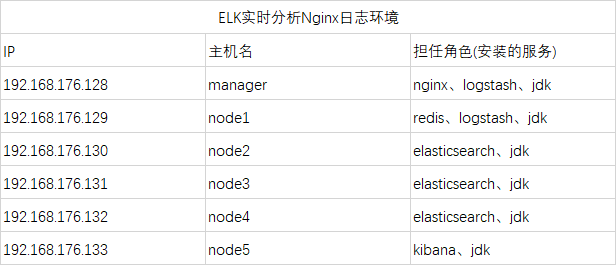
1. 部署环境
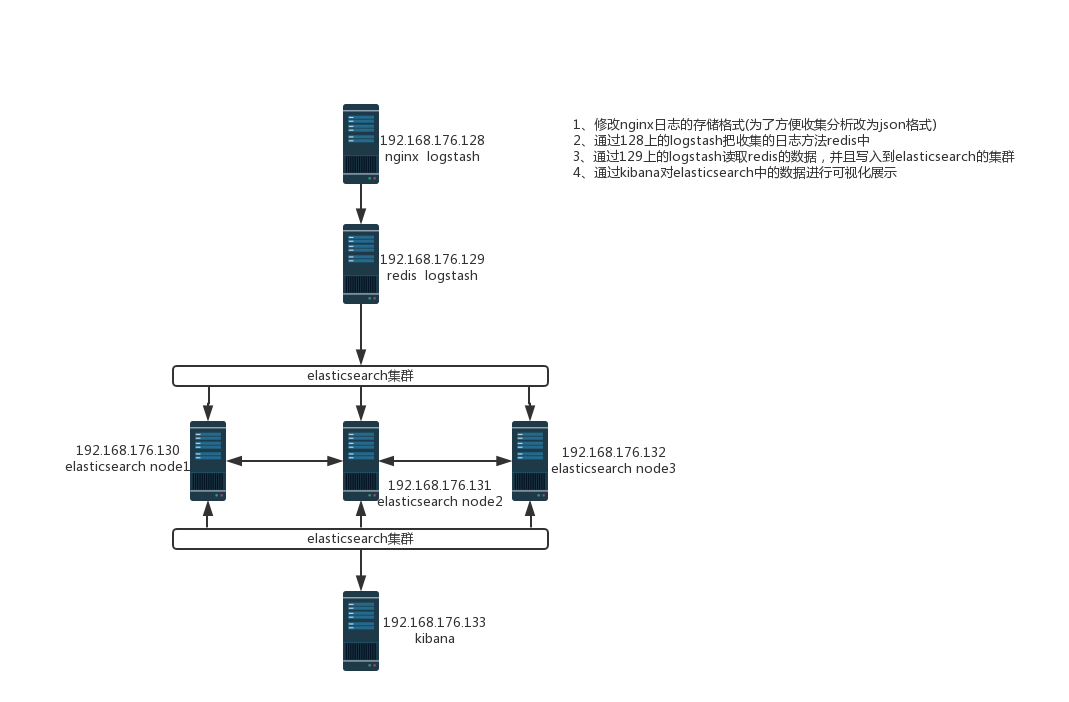
2. 架构拓扑
3. nginx安装
安装在192.168.176.128服务器上
这里安装就简单粗暴了直接yum安装nginx
[root@manager ~]# yum -y install epel-release [root@manager ~]# yum -y install nginx 检查是否安装成功(这里选择了查看版本号) [root@manager ~]# nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.12.2 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/share/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/client_body --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/proxy --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/fastcgi --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/scgi --pid-path=/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/run/lock/subsys/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-file-aio --with-ipv6 --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic --with-http_image_filter_module=dynamic --with-http_geoip_module=dynamic --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_perl_module=dynamic --with-mail=dynamic --with-mail_ssl_module --with-pcre --with-pcre-jit --with-stream=dynamic --with-stream_ssl_module --with-google_perftools_module --with-debug --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-cc1 -m64 -mtune=generic' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-ld -Wl,-E'
设置日志的格式(改为json格式)并测试查看日志
[root@manager ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
修改成下面的部分(运维的一看就能明白是什么意思)
http {
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
log_format json '{ "@timestamp": "$time_iso8601", '
'"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
'"remote_user": "$remote_user", '
'"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", '
'"request_time": "$request_time", '
'"status": "$status", '
'"request_uri": "$request_uri", '
'"request_method": "$request_method", '
'"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
'"http_x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", '
'"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent"}';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log json;

1 # For more information on configuration, see: 2 # * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ 3 # * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/ 4 5 user nginx; 6 worker_processes auto; 7 error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; 8 pid /run/nginx.pid; 9 10 # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic. 11 include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; 12 13 events { 14 worker_connections 1024; 15 } 16 17 http { 18 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' 19 # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' 20 # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; 21 22 log_format json '{ "@timestamp": "$time_iso8601", ' 23 '"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", ' 24 '"remote_user": "$remote_user", ' 25 '"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", ' 26 '"request_time": "$request_time", ' 27 '"status": "$status", ' 28 '"request_uri": "$request_uri", ' 29 '"request_method": "$request_method", ' 30 '"http_referrer": "$http_referer", ' 31 '"http_x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", ' 32 '"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent"}'; 33 34 access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log json; 35 36 sendfile on; 37 tcp_nopush on; 38 tcp_nodelay on; 39 keepalive_timeout 65; 40 types_hash_max_size 2048; 41 42 include /etc/nginx/mime.types; 43 default_type application/octet-stream; 44 45 # Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory. 46 # See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include 47 # for more information. 48 include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; 49 50 server { 51 listen 80 default_server; 52 listen [::]:80 default_server; 53 server_name _; 54 root /usr/share/nginx/html; 55 56 # Load configuration files for the default server block. 57 include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; 58 59 location / { 60 } 61 62 error_page 404 /404.html; 63 location = /40x.html { 64 } 65 66 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 67 location = /50x.html { 68 } 69 } 70 71 # Settings for a TLS enabled server. 72 # 73 # server { 74 # listen 443 ssl http2 default_server; 75 # listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server; 76 # server_name _; 77 # root /usr/share/nginx/html; 78 # 79 # ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt"; 80 # ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key"; 81 # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; 82 # ssl_session_timeout 10m; 83 # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; 84 # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; 85 # 86 # # Load configuration files for the default server block. 87 # include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; 88 # 89 # location / { 90 # } 91 # 92 # error_page 404 /404.html; 93 # location = /40x.html { 94 # } 95 # 96 # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 97 # location = /50x.html { 98 # } 99 # } 100 101 }
检查并启动 nginx 服务
[root@manager ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful [root@manager ~]# systemctl start nginx [root@manager ~]# netstat -lntup | grep nginx tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1888/nginx: master tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 1888/nginx: master
测试访问nginx并查看日志记录
# 测试
[root@manager ~]# curl 192.168.176.128
查看日志(这里可以看到我们自定义的日志格式输出)
[root@manager ~]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
{ "@timestamp": "2018-11-18T01:28:49-05:00", "remote_addr": "192.168.176.128", "remote_user": "-", "body_bytes_sent": "3700", "request_time": "0.000", "status": "200", "request_uri": "/", "request_method": "GET", "http_referrer": "-", "http_x_forwarded_for": "-", "http_user_agent": "curl/7.29.0"}
安装JDK
[root@manager ELK]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk
Nginx 就先到这里,对我们的整个环境这样就足够了
4. redis安装
安装在192.168.176.129服务器上
redis 也是直接yum简单粗暴的安装了
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install epel-release [root@node1 ~]# yum -y install redis 检查是否安装成功(查看版本) [root@node1 ~]# redis-server -v Redis server v=3.2.12 sha=00000000:0 malloc=jemalloc-3.6.0 bits=64 build=7897e7d0e13773f
修改redis配置文件(监听地址和密码)
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/redis.conf 修改两个地方 bind 127.0.0.1 改为 bind 0.0.0.0 # requirepass foot 去掉注释 foot改为自己的密码
查看修改后的配置文件
监听地址 [root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/redis.conf | grep bind # By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens # the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses. # bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1 # bind 127.0.0.1 ::1 # internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the # following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only into bind 0.0.0.0 # 1) The server is not binding explicitly to a set of addresses using the # "bind" directive. # are explicitly listed using the "bind" directive. 密码 [root@node1 ~]# cat /etc/redis.conf | grep requirepass # If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration requirepass 123456
启动服务并登录测试redis
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl start redis [root@node1 ~]# netstat -lntup | grep redis tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2139/redis-server 0 # 不加密码登录(没有权限执行指令) [root@node1 ~]# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS * (error) NOAUTH Authentication required. 127.0.0.1:6379> # 添加密码登录 [root@node1 ~]# redis-cli -a 123456 127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS * (empty list or set) 127.0.0.1:6379>
安装JDK
[root@node1 ELK]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk
redis也是可以了 结束redis部署
5. elasticsearch集群部署
下面的设置安装源在整个环境的所有环境都要执行
# 添加ELK的yum源 [root@node2 ~]# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch [root@node2 ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo [elasticsearch-6.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md # 安装jdk和elasticsearch(这里需要注意的是jdk一定是1.8.0以上的版本) [root@node2 ~]# yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk
在192.168.176.130、131、132 机器上执行
[root@node1 ~]# yum -y install elasticsearch [root@node2 ~]# yum -y install elasticsearch [root@node3 ~]# yum -y install elasticsearch
温馨提示:以上安装要在三台机器上都要执行
配置文件修改
温馨提示:三台机器上都要修改配置文件
三台机器配置文件的不同之处
node.name: 这里的名称每台机器都不能一样 network.host: 这里是本服务器的地址
每台机器的配置文件

1 [root@node2 ELK]# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 2 # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= 3 # 4 # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. 5 # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you 6 # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. 7 # 8 # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists 9 # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. 10 # 11 # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: 12 # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html 13 # 14 # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- 15 # 16 # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: 17 # 18 cluster.name: elk-cluster 19 # 20 # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ 21 # 22 # Use a descriptive name for the node: 23 # 24 node.name: node-1 25 # 26 # Add custom attributes to the node: 27 # 28 #node.attr.rack: r1 29 # 30 # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ 31 # 32 # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): 33 # 34 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch 35 # 36 # Path to log files: 37 # 38 path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch 39 # 40 # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- 41 # 42 # Lock the memory on startup: 43 # 44 #bootstrap.memory_lock: true 45 # 46 # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available 47 # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this 48 # limit. 49 # 50 # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. 51 # 52 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- 53 # 54 # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): 55 # 56 network.host: 192.168.176.130 57 # 58 # Set a custom port for HTTP: 59 # 60 http.port: 9200 61 # 62 # For more information, consult the network module documentation. 63 # 64 # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- 65 # 66 # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: 67 # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] 68 # 69 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.176.130","192.168.176.131","192.168.176.132"] 70 # 71 # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): 72 # 73 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 74 # 75 # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. 76 # 77 # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- 78 # 79 # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: 80 # 81 #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 82 # 83 # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. 84 # 85 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- 86 # 87 # Require explicit names when deleting indices: 88 # 89 #action.destructive_requires_name: true 90 91 # 允许所有跨域连接 为了使用head的可视化工具的解决方法 92 http.cors.enabled: true 93 http.cors.allow-origin: "*"

1 [root@node3 ELK]# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 2 # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= 3 # 4 # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. 5 # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you 6 # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. 7 # 8 # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists 9 # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. 10 # 11 # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: 12 # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html 13 # 14 # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- 15 # 16 # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: 17 # 18 cluster.name: elk-cluster 19 # 20 # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ 21 # 22 # Use a descriptive name for the node: 23 # 24 node.name: node-2 25 # 26 # Add custom attributes to the node: 27 # 28 #node.attr.rack: r1 29 # 30 # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ 31 # 32 # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): 33 # 34 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch 35 # 36 # Path to log files: 37 # 38 path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch 39 # 40 # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- 41 # 42 # Lock the memory on startup: 43 # 44 #bootstrap.memory_lock: true 45 # 46 # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available 47 # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this 48 # limit. 49 # 50 # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. 51 # 52 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- 53 # 54 # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): 55 # 56 network.host: 192.168.176.131 57 # 58 # Set a custom port for HTTP: 59 # 60 http.port: 9200 61 # 62 # For more information, consult the network module documentation. 63 # 64 # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- 65 # 66 # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: 67 # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] 68 # 69 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.176.130","192.168.176.131","192.168.176.132"] 70 # 71 # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): 72 # 73 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 74 # 75 # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. 76 # 77 # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- 78 # 79 # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: 80 # 81 #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 82 # 83 # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. 84 # 85 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- 86 # 87 # Require explicit names when deleting indices: 88 # 89 #action.destructive_requires_name: true 90 91 # 允许所有跨域连接 为了使用head的可视化工具的解决方法 92 http.cors.enabled: true 93 http.cors.allow-origin: "*"

1 [root@node4 ELK]# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 2 # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= 3 # 4 # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. 5 # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you 6 # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. 7 # 8 # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists 9 # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. 10 # 11 # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: 12 # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html 13 # 14 # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- 15 # 16 # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: 17 # 18 cluster.name: elk-cluster 19 # 20 # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ 21 # 22 # Use a descriptive name for the node: 23 # 24 node.name: node-3 25 # 26 # Add custom attributes to the node: 27 # 28 #node.attr.rack: r1 29 # 30 # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ 31 # 32 # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): 33 # 34 path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch 35 # 36 # Path to log files: 37 # 38 path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch 39 # 40 # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- 41 # 42 # Lock the memory on startup: 43 # 44 #bootstrap.memory_lock: true 45 # 46 # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available 47 # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this 48 # limit. 49 # 50 # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. 51 # 52 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- 53 # 54 # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): 55 # 56 network.host: 192.168.176.132 57 # 58 # Set a custom port for HTTP: 59 # 60 http.port: 9200 61 # 62 # For more information, consult the network module documentation. 63 # 64 # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- 65 # 66 # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: 67 # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] 68 # 69 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.176.130","192.168.176.131","192.168.176.132"] 70 # 71 # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): 72 # 73 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 74 # 75 # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. 76 # 77 # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- 78 # 79 # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: 80 # 81 #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 82 # 83 # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. 84 # 85 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- 86 # 87 # Require explicit names when deleting indices: 88 # 89 #action.destructive_requires_name: true 90 91 # 允许所有跨域连接 为了使用head的可视化工具的解决方法 92 http.cors.enabled: true 93 http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
启动elasticsearch服务
温馨提示:三台机器都要启动(elasticsearch监听的端口是9200和9300)
[root@node2 ELK]# systemctl start elasticsearch [root@node3 ELK]# systemctl start elasticsearch [root@node4 ELK]# systemctl start elasticsearch
检查elasticsearch集群
elasticsearch 采用的是接口的方式去查看数据和状态信息
# 查看集群状态 [root@node2 ELK]# curl -X GET "192.168.176.130:9200/_cat/health?v" epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent 1542525784 07:23:04 elk-cluster green 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 - 100.0% # 查看集群性能 [root@node2 ELK]# curl -X GET "192.168.176.130:9200/_cat/nodes?v" ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name 192.168.176.131 26 96 2 0.05 0.07 0.05 mdi * node-2 192.168.176.132 26 96 3 0.06 0.06 0.05 mdi - node-3 192.168.176.130 25 95 0 0.00 0.02 0.05 mdi - node-1
安装elasticsearch的可视化web工具
温馨提示:只在一台机器上安装即可
[root@node2 ELK]# yum -y install epel-release
[root@node2 ELK]# yum -y install git
[root@node2 ELK]# yum -y install nodejs
git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git
cd elasticsearch-head
npm install
npm run start
6. logstash安装
这个环境中我们有两台服务器需要安装logstash 一个收集数据放到redis一个在redis中读放大elasticsearch中
192.168.176.128 这台机器负责收集并写到redis
192.168.176.129 这台机器负责读redis数据写的elasticsearch中
在两台机器上安装logstash
[root@manager ~]# yum -y install logstash [root@node1 ~]# yum -y install logstash 检查安装是否成功(检查版本) [root@manager ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash --version logstash 6.5.0 [root@node1 ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash --version logstash 6.5.0
在192.168.176.128服务器编写配置logstash收集并存入redis的配置文件
# 这个文件不存在,需要自己编辑
[root@manager ELK]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-to-redis.conf
input {
file {
path => ["/var/log/nginx/access.log"]
type => "nginx-access"
tags => ["nginxlog","test"]
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter {
}
output {
redis {
host => ["192.168.176.129"]
password => "123456"
db => "0"
data_type => "list"
key => "nginxlog"
}
}
这里的配置文件就不解释了,elasticsearch的具体参数介绍请看:elasticsearch详解
检查配置文件
[root@manager ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -t -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-to-redis.conf
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:01:37.282 [main] writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/queue"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:01:37.288 [main] writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.dead_letter_queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/dead_letter_queue"}
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:01:37.534 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified
Configuration OK
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:01:38.918 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Using config.test_and_exit mode. Config Validation Result: OK. Exiting Logstash
启动logstash
[root@manager ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -r -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-to-redis.conf
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:04:02.794 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:02.805 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Starting Logstash {"logstash.version"=>"6.5.0"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:02.826 [LogStash::Runner] agent - No persistent UUID file found. Generating new UUID {:uuid=>"14eb7761-ca71-41f7-b67d-f640c80d46ba", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/uuid"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:04.441 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Starting pipeline {:pipeline_id=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>4, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>50}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:19.710 [[main]>worker3] file - No sincedb_path set, generating one based on the "path" setting {:sincedb_path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/plugins/inputs/file/.sincedb_d883144359d3b4f516b37dba51fab2a2", :path=>["/var/log/nginx/access.log"]}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:19.737 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Pipeline started successfully {:pipeline_id=>"main", :thread=>"#<Thread:0x3e9da1b7 run>"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:19.789 [Ruby-0-Thread-1: /usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:6] agent - Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:19.832 [[main]<file] observingtail - START, creating Discoverer, Watch with file and sincedb collections
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:04:20.058 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
这里表示启动成功,去192.168.176.129的redis上查看是否有数据
[root@node1 ELK]# redis-cli -a 123456
127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS *
1) "nginxlog"
127.0.0.1:6379> LLEN nginxlog
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE nginxlog 0 1
1) "{"message":"{ \"@timestamp\": \"2018-11-18T01:28:49-05:00\", \"remote_addr\": \"192.168.176.128\", \"remote_user\": \"-\", \"body_bytes_sent\": \"3700\", \"request_time\": \"0.000\", \"status\": \"200\", \"request_uri\": \"/\", \"request_method\": \"GET\", \"http_referrer\": \"-\", \"http_x_forwarded_for\": \"-\", \"http_user_agent\": \"curl/7.29.0\"}","@timestamp":"2018-11-18T08:04:20.185Z","host":"manager","tags":["nginxlog","test"],"path":"/var/log/nginx/access.log","@version":"1","type":"nginx-access"}"
127.0.0.1:6379>
在192.168.176.129上编写读取redis数据写到elasticsearch中的配置文件
[root@node1 ELK]# cat /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-from-redis.conf
input {
redis {
host => "192.168.176.129"
port => 6379
password => "123456"
db => "0"
data_type => "list"
key => "nginxlog"
}
}
filter {
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.176.130:9200","http://192.168.176.131:9200","http://192.168.176.132:9200"]
index => "nginxlogs-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
检查配置文件
[root@node1 ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -t -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-from-redis.conf WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console [WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:12:45.966 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified Configuration OK [INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:12:47.990 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Using config.test_and_exit mode. Config Validation Result: OK. Exiting Logstash
启动logstash
[root@node1 ELK]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -r -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-from-redis.conf
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:14:53.077 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:53.090 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Starting Logstash {"logstash.version"=>"6.5.0"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:53.110 [LogStash::Runner] agent - No persistent UUID file found. Generating new UUID {:uuid=>"f50b6c39-c81a-4a9d-b329-82aea82ddb2d", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/uuid"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:55.989 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Starting pipeline {:pipeline_id=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>4, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>50}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.334 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Elasticsearch pool URLs updated {:changes=>{:removed=>[], :added=>[http://192.168.176.130:9200/, http://192.168.176.131:9200/, http://192.168.176.132:9200/]}}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.340 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Running health check to see if an Elasticsearch connection is working {:healthcheck_url=>http://192.168.176.130:9200/, :path=>"/"}
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.481 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>"http://192.168.176.130:9200/"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.642 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - ES Output version determined {:es_version=>6}
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.646 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Detected a 6.x and above cluster: the `type` event field won't be used to determine the document _type {:es_version=>6}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.647 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Running health check to see if an Elasticsearch connection is working {:healthcheck_url=>http://192.168.176.131:9200/, :path=>"/"}
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.720 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>"http://192.168.176.131:9200/"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.746 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Running health check to see if an Elasticsearch connection is working {:healthcheck_url=>http://192.168.176.132:9200/, :path=>"/"}
[WARN ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.811 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>"http://192.168.176.132:9200/"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.854 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - New Elasticsearch output {:class=>"LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch", :hosts=>["http://192.168.176.130:9200", "http://192.168.176.131:9200", "http://192.168.176.132:9200"]}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.892 [Ruby-0-Thread-5: :1] elasticsearch - Using mapping template from {:path=>nil}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.908 [Ruby-0-Thread-5: :1] elasticsearch - Attempting to install template {:manage_template=>{"template"=>"logstash-*", "version"=>60001, "settings"=>{"index.refresh_interval"=>"5s"}, "mappings"=>{"_default_"=>{"dynamic_templates"=>[{"message_field"=>{"path_match"=>"message", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false}}}, {"string_fields"=>{"match"=>"*", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false, "fields"=>{"keyword"=>{"type"=>"keyword", "ignore_above"=>256}}}}}], "properties"=>{"@timestamp"=>{"type"=>"date"}, "@version"=>{"type"=>"keyword"}, "geoip"=>{"dynamic"=>true, "properties"=>{"ip"=>{"type"=>"ip"}, "location"=>{"type"=>"geo_point"}, "latitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}, "longitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}}}}}}}}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.913 [[main]>worker3] redis - Registering Redis {:identity=>"redis://<password>@192.168.176.129:6379/0 list:nginxlog"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:56.945 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] pipeline - Pipeline started successfully {:pipeline_id=>"main", :thread=>"#<Thread:0x300817f0 run>"}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:57.019 [Ruby-0-Thread-1: /usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:6] agent - Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:57.038 [Ruby-0-Thread-5: :1] elasticsearch - Installing elasticsearch template to _template/logstash
[INFO ] 2018-11-18 03:14:57.373 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
上的输出表示启动成功,下面还会输出一些数据

这些就是我们的日志数据,在redis里面读出来的一个debug信息
我们查看129中的redis是不是已经空了
[root@node1 ~]# redis-cli -a 123456 127.0.0.1:6379> LLEN nginxlog (integer) 11 127.0.0.1:6379> LLEN nginxlog (integer) 0 127.0.0.1:6379>
查看elasticsearch里面是不是多出来一个索引
[root@node2 elasticsearch-head-master]# curl "192.168.176.130:9200/_cat/indices?v" health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size green open bank kk8k6Y8eRCWiLDR3fBCoHA 5 1 1000 0 958.1kb 475.1kb green open nginxlogs-2018.11.18 IocfOyAIT4-cxC-7O9kMtw 5 1 11 0 72.1kb 36kb
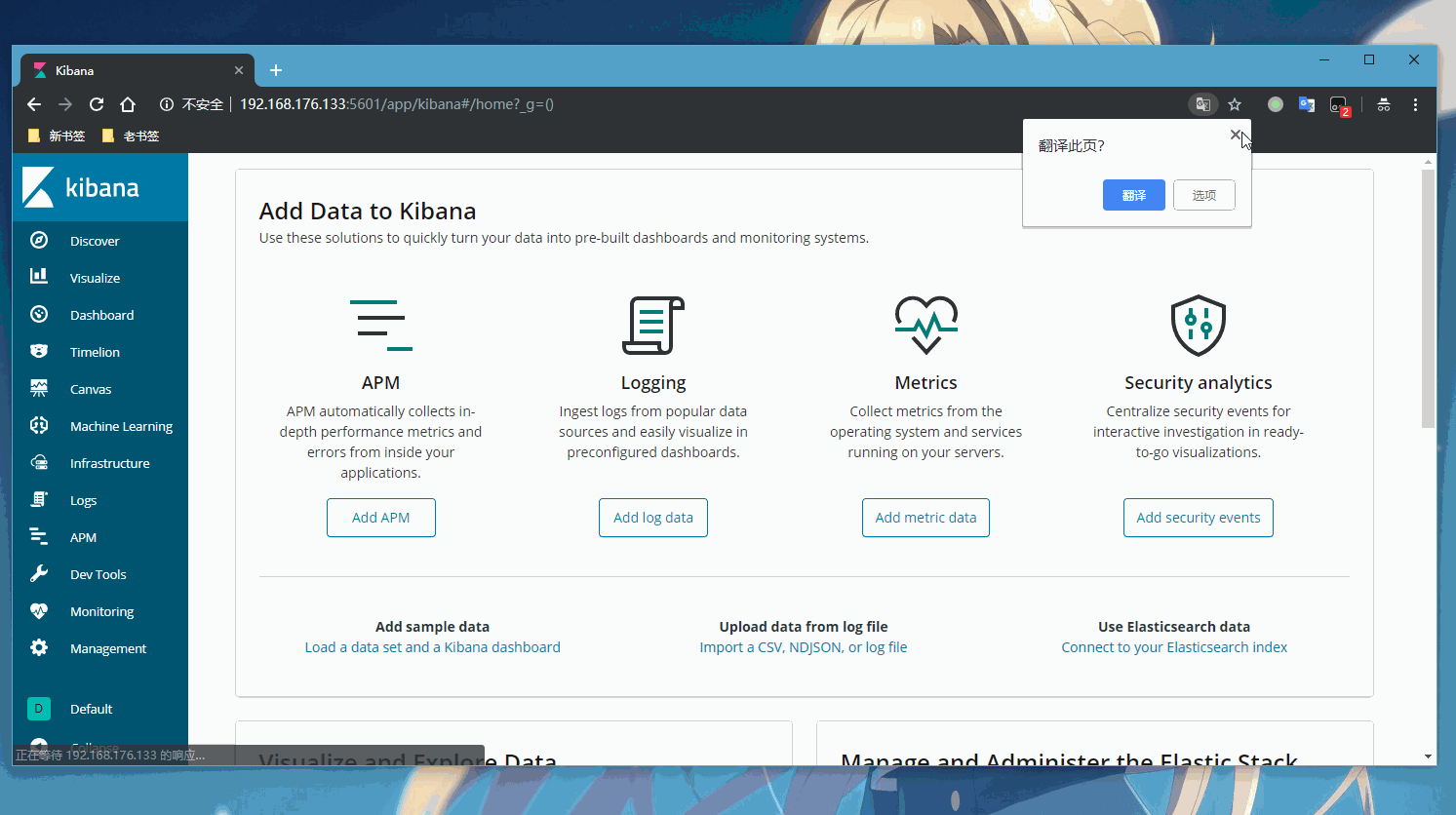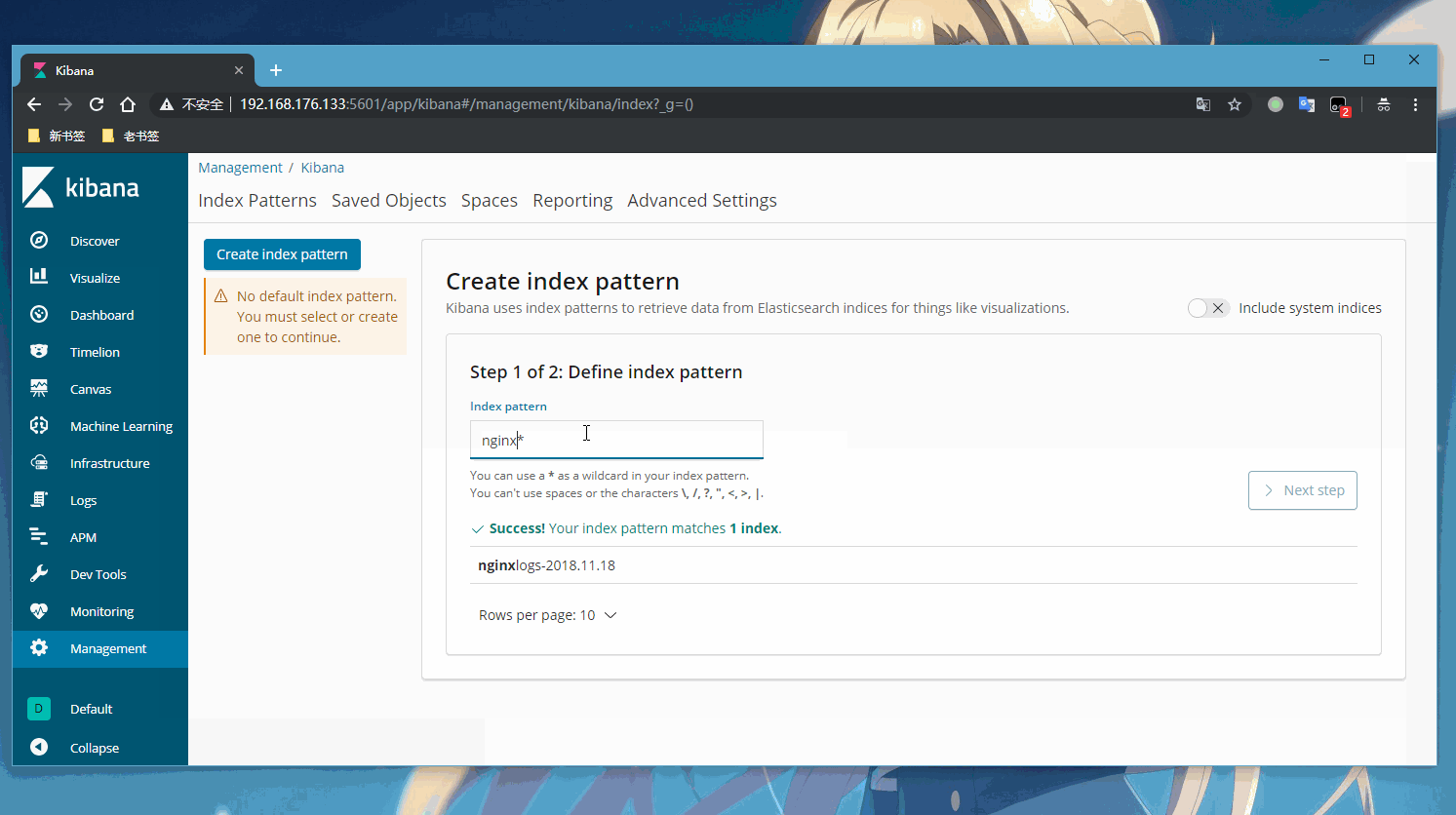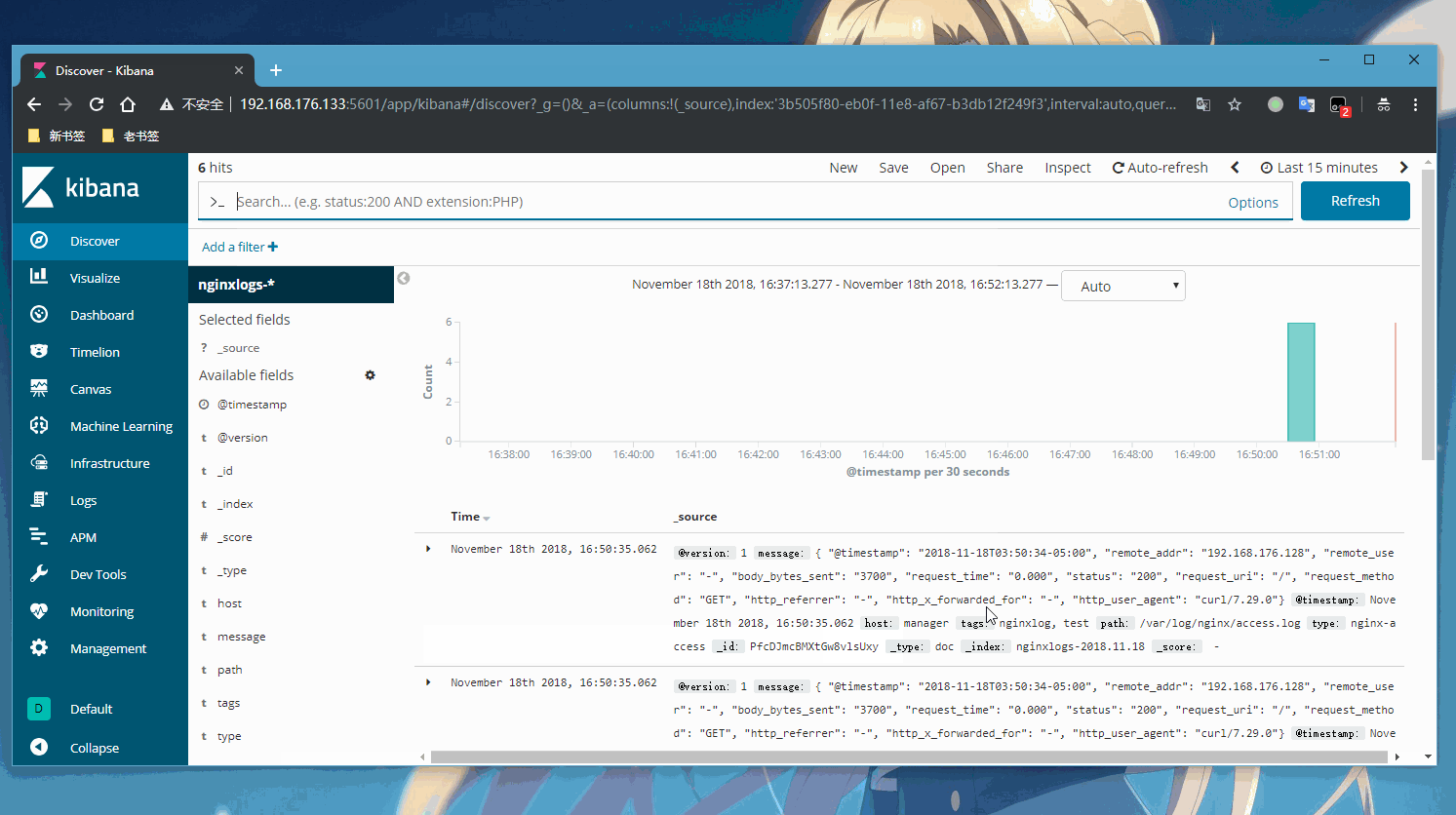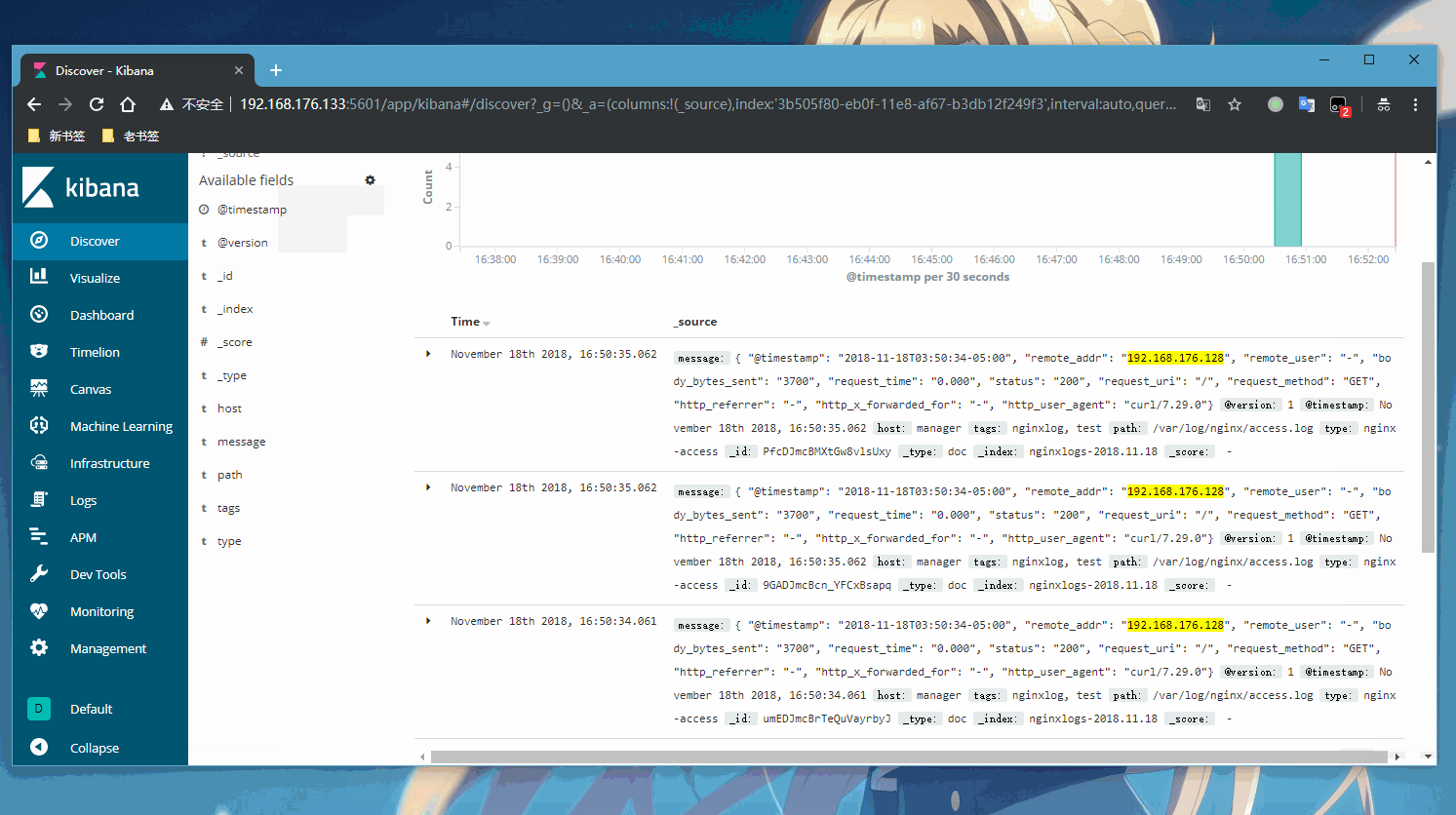
这里的nginxlogs-2018.11.18索引nginx的日志数据
接下了就用kibana展示出啦
7. kibana安装
在192.168.176.133的服务器上安装kibana
[root@node5 ~]# yum -y install kibana # 查看是否安装成功(查看版本) [root@node5 ELK]# /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana --version 6.5.0
编辑kibana的配置文件
需要修改的地方:
# 监听端口 server.port:5601 去掉注释即可 # 监听地址 server.host: "localhost" 去掉注释修改为 server.host: "0.0.0.0" # elasticsearch地址 elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200" 去掉注释修改为 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.176.130:9200"

1 [root@node5 ELK]# cat /etc/kibana/kibana.yml 2 # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. 3 server.port: 5601 4 5 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. 6 # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. 7 # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. 8 server.host: "0.0.0.0" 9 10 # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. 11 # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath 12 # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. 13 # This setting cannot end in a slash. 14 #server.basePath: "" 15 16 # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with 17 # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. 18 # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will 19 # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. 20 #server.rewriteBasePath: false 21 22 # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. 23 #server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576 24 25 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. 26 #server.name: "your-hostname" 27 28 # The URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for all your queries. 29 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.176.130:9200" 30 31 # When this setting's value is true Kibana uses the hostname specified in the server.host 32 # setting. When the value of this setting is false, Kibana uses the hostname of the host 33 # that connects to this Kibana instance. 34 #elasticsearch.preserveHost: true 35 36 # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and 37 # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. 38 #kibana.index: ".kibana" 39 40 # The default application to load. 41 #kibana.defaultAppId: "home" 42 43 # If your Elasticsearch is protected with basic authentication, these settings provide 44 # the username and password that the Kibana server uses to perform maintenance on the Kibana 45 # index at startup. Your Kibana users still need to authenticate with Elasticsearch, which 46 # is proxied through the Kibana server. 47 #elasticsearch.username: "user" 48 #elasticsearch.password: "pass" 49 50 # Enables SSL and paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and SSL key files, respectively. 51 # These settings enable SSL for outgoing requests from the Kibana server to the browser. 52 #server.ssl.enabled: false 53 #server.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/server.crt 54 #server.ssl.key: /path/to/your/server.key 55 56 # Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files. 57 # These files validate that your Elasticsearch backend uses the same key files. 58 #elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/your/client.crt 59 #elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/your/client.key 60 61 # Optional setting that enables you to specify a path to the PEM file for the certificate 62 # authority for your Elasticsearch instance. 63 #elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: [ "/path/to/your/CA.pem" ] 64 65 # To disregard the validity of SSL certificates, change this setting's value to 'none'. 66 #elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: full 67 68 # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch to respond to pings. Defaults to the value of 69 # the elasticsearch.requestTimeout setting. 70 #elasticsearch.pingTimeout: 1500 71 72 # Time in milliseconds to wait for responses from the back end or Elasticsearch. This value 73 # must be a positive integer. 74 #elasticsearch.requestTimeout: 30000 75 76 # List of Kibana client-side headers to send to Elasticsearch. To send *no* client-side 77 # headers, set this value to [] (an empty list). 78 #elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist: [ authorization ] 79 80 # Header names and values that are sent to Elasticsearch. Any custom headers cannot be overwritten 81 # by client-side headers, regardless of the elasticsearch.requestHeadersWhitelist configuration. 82 #elasticsearch.customHeaders: {} 83 84 # Time in milliseconds for Elasticsearch to wait for responses from shards. Set to 0 to disable. 85 #elasticsearch.shardTimeout: 30000 86 87 # Time in milliseconds to wait for Elasticsearch at Kibana startup before retrying. 88 #elasticsearch.startupTimeout: 5000 89 90 # Logs queries sent to Elasticsearch. Requires logging.verbose set to true. 91 #elasticsearch.logQueries: false 92 93 # Specifies the path where Kibana creates the process ID file. 94 #pid.file: /var/run/kibana.pid 95 96 # Enables you specify a file where Kibana stores log output. 97 #logging.dest: stdout 98 99 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output. 100 #logging.silent: false 101 102 # Set the value of this setting to true to suppress all logging output other than error messages. 103 #logging.quiet: false 104 105 # Set the value of this setting to true to log all events, including system usage information 106 # and all requests. 107 #logging.verbose: false 108 109 # Set the interval in milliseconds to sample system and process performance 110 # metrics. Minimum is 100ms. Defaults to 5000. 111 #ops.interval: 5000 112 113 # Specifies locale to be used for all localizable strings, dates and number formats. 114 #i18n.locale: "en"
在配置文件中还有很多的配置项,会有一篇专门的文章介绍
启动kibana
[root@node5 ELK]# systemctl start kibana [root@node5 ELK]# netstat -lntup | grep 5601 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5601 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2693/node
登录kibana的web页面查看我们nginx实时收集的日志