properties文件:项目当中比较常见的配置文件。
特点:以键值对的形式保存数据
作用:通过将系统配置定义在properties文件的形式来实现代码解耦。
解析:
Properties properties = new Properties();
File file = new File("log4j.properties");
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(file);
properties.load(inStream);
获取:
properties结构:跟map一样是属于字典类型的数据结构。
取数据:properties.getProperty(key)。
IO流:
流向:
输入流 read 读
- InputStream
- FileInputStream
- FileReader
输出流 write 写
- OutputStream
- FileOutputStream
- FileWriter
类型
字节流(读写任意文件)
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
字符流(只能读写纯文本文件)中文
- FileReader
- FileWriter
用完之后关闭流。
解析案例:
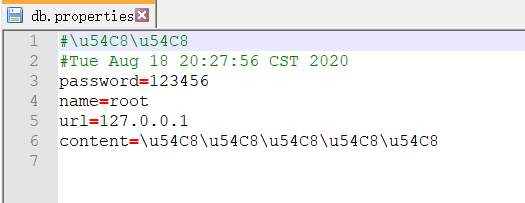
package com.test.propertis;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Properties 和 HashMap 是兄弟, 都实现了Map接口。
//Properties 因为它是操作配置文件的类,所以泛型一般采用String,String
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("url","127.0.0.1");
prop.setProperty("name","root");
prop.setProperty("password","123456");
System.out.println(prop);
System.out.println(prop.getProperty("url"));
//1、创建输出流,怼到项目的db.properties文件上。
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/test/resources/db.properties");
//2、把java程序中的内容写到文件中
prop.store(fos,"哈哈");
//3、关流
fos.close();
Properties prop = new Properties();
//1、创建输出流,怼到项目的db.properties文件上。
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/test/resources/db.properties");
//2、把文件中的内容读到java程序中
prop.load(fis);
System.out.println(prop);
//3、关流
fis.close();
}