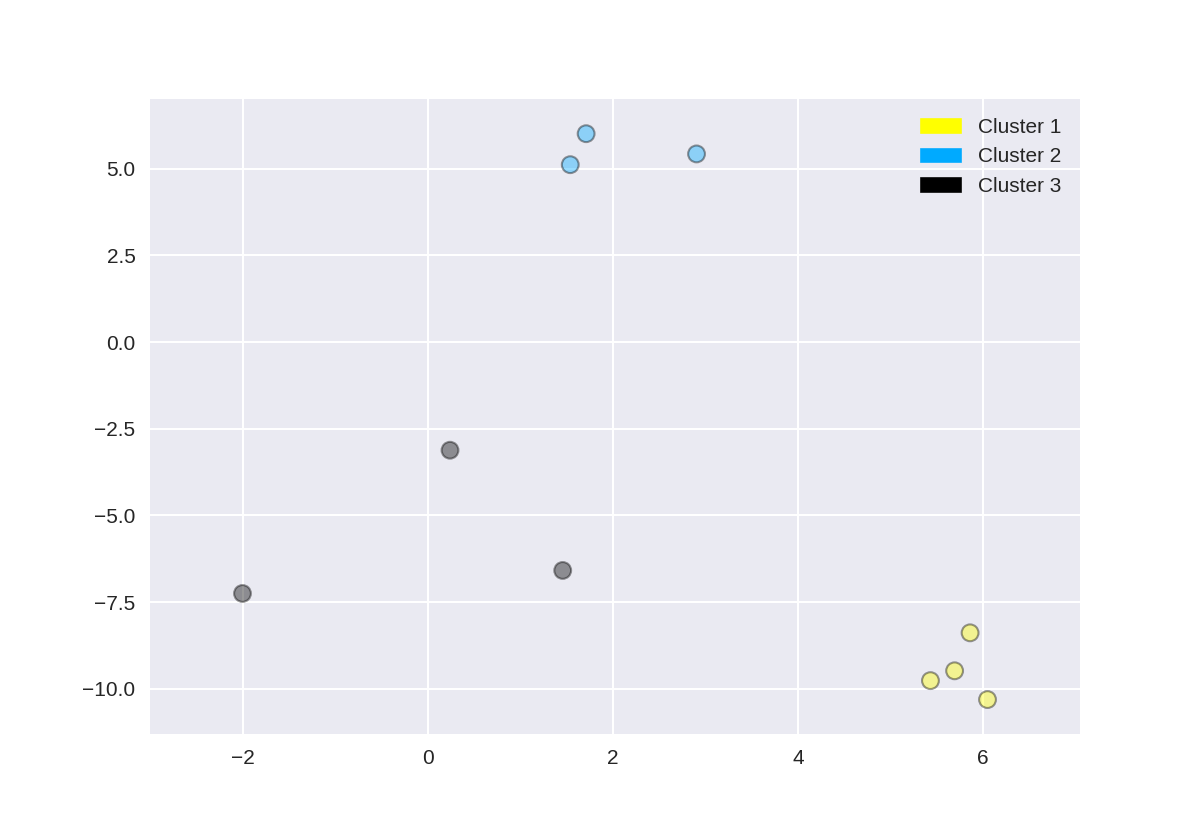
[[ 5.69192445 -9.47641249] [ 1.70789903 6.00435173] [ 0.23621041 -3.11909976] [ 2.90159483 5.42121526] [ 5.85943906 -8.38192364] [ 6.04774884 -10.30504657] [ -2.00758803 -7.24743939] [ 1.45467725 -6.58387198] [ 1.53636249 5.11121453] [ 5.4307043 -9.75956122]]
这里的树状图对应于使用Ward方法的10点以上的凝聚聚类。 点的索引0..9对应于上面X数组中点的索引。
例如,点0(5.69,-9.47)和点9(5.43,-9.76)是最接近的两个点,并且首先聚集在一起。
1 from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import ward, dendrogram 2 plt.figure() 3 dendrogram(ward(X)) 4 plt.show()
DBSCAN集群(基于密度的聚类)
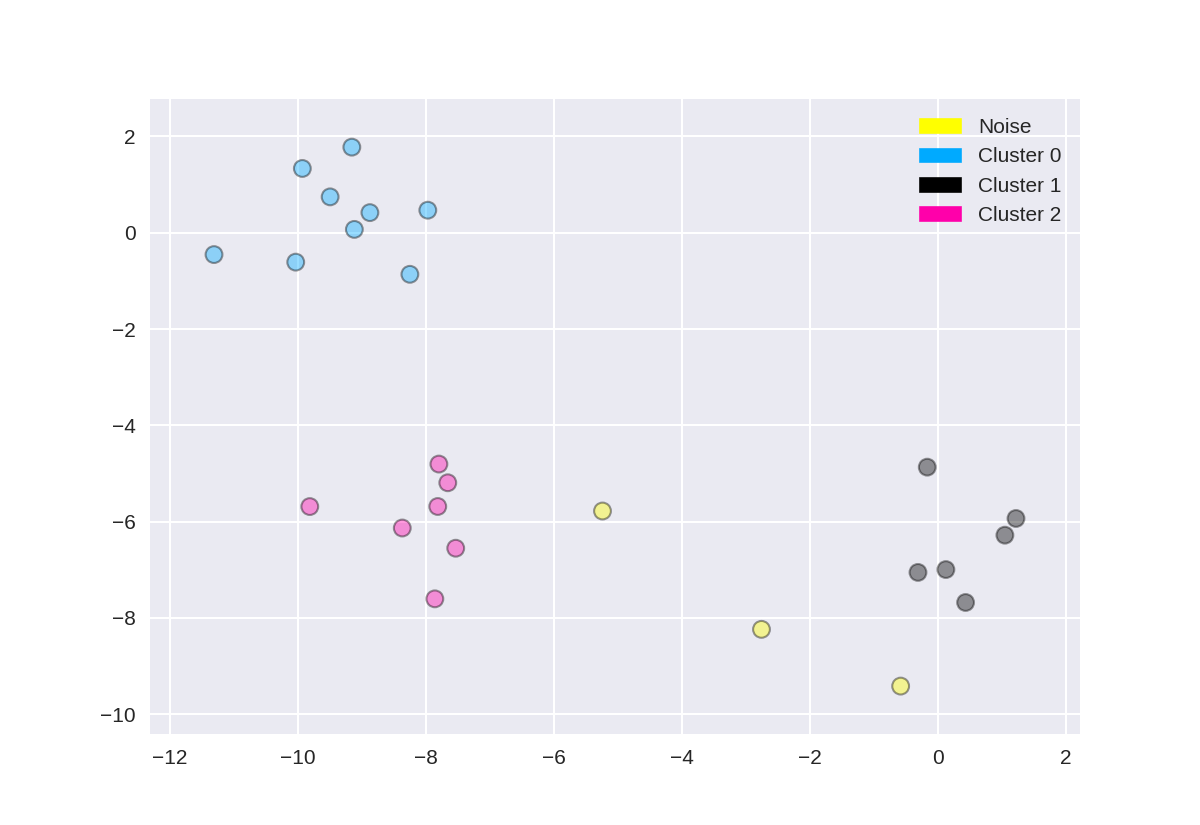
1 from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN 2 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs 3 4 X, y = make_blobs(random_state = 9, n_samples = 25) 5 6 dbscan = DBSCAN(eps = 2, min_samples = 2) 7 8 cls = dbscan.fit_predict(X) 9 print("Cluster membership values: {}".format(cls)) 10 11 plot_labelled_scatter(X, cls + 1, 12 ['Noise', 'Cluster 0', 'Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2'])
Cluster membership values: [ 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 2 2 -1 1 2 0 0 -1 0 0 1 -1 1 1 2 2 2 1]