1.构造数据
为了操作方便, 先构造以下数据
1.1 学生表
create table `student` ( `id` int unsigned primary key auto_increment, `name` char(32) not null unique, `sex` enum('男', '女') not null, `city` char(32) not null, `description` text, `birthday` date not null default '1995-1-1', `money` float(7, 2) default 0, `only_child` boolean ) charset=utf8; insert into `student` (`name`, `sex`, `city`, `description`, `birthday`, `money`, `only_child`) values ('郭德纲', '男', '北京', '班长', '1997/10/1', rand() * 100, True), ('陈乔恩', '女', '上海', NULL, '1995/3/2', rand() * 100, True), ('赵丽颖', '女', '北京', '班花, 不骄傲', '1995/4/4', rand() * 100, False), ('王宝强', '男', '重庆', '超爱吃火锅', '1998/10/5', rand() * 100, False), ('赵雅芝', '女', '重庆', '全宇宙三好学生', '1996/7/9', rand() * 100, True), ('张学友', '男', '上海', '奥林匹克总冠军!', '1993/5/2', rand() * 100, False), ('陈意涵', '女', '上海', NULL, '1994/8/30', rand() * 100, True), ('赵本山', '男', '南京', '副班长', '1995/6/1', rand() * 100, True), ('张柏芝', '女', '上海', NULL, '1997/2/28', rand() * 100, False), ('吴亦凡', '男', '南京', '大碗宽面要不要?', '1995/6/1', rand() * 100, True), ('鹿晗', '男', '北京', NULL, '1993/5/28', rand() * 100, True), ('关晓彤', '女', '北京', NULL, '1995/7/12', rand() * 100, True), ('周杰伦', '男', '台北', '小伙人才啊', '1998/3/28', rand() * 100, False), ('马云', '男', '南京', '一个字:贼有钱', '1990/4/1', rand() * 100, False), ('马化腾', '男', '上海', '马云死对头', '1990/11/28', rand() * 100, False);
1.2成绩表
create table score ( `id` int unsigned primary key auto_increment, `math` float not null default 0, `english` float not null default 0 ) charset=utf8; insert into score (`math`, `english`) values (49, 71), (62, 66.7), (44, 86), (77.5, 74), (41, 75), (82, 59.5), (64.5, 85), (62, 98), (44, 36), (67, 56), (81, 90), (78, 70), (83, 66), (40, 90), (90, 90);
2.常用的查询语句
2.1SELECT : 字段表达式
- SELECT 既可以做查询, 也可以做输出
- 示例
select rand(); -- 随机数 select unix_timestamp(); -- 显示Unix时间戳 select id, name from student;
2.2FROM 子句
- 语法: select 字段 from 表名;
- FROM 后面是数据源, 数据源可以写多个, 数据源一般是表名, 也可以是其他查询的结果;
- 示例
SELECT student.name, score.math FROM student, score;
2.3WHERE 子句: 按指定条件过滤
- 语法: select 字段 from 表名 where 条件;
- WHERE 是做条件查询, 只返回结果为 True 的数据
- 示例
select name from student where city = '上海';
- 空值判断: is null | is not null
select `name` from `student` where `description` is null; select `name` from `student` where `description` is not null;
- 范围判断:
- between ... and ...
- not between ... and ...
select id, math from score where math between 60 and 70; select id, math from score where math not between 60 and 70; select * from score where math>=80 and english<=60; -- 直接做比较判断
2.4HAVING
- HAVING 和WHERE 功能类似,都可以用来实现条件查询。很多情况下可以用where 或者having ,甚至可以混合使用。
- 示例:
select `name`, `birthday` from `student` where `birthday` > '1995-1-1'; select `name`, `birthday` from `student` having `birthday` > '1995-1-1'; select * from student where id>=3 and city='北京'; select * from student having id>=3 and city='北京'; select * from student where id>=3 having city='北京'; -- 混用
但是他们也有区别。
- 只能使用where不能使用having的情况。
select `name`, `birthday` from `student` where id > 2; -- 报错,having的条件查询,只能包含在前面的搜索结果里 select `name`, `birthday` from `student` having id > 2;
- 只能使用having不能使用where的情况。
select name as n,birthday as b,id as i from student having i > 2; -- 报错,where只识别存在的字段 select name as n,birthday as b,id as i from student where i > 2; -- 取出每个城市中满足最小出生年份大于1995的 select city, group_concat(birthday) from student group by city having min(birthday) > '1995-1-1';
2.5GROUP BY : 分组查询
- 按照某一字段进行分组, 会把该字段中值相同的归为一组, 将查询的结果分类显示, 方便统计。
- 如果有 WHERE 要放在 WHERE 的后面
- 语法: select 字段 from 表名 group by 分组字段;
- 示例
select sex, count(id) from student group by sex; -- 在group将需要的结果通过 “聚合函数” 拼接 select sex, group_concat(name) from student group by sex;
2.6ORDER BY : 按字段排序
- ORDER BY 主要作用是排序
- ORDER BY 写在 GROUP BY 后面 ,如果有 HAVING 也要写在 HAVING 的后面
- 语法: select 字段 from 表名 order by 排序字段 asc|desc;
- 分为升序 asc 降序 desc, 默认 asc (可以不写)
- 示例
select * from student order by age; select * from student order by age desc; select city,avg(money),group_concat(name),sum(money) from student group by city having sum(money)>70 order by sum(money);
2.7LIMIT : 限制取出数量
语法:
select 字段 from 表名 limit m; -- 从第 1 行到第 m 行 select 字段 from 表名 limit m, n; -- 从第 m 行开始,往下取 n 行 select 字段 from 表名 limit m offset n; -- 跳过前 n 行, 取后面的 m 行
2.8DISTINCT : 去重
示例:
select distinct city from student;
2.9dual表
dual 是一个虚拟表, 仅仅为了保证 select ... from ... 语句的完整性
3.函数
3.1聚合函数


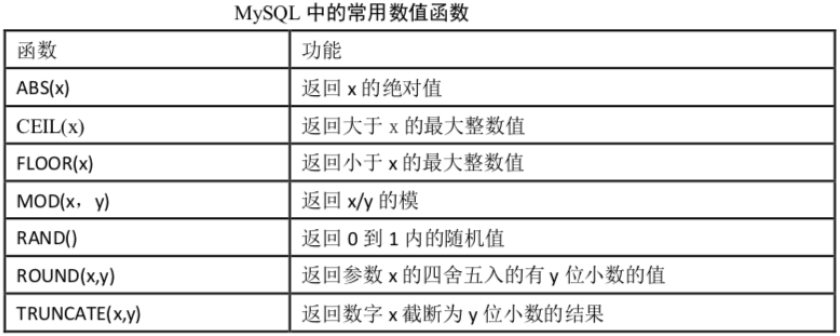
3.2数值计算类函数
3.3日期计算类函数

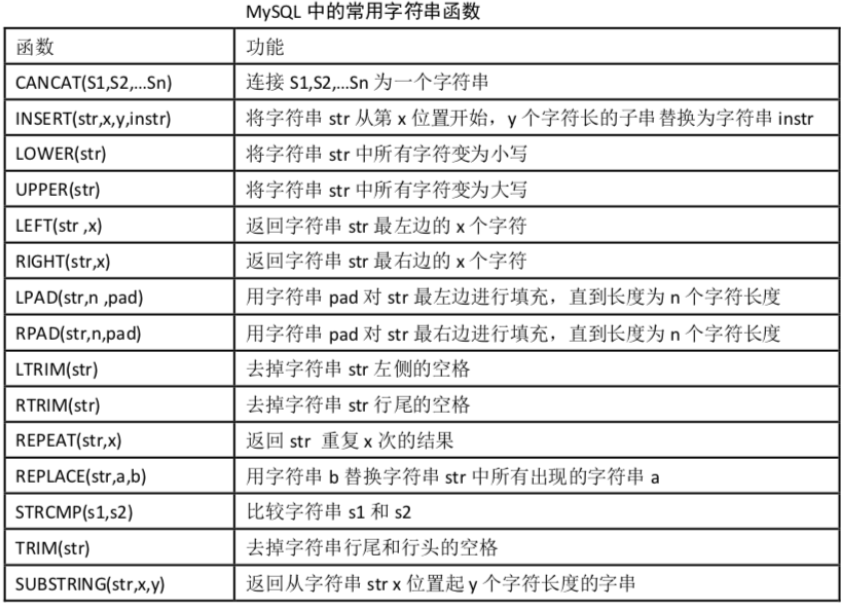
3.4字符串相关函数
3.5其他函数

4.多表查询
4.1UNION 联合查询
UNION 操作符用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集。
union要求:
- 1. 两边 select 语句的字段数必须一样
- 2. 两边可以具有不同数据类型的字段
- 3. 字段名默认按照左边的表来设置
- 4. 用法:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1
UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table2;
4.2INNER JOIN : 内连接 (交集)
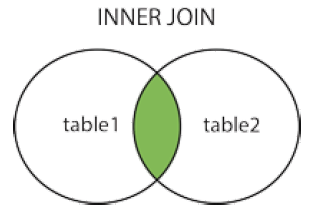
- INNER JOIN 关键字在表中存在至少一个匹配时返回行。
- 语法
SELECT 字段 FROM 表1 INNER JOIN 表2 ON 表1.字段=表2.字段; -- 或: SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
4.3LEFT JOIN : 左连接
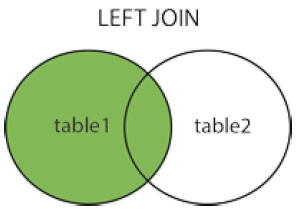 LEFT JOIN 关键字从左表(table1)返回所有的行,即使右表(table2)中没有匹配。如果右表中没有匹配,则结果为 NULL。
LEFT JOIN 关键字从左表(table1)返回所有的行,即使右表(table2)中没有匹配。如果右表中没有匹配,则结果为 NULL。
语法
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name; -- 或: SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
4.4RIGHT JOIN : 右连接

RIGHT JOIN 关键字从右表(table2)返回所有的行,即使左表(table1)中没有匹配。如果左表中没有匹配,则结果为 NULL。
语法
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name; -- 或: SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 RIGHT OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
4.5FULL JOIN : 全连接

- FULL JOIN 的连接方式是只要左表(table1)和右表(table2)其中一个表中存在匹配,则返回行。相当于结合了 LEFT JOIN 和 RIGHT JOIN 的结果。
- ==特别注意: MySQL 并不支持 full join==
- 语法
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
4.6子查询
查询的语句中还有一个查询
select name from student where id in (select id from score where math > 10);
5.视图表
5.1视图表的特点
- 视图是数据的特定子集,是从其他表里提取出数据而形成的虚拟表,或者说临时表。
- 创建视图表依赖一个查询。
- 视图是永远不会自己消失的除非手动删除它。
- 视图有时会对提高效率有帮助。临时表不会对性能有帮助,是资源消耗者。
- 视图一般随该数据库存放在一起,临时表永远都是在 tempdb 里的。
- 视图适合于多表连接浏览时使用;不适合增、删、改,这样可以提高执行效率。
- 一般视图表的名称以 v_ 为前缀,用来与正常表进行区分。
- 对原表的修改会影响到视图中的数据。
5.2创建视图
- 语法: create view 视图名 as 查询语句
- 示例:
create view v_user_score as select a.id, a.name, b.math, b.english from student a inner join score b on a.id=b order by id; -- 查询 select * from v_user_score; -- 删除 drop view v_user_score;