由于浅拷贝使多个对象共用一块内存地址,调用析构函数时导致一块内存被多次释放,导致程序奔溃。
实现string类的时候通常显示的定义拷贝构造函数和运算符重载函数。
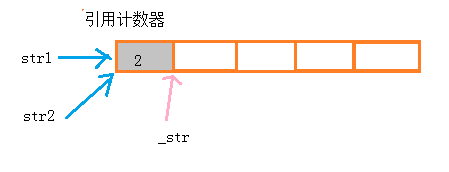
由于释放内存空间,开辟内存空间时花费时间,因此,在我们在不需要写,只是读的时候就可以不用新开辟内存空间,就用浅拷贝的方式创建对象,当我们需要写的时候才去新开辟内存空间。这种方法就是写时拷贝。
在构造函数中开辟新的空间时多开辟4个字节的空间,用来存放引用计数器,记录这快空间的引用次数。
- #include<iostream>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- using namespace std;
- class String
- {
- public:
- String(char *str = "")
- :_str(new char[strlen(str) + 5])
- {
- *(int *)_str = 1;
- _str += 4;
- strcpy(_str, str);
- }
- ~String()
- {
- if (_str != NULL)
- {
- _Release();
- }
- }
- String(const String& str)
- {
- _str = str._str;
- ++_GetRefCount();
- }
- String& operator=(const String& str)
- {
- if (this != &str)
- {
- _Release();
- _str = str._str;
- ++ _GetRefCount();
- }
- return *this;
- }
- char& operator[](int index)//写时拷贝
- {
- if (_GetRefCount()>1)//当引用次数大于1时新开辟内存空间
- {
- --_GetRefCount();//原来得空间引用计数器减1
- char *str = new char[strlen(_str) + 5];
- strcpy(str+4, _str);
- _str = str+4;
- _GetRefCount()++;
- }
- return _str[index];
- }
- friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, const String& str)
- {
- output << str._str;
- return output;
- }
- private:
- int& _GetRefCount()
- {
- return *(int *)(_str - 4);
- }
- void _Release()
- {
- if (--_GetRefCount() == 0)
- {
- delete[] (_str-4);
- }
- }
- private:
- char *_str;
- };
==============》
将_pCount与_str所指向的空间放在一起,即只用new开辟一次空间
class String
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,String& s);
public:
String(const char*str = "")
:_str(new char[strlen(str)+1+4])
{
*(int *)_str = 1; //*_pCount = 1
_str = _str+4; //找到数据存放的位置
strcpy(_str,str);
GetCount() = 1;
}
String(const String& str)
:_str(str._str)
{
++GetCount();
}
~String()
{
if(--GetCount() == 0)
{
delete[] (_str-4);
}
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
if (--GetCount() == 0)
{
delete[] (_str-4);
}
++GetCount();
_str = s._str;
}
return *this;
}
private:
int& GetCount() //获得_pCount
{
return *((int *)_str-1);
}
private:
char *_str;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,String& s)
{
os<<s._str;
return os;
}
void test1()
{
String str1("abcde");
String str2(str1);
String str3;
str3 = str2;
cout<<str1<<endl;
cout<<str2<<endl;
cout<<str3<<endl;
}