今天回顾了Java的线程的一些知识
例1:下面代码存有详细的解释 主要是继承Thread类与实现Runnable接口 以及start()和run()方法
package com.date0607;
/**
* 在一个程序中同时运行的多个独立流程,每一个独立流程就是一个线程。
* 线程开发两种方式:继承Thread类与实现Runnable接口.
* start() 执行是无序的,不固定的。run() 执行有先后顺序。
* 继承Thread是面向对象的编程方式。
* 实现Runnable接口解决了单一继承限制
*/
class MyThread1 extends Thread{
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " $$$");
}
}
}
class MyThread2 extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " ###");
}
}
}
class MyRunnable2 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " @@@");
}
}
}
public class Test_0607_Demo01 {
public static void main(String [] args){
Thread t1 = new MyThread1();
Thread t2 = new MyThread2();
Runnable target = new MyRunnable2();
Thread t3 = new Thread(target);
//初始状态
//t1.start();
//t2.start();
//运行状态
t1.run();
t2.run();
t3.run();
}
}
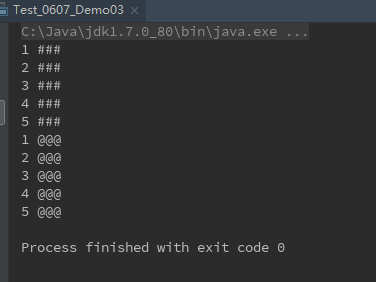
运行结果 自己执行试试哦
例2 sleep()方法,1000是1秒
package com.date0607;
/**
* sleep()可以控制下线程,但是不准备。
* sleep(1000) 1000指1s。
*/
class MyThread3 extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " ###");
}
try{
Thread.sleep(20000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
}
}
class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " @@@");
}
try{
Thread.sleep(20000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
}
}
public class Test_0607_Demo02{
public static void main(String [] args){
Thread t2 = new MyThread3();
Runnable target = new MyRunnable3();
Thread t3 = new Thread(target);
t2.run();
t3.run();
}
}
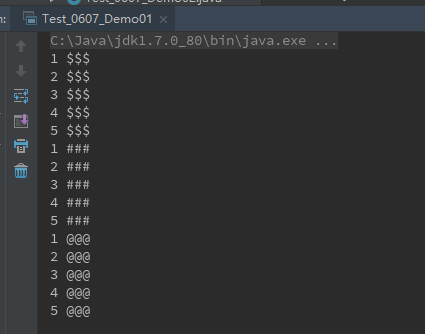
运行结果 等待20秒,执行下一个线程
例3 join()的使用方法
package com.date0607;
/**
*join方法也会导致阻塞。
* 特点:如果当前线程中掉用了另外一个线程的join方法,当前线程会立即阻塞,直到另外一个线程执行完成。
*/
class MyThread33 extends Thread{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " ###");
}
}
}
class MyThread44 extends Thread{
Thread t;
public void run(){
try{
t.join();
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
System.out.println(i + " @@@");
}
}
}
public class Test_0607_Demo03{
public static void main(String [] args){
MyThread33 t1 = new MyThread33();
MyThread44 t2 = new MyThread44( );
t2.t= t1;
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
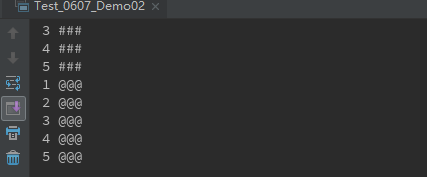
运行结果