传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1693
Eat the Trees
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
Most
of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge
is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to
end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
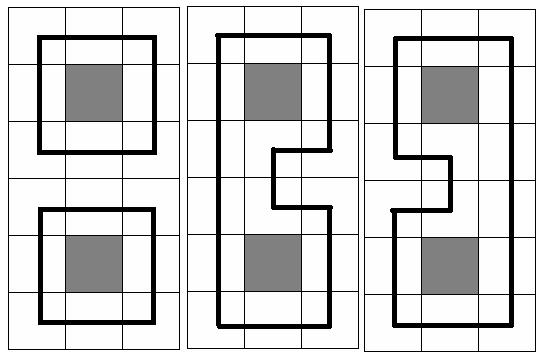
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))

Input
The
input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is
the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2
6 3
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees.
Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
Source
最简单的插头dp,代码风格来自baidu...
自己一定要画图模拟。。
然后一定要看论文而不是ppt
Codes:
1 #include<set> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<cstring> 6 #include<iostream> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 using namespace std; 9 #define For(i,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 10 #define Rep(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) 11 12 int T,n,m,G[13][13]; 13 long long dp[13][13][1<<13]; 14 15 void DP(){ 16 dp[0][m][0] = 1; 17 For(i,n){ 18 Rep(j,0,1<<m) dp[i][0][j<<1] = dp[i-1][m][j]; 19 For(j,m){ 20 int x = 1<<(j-1) , y = 1<<j; 21 Rep(k,0,(1<<(m+1)) - 1) 22 if(G[i][j]){ 23 dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k^x^y]; 24 if((k&x)&&(k&y)) continue; 25 if(!(k&x)&&!(k&y)) continue; 26 dp[i][j][k] += dp[i][j-1][k]; 27 } 28 else{ 29 if(!(k&x)&&!(k&y)) dp[i][j][k] = dp[i][j-1][k]; 30 else dp[i][j][k] = 0; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 void init(){ 37 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 38 memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); 39 For(i,n) 40 For(j,m) scanf("%d",&G[i][j]); 41 DP(); 42 } 43 44 int main(){ 45 scanf("%d",&T); 46 For(i,T) { 47 init(); 48 printf("Case %d: There are %I64d ways to eat the trees. ",i,dp[n][m][0]); 49 } 50 return 0; 51 }