1. 核心层次
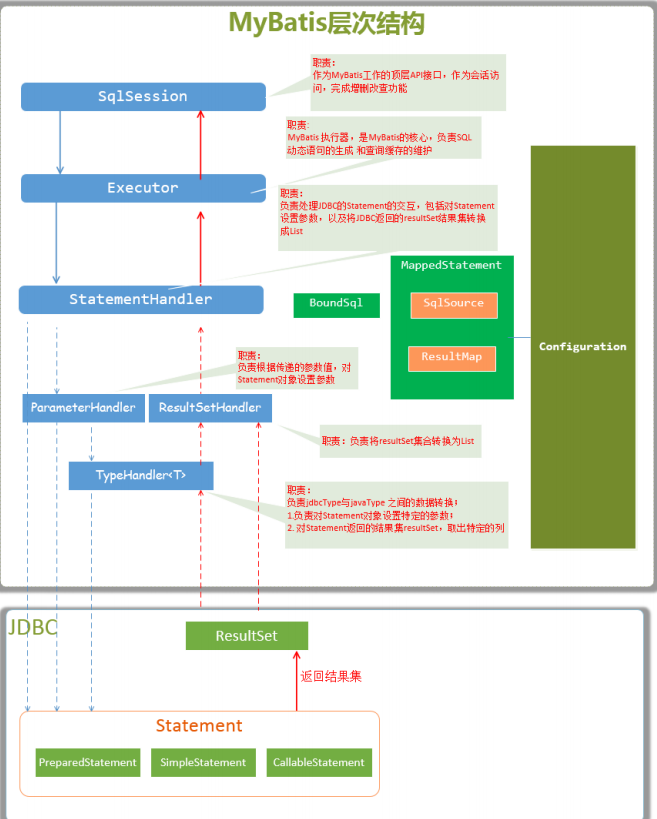
2. SqlSession
先从顶层的SqlSession接口开始说起。SqlSession是MyBatis提供的面向用户的API,表示和数据库的会话对象,用于完成对数据库的一系列CRUD操作以及获取mappers和管理事务等。
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key.
* @param <T> the returned object type
* @param statement
* the statement
* @return Mapped object
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter.
* @param <T> the returned object type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Mapped object
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter,
* within the specified row bounds.
* @param <E> the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return List of mapped object
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* Eg. Return a of Map[Integer,Author] for selectMap("selectAuthors","id")
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param <K> the returned Map keys type
* @param <V> the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param <T> the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
<T> Cursor<T> selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter using a {@code ResultHandler} and
* {@code RowBounds}.
*
* @param statement
* Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter
* the parameter
* @param rowBounds
* RowBound instance to limit the query results
* @param handler
* ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Execute an insert statement.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement);
/**
* Execute an insert statement with the given parameter object. Any generated
* autoincrement values or selectKey entries will modify the given parameter
* object properties. Only the number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* Note that database connection will not be committed if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the commit call {@link SqlSession#commit(boolean)}
*/
void commit();
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* @param force forces connection commit
*/
void commit(boolean force);
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the rollback call {@link SqlSession#rollback(boolean)}
*/
void rollback();
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* @param force forces connection rollback
*/
void rollback(boolean force);
/**
* Flushes batch statements.
* @return BatchResult list of updated records
* @since 3.0.6
*/
List<BatchResult> flushStatements();
/**
* Closes the session.
*/
@Override
void close();
/**
* Clears local session cache.
*/
void clearCache();
/**
* Retrieves current configuration.
* @return Configuration
*/
Configuration getConfiguration();
/**
* Retrieves a mapper.
* @param <T> the mapper type
* @param type Mapper interface class
* @return a mapper bound to this SqlSession
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> type);
/**
* Retrieves inner database connection.
* @return Connection
*/
Connection getConnection();
}
SqlSession接口一共有两个实现类,分线程不安全的DefaultSqlSession和线程安全的SqlSessionManager。
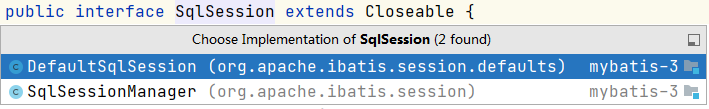
SqlSessionManager比较特殊,它不仅仅是实现SqlSession,还实现了SqlSessionFactory接口。他其实是相于把两者结合起来,用了一个ThreadLocal来保存每次的SqlSession来实现线程安全,运用JDK动态代理来控制每次会话的事务处理,从ThreadLocal中读取SqlSession用来复用,避免多次创建的资源浪费,享元模式?
这边只是先大概的讲一讲,其实SqlSessionManager就是一个组合模式罢了,走的还是默认操作这一套,只是做了套了一层壳子罢了,留在后面细讲。
2. DefaultSqlSession
DefaultSqlSession是SqlSession默认实现类。SqlSession通过工厂SqlSessionFactory创建。而SqlSessionFactory工厂的默认实现类是DefaultSqlSessionFactory。而DefaultSqlSessionFactory是从SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中生成的。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment) {
return build(reader, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties) {
return build(reader, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment) {
return build(inputStream, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties) {
return build(inputStream, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
这里用到工厂模式和建造者模式,这两个模式其实很容易搞混,他们都属于设计模式中的创建型模式。
区别在于:
1.工厂模式一般都是创建一个产品,注重的是把这个产品创建出来就行,只要创建出来,不关心这个产品的组成细节。
2.建造者模式也是创建一个产品,但是不仅要把这个产品创建出来,还要关系这个产品的组成细节。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder就提供了许多不同的方法用来生成SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, props);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, "development-hsql")