一.java.lang包中的类不需要导包
1.特点:
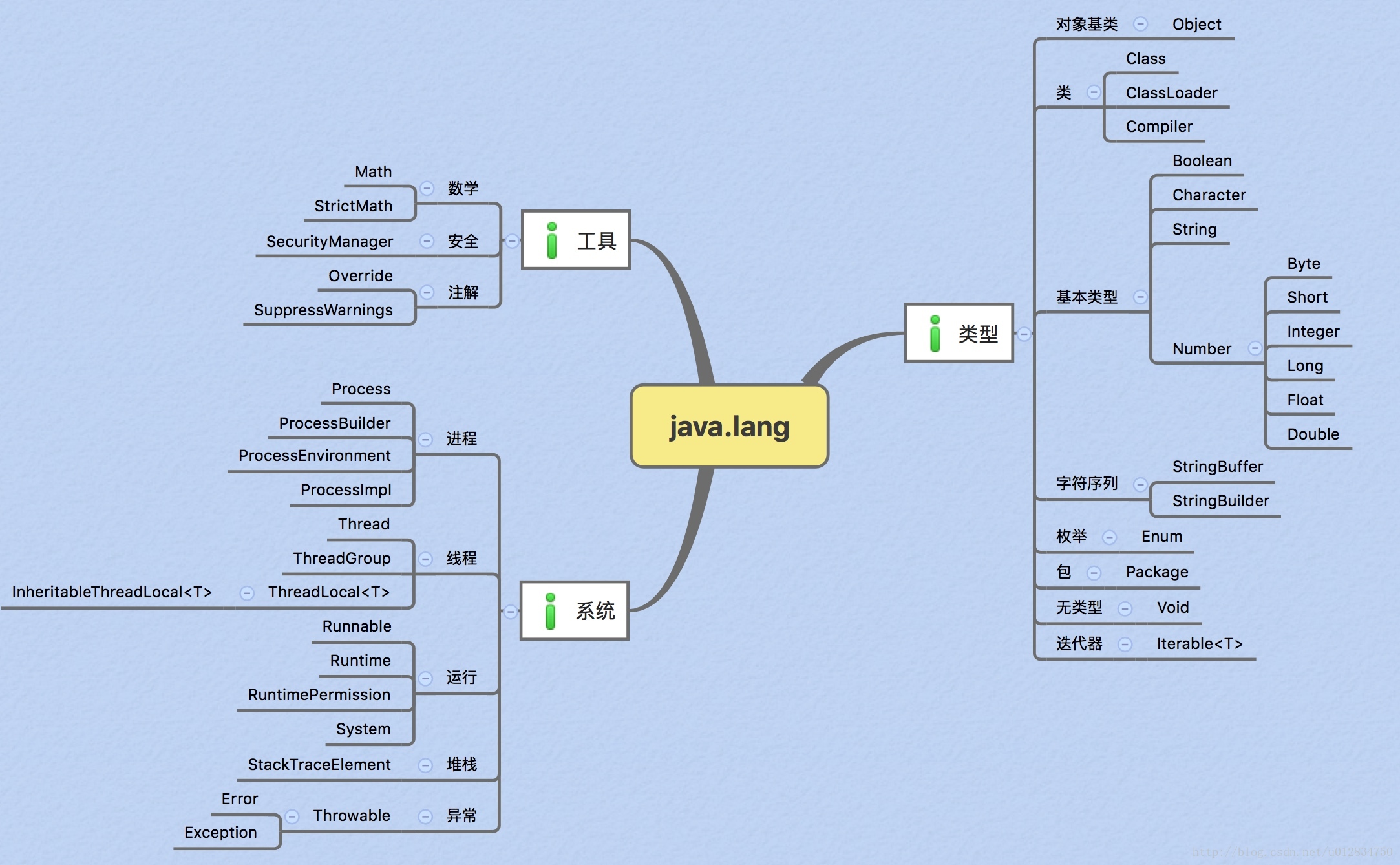
java.lang包是java语言的核心,它提供了java中的基础类。包括基本Object类、Class类、String类、基本类型的包装类、基本的数学类等等最基本的类。
2. 8种基本类型初始化默认值:
注:char类型初始化默认值为null(也就是'u0000')
|
Java中8种基本数据类型总结 |
|||||
|
序号 |
数据类型 |
大小/位 |
封装类 |
默认值 |
可表示数据范围 |
|
1 |
byte(位) |
8 |
Byte |
0 |
-128~127 |
|
2 |
short(短整数) |
16 |
Short |
0 |
-32768~32767 |
|
3 |
int(整数) |
32 |
Integer |
0 |
-2147483648~2147483647 |
|
4 |
long(长整数) |
64 |
Long |
0 |
-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807 |
|
5 |
float(单精度) |
32 |
Float |
0.0 |
1.4E-45~3.4028235E38 |
|
6 |
double(双精度) |
64 |
Double |
0.0 |
4.9E-324~1.7976931348623157E308 |
|
7 |
char(字符) |
16 |
Character |
空 |
0~65535 |
|
8 |
boolean |
8 |
Boolean |
flase |
true或false |
3.其它类型默认值都是null
二.java类的使用
0. Object类:
特征:所有类的基类,即使不显示继承也会继承Object类并拥有Object类中的方法。
1 public final native Class<?> getClass() //返回此 Object 运行时的类 2 3 public native int hashCode() //返回对象的哈希码 4 5 public boolean equals(Object obj) //判断其他对象与此对象是否“相等” 6 7 protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException //创建并返回此对象的一个副本 8 9 public String toString() //返回对象的字符串表示 10 11 public final native void notify() //唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的单个线程 12 13 public final native void notifyAll() //唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的所有线程 14 15 public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待 timeout 时长 16 17 public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待 timeout 时长,或其他线程中断当前线程 18 19 public final void wait() throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待
1.Objects类:
1 /** 2 * 1.Objects类:java.util.Objects 3 * JDK1.7开始添加了一个工具类 4 * 用于计算对象的hashcode,返回对象的字符串表示形式,比较两个对象等 5 * 这些方法都是空指针安全的 6 */ 7 String s = null; 8 String s1 = "s1"; 9 10 //报错:java.lang.NullPointerException,由于s为null所以不能调用任何方法 11 //System.out.println(s.equals(s1)); 12 13 System.out.println(Objects.equals(s,s1)); //false
2.Date类:
1 /** 2 * 2.Date类:日期时间类,java.util.Date 3 * 精确到毫秒 4 */ 5 System.out.println(new Date()); //显示当前日期 6 System.out.println(new Date(1000000000L)); //将毫秒值转换为日期 7 System.out.println(new Date().getTime()); //将系统当前时间转换为毫秒显示 8 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); //返回系统当前时间以毫秒显示
3.DateFormat类:
1 /** 2 * 3.DateFormat类:是时间/日期格式化的抽象类,java.text.DateFormat 3 * 作用: 4 * 格式化:日期-->文本,解析:文本-->日期 5 * 成员方法: 6 * String format(Date date):将日期转化为字符串 7 * Date parse(String source):将字符串解析为日期 8 * 9 * 由于DateFormat类为抽象类,我们使用SimpleDateFormat类来使用 10 * SimpleDateFormat构造方法: 11 * SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) 12 * 参数: 13 * String pattern:传递的指定模式 14 * 模式:区分大小写 15 * y 年,M 月,d 日,H 时,m 分,s 秒 16 * 一般默认模式: 17 * yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss 18 * 模式的字母不能修改,但是连接符可以修改 19 * yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒 20 */ 21 //格式化: 22 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").format(new Date())); 23 //解析: 24 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").parse("2019年12月26日 18时33分35秒"));
4.Calendar类:
1 /** 2 * 4.Calendar类:日历类,java.util.Calendar,抽象类,提供操作日历的方法 3 * 使用静态方法getInstance()返回Calendar类的子类对象 4 * 常用的成员方法: 5 * public int get(int field):返回给定日历字段的值 6 * public void set(int field,int value):将给定日历字段设置为给定值 7 * public abstract void add(int field, int amount):根据日历的规则,给日历字段添加或减去指定时间量 8 * public Date getTime():返回一个表示此Calendar时间值的Date对象 9 * 成员方法参数: 10 * int feild:日历类字段,可以使用Calendar类的静态成员变量获取 11 * YEAR = 1 年 12 * MONTH = 2 月 13 * DATE = 5 日 14 * DAY_OF_MONTH = 5 月中的某一天 15 * HOUR = 10 时 16 * MINUTE = 12 分 17 * SECOND = 13 秒 18 */ 19 Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); 20 21 //返回当前年 22 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 23 24 //设置当前年 25 c.set(Calendar.YEAR,9999); 26 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 27 28 //增加年 29 c.add(Calendar.YEAR,3); 30 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 31 32 //获取日期 33 System.out.println(c.getTime());
5.System类:
1 /** 2 * 5.System类:获取与系统相关的信息或操作系统操作,java.lang.System 3 * 4 */ 5 //返回以毫秒为单位的系统时间 6 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); 7 8 //将数组指定的数据拷贝到另一个数组中 9 int[] src = {1,2,3,4,5}; 10 int[] dest = {6,7,8,9,0}; 11 System.arraycopy(src,0,dest,0,3); 12 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dest)); //[1, 2, 3, 9, 0]
6.StringBuilder类:
1 /** 2 * 6.StringBuilder类:字符串缓冲区,可变的字符串,初始值为16个字符 3 * String类不可变字符串 4 */ 5 //空的构造函数 6 StringBuilder bu1 = new StringBuilder(); 7 System.out.println(bu1); 8 9 //带参构造函数 10 StringBuilder bu2 = new StringBuilder("abc"); 11 System.out.println(bu2); 12 13 //链式编程 14 bu2.append(1).append(true).append("你好"); 15 System.out.println(bu2); 16 17 //StringBuilder->String 18 String bu2tos = bu2.toString(); 19 System.out.println(bu2tos); 20 21 //String->StringBuilder 22 bu2.append(bu2tos); 23 System.out.println(bu2);
7.包装类:
1 /** 2 * 7.包装类:8个,java.lang中 3 * 由于基本类型好用但是没有对应的方法操作基本类型, 4 * 我们定义一个类,将基本数据类型封装起来并在这个类中定义一些方法用于操作 5 * 基本类型 包装类 6 * byte Byte 7 * short Short 8 * int Integer 9 * long Long 10 * float Float 11 * double Double 12 * char Character 13 * boolean Boolean 14 * 15 * 16 * 从JDK1.5开始,支持自动装箱和自动拆箱 17 * 装箱:基本类型->包装类 18 * 拆箱:包装类->基本类型 19 */ 20 //int -> Integer 21 Integer i = Integer.valueOf(11111); 22 System.out.println(i); 23 24 //String -> Integer 25 i = Integer.valueOf("22222222"); 26 System.out.println(i); 27 28 //Integer -> int 29 int num = i.intValue(); 30 System.out.println(num); 31 32 //由于泛型必须是非基本类型 33 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 34 35 //自动装箱:list.add(new Integer(1)) 36 list.add(1); 37 //自动拆箱:list.get(0).intValue(); 38 int a = list.get(0); 39 40 //基本类型转字符串 41 String ss = 100 + ""; 42 System.out.println(ss); 43 ss = Integer.toString(123); 44 System.out.println(ss); 45 ss = String.valueOf(444); 46 System.out.println(ss); 47 48 //字符串转基本类型 49 int nn = Integer.parseInt(ss); 50 System.out.println(nn);
8.UUID类:
- 表示通用唯一标识符 (UUID) 的类。 UUID 表示一个 128 位的值。
- 作用:生成唯一的编号
- 常用方法:UUID.randomUUID() 用于生成唯一的编号
1 UUID u; 2 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 3 u = UUID.randomUUID(); 4 System.out.println(u.toString().replaceAll("-","")); 5 }
9.Format类:
- Format类是一个用于格式化语言环境敏感的信息(如日期、消息和数字)的抽象基类。
- 拥有的子类:
- DateFormat:为抽象日期类
- SimpleDateFormat:是一个以与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。
- MessageFormat:提供了以与语言无关方式生成连接消息的方式。
- NumberFormat:是所有数值格式的抽象基类。
- ChoiceFormat:是一个允许将格式应用到某个范围的数。
- DecimalFormat:用于格式化十进制数字。
- DateFormat:为抽象日期类
(1)ChoiceFormat:
注:
- 两个数组长度必须相同,才能进行格式化。
- 当数字小于数组第一个数时,输出第一个数。当数字大于数组最后一个数时输出最后一个数。
- 输出规则 :当且仅当 limit[j] <= X < limit[j+1] 时,X 匹配 j (就是输出左侧数字)
1 double[] limits = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 2 String[] formats = {"星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日"}; 3 ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats); 4 System.out.println(format.format(-100)); //星期一 5 System.out.println(format.format(3.6)); //星期一
(2)DecimalFormat:
- 使用‘0’和‘#’号表示数字,区别在于‘#’号会省略末尾多余的0
1 // 取整数部分 2 String s1 = new DecimalFormat("0").format(12345.1512134567); 3 System.out.println(s1);//12345 4 5 // 取小数点后1位,四舍五入 6 String s2 = new DecimalFormat("0.0").format(12345.1512134567); 7 System.out.println(s2);//12345.2 8 9 // 取小数点后3位,不足部分取0 10 String s3 = new DecimalFormat("0.000").format(12345.1); 11 System.out.println(s3);//12345.100 12 13 // 百分比 14 String s4 = new DecimalFormat("0.0%").format(12345.1512134567); 15 System.out.println(s4);// 1234515.1% 16 17 // 科学计数法 18 String s5 = new DecimalFormat("0.00E0").format(12345.1512134567); 19 System.out.println(s5);//1.23E4 20 21 // 每三位以逗号分开 22 String s6 = new DecimalFormat(",000.000").format(12345.1512134567); 23 System.out.println(s6);//12,345.151 24 25 //小数点后3位,如果是0则不显示 26 String s7 = new DecimalFormat("#.###").format(123.300); 27 System.out.println(s7);//123.3 28 29 //将格式嵌入文本 30 System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("每秒#.###米。").format(123.300));//每秒123.3米。
9.Arrays类:
- Arrays是一个针对数组的工具类,可以进行复制,转换,排序,搜索,比较,填充等功能
(1).复制
- copyOfRange(int[] original, int from, int to):
- 第一个参数表示源数组
- 第二个参数表示开始位置(取得到)
- 第三个参数表示结束位置(取不到)
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 6 //1.Arrays复制 7 int[] b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, 3); 8 for (int i : b) { 9 System.out.print(i + " "); 10 } 11 System.out.println(); 12 13 //2.System复制 14 System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, 3); 15 for (int i : b) { 16 System.out.print(i + " "); 17 } 18 19 } 20 }
(2).转换为字符串
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.返回一维数组的字符串形式 5 int[] a = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 6 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 7 8 //2.返回多维数组的字符串形式 9 int[][][] b = {{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}}, {{11, 12, 13}, {21, 22, 23}}}; 10 System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(b)); 11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b)); 12 13 /** 14 * 输出: 15 * [18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9] 16 * [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], [[11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23]]] 17 * [[[I@135fbaa4, [[I@45ee12a7] 18 */ 19 } 20 }
(3).数组排序
1 public class ArraysSortTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.Arrays自带升序排序 5 Integer[] nums1 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 6 Arrays.sort(nums1); 7 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1)); 8 9 //2.自定义类 10 Integer[] nums2 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 11 Comparator<Integer> comparator = new MyComparator(); 12 Arrays.sort(nums2, comparator); 13 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums2)); 14 15 //3.匿名内部类 16 Integer[] nums3 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 17 Arrays.sort(nums3, new Comparator<Integer>() { 18 @Override 19 public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { 20 return b - a; 21 } 22 }); 23 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums3)); 24 25 //4.lambda表达式 26 Integer[] nums4 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 27 Arrays.sort(nums4, (a, b) -> b - a); 28 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums4)); 29 } 30 } 31 32 33 class MyComparator implements Comparator<Integer> { 34 @Override 35 public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { 36 return b - a; 37 } 38 }
补充:
Comparable和Comparator区别比较:
- Comparable是排序接口,若一个类实现了Comparable接口,就意味着“该类支持排序”。而Comparator是比较器,我们若需要控制某个类的次序,可以建立一个“该类的比较器”来进行排序。
- Comparable相当于“内部比较器”,而Comparator相当于“外部比较器”。
- 两种方法各有优劣, 用Comparable 简单, 只要实现Comparable 接口的对象直接就成为一个可以比较的对象,但是需要修改源代码。 用Comparator 的好处是不需要修改源代码, 而是另外实现一个比较器, 当某个自定义的对象需要作比较的时候,把比较器和对象一起传递过去就可以比大小了, 并且在Comparator 里面用户可以自己实现复杂的可以通用的逻辑,使其可以匹配一些比较简单的对象,那样就可以节省很多重复劳动了
(4).搜索
注意:搜索之前必须排序
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 6 Arrays.sort(a); 7 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 8 9 //二分搜索之前必须排序 10 System.out.println("数字62出现在数组中的位置"+Arrays.binarySearch(a,62)); 11 12 /**输出: 13 * [9, 18, 62, 65, 68, 82] 14 * 数字62出现在数组中的位置2 15 */ 16 } 17 }
(5).判断两个数组内容是否相同
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 int b[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 6 int c[] = new int[]{99, 62, 68, 82, 65, 8}; 7 8 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,b)); 9 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,c)); 10 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(b,c)); 11 12 /** 13 * 输出: 14 * true 15 * false 16 * false 17 */ 18 } 19 }
(6).填充
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int[] a = new int[10]; 5 6 //1.填充全部 7 Arrays.fill(a, 5); 8 9 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 10 11 /** 12 * 输出: 13 * [5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5] 14 */ 15 16 //2.填充下标[2,4]为1 17 Arrays.fill(a, 2, 5, 1); 18 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 19 20 /** 21 * 输出: 22 * [5, 5, 1, 1, 1, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5] 23 */ 24 } 25 }