1. 几个景点算法:
1. 修路问题:最小生成树(加权值)+ 普利姆
2. 最短路径:图+弗洛伊德算法
3. 汉诺塔: 分支的算法
4. 八皇后:回朔法、
5. 丢手帕 : 约瑟夫问题
2. 线性结构 与非线性结构
1.线性结构 :数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系
顺序存储结构 , 链式存储结构
(数组,队列,链表和栈)
2 . 非线性结构:(二维数组,多维数组,广义表,树结构,图结构)
3. 稀疏数组
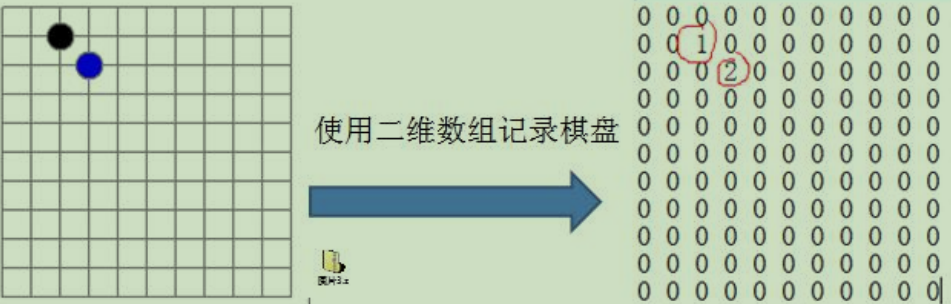
因为该数组中记录了很多值是默认值0,记录了很多没有意义的数据 -》 稀疏数组

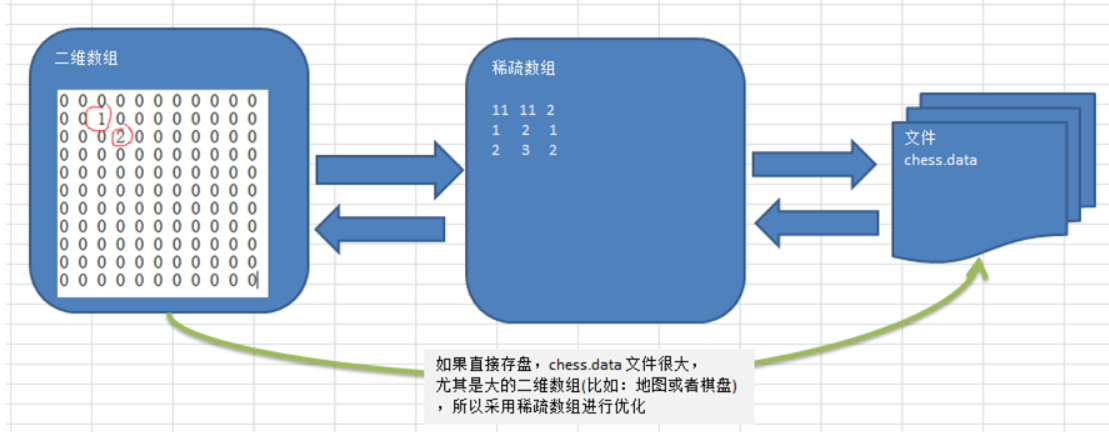
代码实现原始二维数组与稀疏数组之间的转化


import org.junit.Test; public class XiShuJuZhen { //创建一个原始的二维数组 11*11 @Test public void testArray() { int[][] charArray = new int[11][11]; //0表示没有棋子,1 表示黑子 2表示蓝子 charArray[1][2] = 1; charArray[2][3] = 2; charArray[4][5] = 2; System.out.println("输出原始的二维数组"); for (int[] is : charArray) { for (int is2 : is) { System.out.print(" "+is2); } System.out.println(); } /* * 将二维数组转为稀疏数组的思路 * (1).先遍历二维数组,得到非0整数的个数 */ int sum = 0; for(int i=0;i<11;i++) { for(int j=0;j<11;j++) { if(charArray[i][j]!=0) { sum++; } } } System.out.println("sum = "+sum); //2 .创建对应的稀疏数组 int sparseArr[][] = new int[sum+1][3] ; //给稀疏数组赋值 sparseArr[0][0] = 11; //有11行 sparseArr[0][1] = 11; //有11列 sparseArr[0][2] = sum; //有多少个值 int count= 0; //count 用于记录是第几个非0数据 for(int i=0;i<11;i++) { for(int j=0;j<11;j++) { if(charArray[i][j]!=0) { count++; sparseArr[count][0] = i; //第0 列,第count行 sparseArr[count][1] = j; //第1列,第count行 sparseArr[count][2] =charArray[i][j];//第2列 存入的是二维数组不为0的值 } } } System.out.println("输出稀疏数组的形式"); for (int[] is : sparseArr) { for (int is2 : is) { System.out.print(" "+is2); } System.out.println(); } //恢复成二维数组 //先读取稀疏数组的第一行将新创建的数组进行赋值确定数组大小 int[][] charArray1 = new int[sparseArr[0][0]][sparseArr[0][0]]; //再读取稀疏数组的后几行,从第二行开始,并赋给原始的二维数组 for(int i=1;i<sparseArr.length;i++) { //为原始数组进行赋值 charArray1[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]] = sparseArr[i][2]; } System.out.println("恢复后的原始二维数组"); for (int[] is : charArray1) { for (int is2 : is) { System.out.print(" "+is2); } System.out.println(); } } }
使用IO流将数据保存起来 其实我没有明白是什么意思,然后我就写了一个IO流将数据以文本的方式保存起来了


public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个字节流输出流 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/lucenezhulina/a.txt"); //将字节流转化为字符流 OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream); //使用缓冲区进行缓冲 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter); // bufferedWriter.write("朱李纳"); //0表示没有棋子,1 表示黑子 2表示蓝子 String str1 = "int[][] charArray = new int[11][11];"; String str2 = "charArray[1][2] = 1;"; String str3 = "charArray[2][3] = 2;"; String str4 = "charArray[4][5] = 2;"; bufferedWriter.write(str1); bufferedWriter.write(str2); bufferedWriter.write(str3); bufferedWriter.write(str4); bufferedWriter.close(); //创建 一个字节输入流 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/lucenezhulina/a.txt"); //将字节流转化为字符流 InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream); //使用缓冲流 BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader); String readLine = bufferedReader.readLine(); System.out.println(readLine); //读取数据 /* while(true) { String readLine = bufferedReader.readLine(); if(readLine==null) { break; } System.out.println(readLine); }*/ bufferedReader.close(); }
改进后的代码
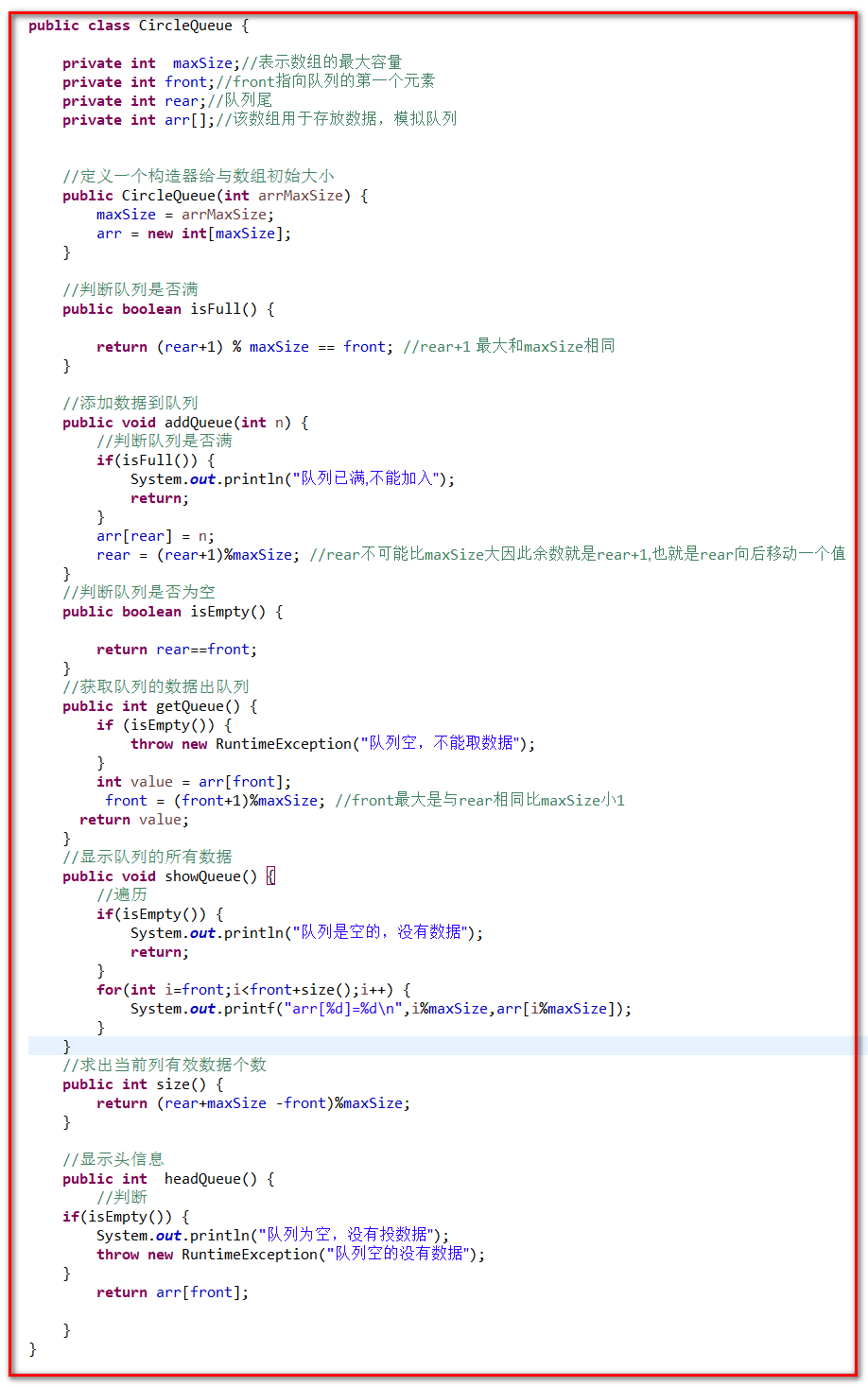

import java.awt.event.FocusAdapter; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.management.RuntimeErrorException; import org.junit.Test; public class CircleQueue { private int maxSize;//表示数组的最大容量 private int front;//front指向队列的第一个元素 private int rear;//队列尾 private int arr[];//该数组用于存放数据,模拟队列 //定义一个构造器给与数组初始大小 public CircleQueue(int arrMaxSize) { maxSize = arrMaxSize; arr = new int[maxSize]; } //判断队列是否满 public boolean isFull() { return (rear+1) % maxSize == front; //rear+1 最大和maxSize相同 } //添加数据到队列 public void addQueue(int n) { //判断队列是否满 if(isFull()) { System.out.println("队列已满,不能加入"); return; } arr[rear] = n; rear = (rear+1)%maxSize; //rear不可能比maxSize大因此余数就是rear+1,也就是rear向后移动一个值 } //判断队列是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { return rear==front; } //获取队列的数据出队列 public int getQueue() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据"); } int value = arr[front]; front = (front+1)%maxSize; //front最大是与rear相同比maxSize小1 return value; } //显示队列的所有数据 public void showQueue() { //遍历 if(isEmpty()) { System.out.println("队列是空的,没有数据"); return; } for(int i=front;i<front+size();i++) { System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d ",i%maxSize,arr[i%maxSize]); } } //求出当前列有效数据个数 public int size() { return (rear+maxSize -front)%maxSize; } //显示头信息 public int headQueue() { //判断 if(isEmpty()) { System.out.println("队列为空,没有投数据"); throw new RuntimeException("队列空的没有数据"); } return arr[front]; } } public class TestCircleQueue { @Test public void test01() { //创建一个队列对象 CircleQueue arrayQueue = new CircleQueue(4); //接收用户输入 char key = ' '; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); boolean loop = true; //输出一个菜单 while(loop) { System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列"); System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序"); System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列"); System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据"); System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据"); key = sc.next().charAt(0);//接收一个字符 switch (key) { case 's': arrayQueue.showQueue(); break; case 'e': //退出程序 sc.close(); loop = false; break; case 'h': //查看队列头的数据 try { int res = arrayQueue.headQueue(); System.out.println("队列头的数据是: "+res); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } break; case 'a': System.out.println("输入一个数"); int value = sc.nextInt(); arrayQueue.addQueue(value); break; case 'g': //取出数据 try { int res = arrayQueue.getQueue(); System.out.println("取出的数据是:"+res); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } break; default: break; } } System.out.println("程序退出"); } }
使用循环链表,这种方式不能进行排序,如果插入的顺序不一样,不能自动的进行排序


class SingleLinkedListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //进行测试 //先创建节点 HeroNode heroNode1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江" , "及时雨"); HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义" , "玉麒麟"); HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用" , "智多星"); HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲" , "豹子头"); //创建链表 SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); //加入 /* singleLinkedList.add(heroNode1); singleLinkedList.add(heroNode2); singleLinkedList.add(heroNode3); singleLinkedList.add(heroNode4);*/ //加入按照编号的顺序 singleLinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode1); singleLinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode4); singleLinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode2); singleLinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode3); //遍历 singleLinkedList.list(); } } //定义SingleLinkedList 管理我们的英雄 class SingleLinkedList{ //先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动,不存放具体的数据 private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0,"",""); //添加节点到单向链表 /** * 思路:当不考虑编号顺序时 * 1.找到当前链表的最后节点 * 2.将最后节点的这个next指向新的节点 */ public void add(HeroNode heroNode) { //因为head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助遍历temp HeroNode temp = head; //遍历链表,找到最后 while(true) { //找到链表的最后 if (temp.next==null) { break; } //如果没有找到就将temp后移 temp=temp.next; } //当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后 //将最后节点的这个next指向新的节点 temp.next = heroNode; } //第二种方式在添加英雄时,根据排名将英雄添加到指定位置 //如果有这个排名,择添加失败并给出提示 public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) { //应为头结点不能动,我们通过一个辅助变量帮助找到添加的位置 HeroNode temp = head; boolean flag = false; //标识添加的这个编号是否存在默认是false while (true) { if(temp.next==null) {//说明temp节点已经在链表的最后 break; } if (temp.next.no>heroNode.no) {//位置找到,就在temp的后面插入 break; }else if(temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {//说明希望添加的heroNode的编号已然存在 flag = true;//说明编号存在 break; } temp = temp.next; //后移,遍历当前的链表 } //判断flag的值 if (flag) { //不能添加,说明编号存在 System.out.printf("准备插入的英雄的编号 %d 已经存在了,不能加入 ",heroNode.no); }else { //插入到链表中,temp的后面 heroNode.next = temp.next; temp.next = heroNode; } } //显示链表 遍历 public void list() { //判断链表是否为空 if(head.next == null) { System.out.println("链表为空"); return; } //因为头结点不能动,需要一个辅助变量来遍历 HeroNode temp = head.next; while(true) { //判断是否到链表最后 if (temp==null) { break; } //输出这个节点的信息 System.out.println(temp); //将这个temp后移 temp = temp.next; } } } //定义HeroNode ,每一个HeroNode对象就是一个节点 class HeroNode{ public int no; public String name; public String nickname; //昵称 public HeroNode next; //指向下一个节点 //构造器 传入三个参数一个编号,姓名,昵称 public HeroNode(int hNo,String hName,String hNickName) { this.no = hNo; this.name = hName; this.nickname = hNickName; } @Override public String toString() { return "HeroNode [no=" + no + ", name=" + name + ", nickname=" + nickname + ", next=" + next + "]"; } }
单链表的修改操作


//修改节点的信息,根据no编号来修改,即no不能改 public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) { //判断是否为空 if (head.next==null) { System.out.println("链表为空"); return; } //找到需要修改的节点,根据no编号 //定义一个辅助变量 HeroNode temp = head.next; boolean flag = false; //表示是否找到该节点 while(true) { if(temp==null) { break;//已经遍历完链表 在遍历的过程中temp一直在向后走到达最后一个next为null }if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no) { //找到 flag = true; break; } temp = temp.next; } //根据flag判断是否找到要修改的节点 if(flag==true) { temp.name = newHeroNode.name; temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname; }else { //没有找到 System.out.printf("没有找到编号为 %d 的节点,不能修改 ",newHeroNode.no); } }

//测试修改节点的代码 HeroNode heroNode = new HeroNode(2, "小卢", "玉麒麟"); singleLinkedList.update(heroNode); System.out.println("修改后"); singleLinkedList.list();

删除节点
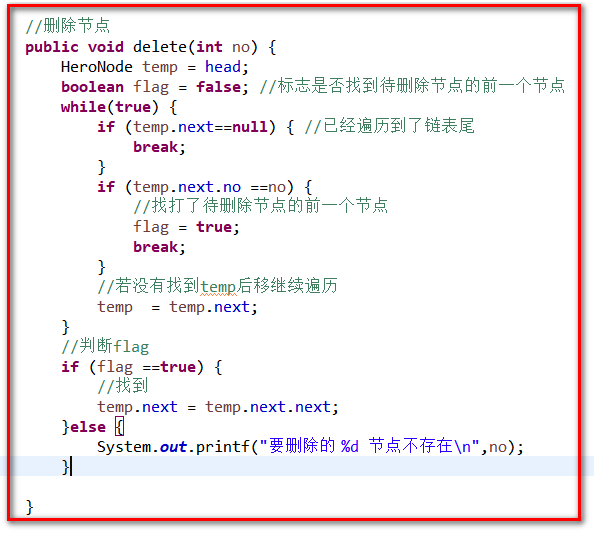

//删除节点 public void delete(int no) { HeroNode temp = head; boolean flag = false; //标志是否找到待删除节点的前一个节点 while(true) { if (temp.next==null) { //已经遍历到了链表尾 break; } if (temp.next.no ==no) { //找打了待删除节点的前一个节点 flag = true; break; } //若没有找到temp后移继续遍历 temp = temp.next; } //判断flag if (flag ==true) { //找到 temp.next = temp.next.next; }else { System.out.printf("要删除的 %d 节点不存在 ",no); } }

//删除一个节点 singleLinkedList.delete(1); System.out.println("删除后链表结构"); singleLinkedList.list();
几个经典面试题:
将单链表进行翻转

//将单链表进行翻转 public static void reverseLinked(HeroNode heroNode) { //如果当前链表为空,或者只有一个节点就无需翻转 直接返回 if (heroNode.next==null|| heroNode.next.next==null) { return ; } //定义一个辅助的指针,帮我们遍历原来的链表 HeroNode current =heroNode.next; HeroNode next = null; //指向当前节点current的下一个节点 相当一next代替current向后移动 HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "", ""); //遍历原来的链表每遍历一个节点就将其取出,并放在新的链表reverseHead的最前端 while(current !=null) { next = current.next; //先暂时保留current的下一个节点 current.next = reverseHead.next; //将当前节点的下一个节点置为空 目的是使 // 当前current 称为新链表的第一个节点 reverseHead.next = current; //当前节点称为了新链表的第一个节点 current = next; //现在current指向了原来链表的下一个节点,也就是让current后移 } //最后将head.next指向reverseHead.next,实现单链表的反转 heroNode.next = reverseHead.next; }
测试:

//测试单链表的反转 System.out.println("反转后链表的情况"); reverseLinked(singleLinkedList.getHead()); singleLinkedList.list();
查找单链表中的倒数第k个节点 新浪面试题

//查找单链表中的倒数第k个节点 新浪面试题 /* * 思路:编写一个方法,接收head节点同时接收一个index,index 表示倒数第index个节点 * 先把链表从头到尾遍历,然后减去index就是我需要遍历的长度 */ public static HeroNode returnSignIndexNode(HeroNode heroNode,int index) { //如果链表尾空就返回null if (heroNode.next==null) { return null; } //第一次遍历获取链表的长度 int size = getLength(heroNode); //第二次遍历 size-index位置就是我们倒数的第k的节点 //先做一个index的校验 if(index<=0||index>size) { return null; } //定义辅助变量,for循环定位到倒数的index HeroNode current = heroNode.next; for(int i=0;i<size-index;i++) { current = current.next; } return current; }
测试:

//测试是否得到了倒数第k个节点 HeroNode res = returnSignIndexNode(singleLinkedList.getHead(), 1); System.out.println("倒数第1 res = "+res);
查找单链表有效节点的个数不统计头结点

//查找单链表有效节点的个数不统计头结点 public static int getLength(HeroNode heroNode) { if(heroNode.next ==null) { //空链表 return 0; } int count = 0; HeroNode current; current = heroNode.next; while(current!=null) { count++; current = current.next; } return count; }
测试:

//测试一下 求单链表中有效节点的个数 System.out.println("有效的节点个数:"+getLength(singleLinkedList.getHead()));
从尾到头打印单链表

/* * 从尾到头打印单链表 * 思路:方式一:先将单链表进行翻转操作,然后再遍历即可,这样做的问题是会破坏原来的单链表的结构 * 不建议。 * 方式二:可以利用栈这个数据结构,将个个节点压入栈中,然后利用栈的先进后出的特点,就实现了 * 逆序打印的效果。 */ public static void reversePrint(HeroNode heroNode) { if(heroNode.next==null) { return; //空链表,不能打印 } //创建一个栈,将各个节点压入栈中 Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<HeroNode>(); HeroNode current = heroNode.next; //将链表的所有的节点压入栈中 while(current!=null) { stack.push(current); current = current.next; //current后移 } //将栈中的节点进行打印,pop 出栈 while(stack.size()>0) { System.out.println(stack.pop());//先进后出 出栈 } }
测试

System.out.println("测试逆序打印单链表,没有改变原来链表的结构"); reversePrint(singleLinkedList.getHead());
