可以通过Gson使用两种方法,将json字符串转换为对象,以下面该段报文做测试
{ "id": 84041462, "lastName": "小华", "age":32, "balance":666255.32, "hobbyDesc": { "subject": "数学", "score":25, "sport_desc":"跑步有益健康" } }
1. 创建实体类,通过 fromJson方法将json数据封装进对象中
如上,将上面报文按层次解析并创建两个对象
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName; public class HobbyDesc { private String subject; private int score; @SerializedName("sport_desc") private String sportDesc; //***
public class Account { private String id; private String lastName; private int age; private double balance; private HobbyDesc hobbyDesc;
//***
解析
String jsonStr = "{
" +
" "id": 84041462,
" +
" "lastName": "小华",
" +
" "age":32,
" +
" "balance":666255.32,
" +
" "hobbyDesc": {
" +
" "subject": "数学",
" +
" "score":25,
" +
" "sport_desc":"跑步有益健康"
" +
" }
" +
"
" +
"}";
Account account = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr,Account.class);

同时也可以看到,对象中定义为字符串类型的字段也可以接受json串的数值类型,没有转换问题。
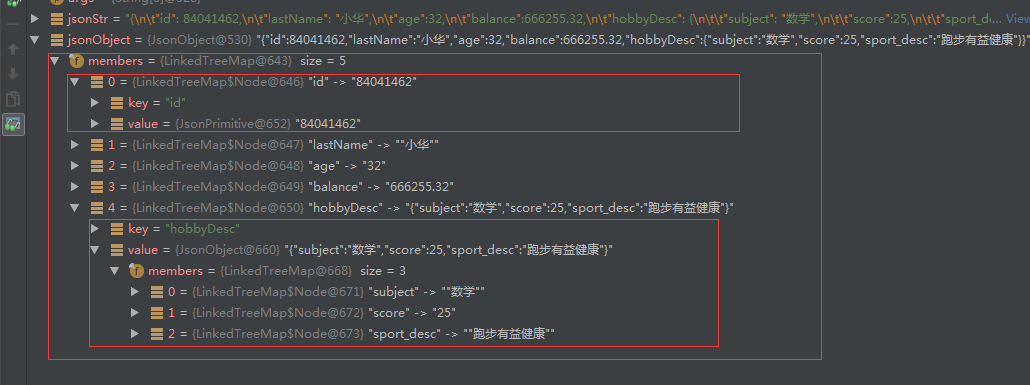
2. 解析为jsonObject对象
直接使用Gson API解析
String jsonStr = "{
" +
" "id": 84041462,
" +
" "lastName": "小华",
" +
" "age":32,
" +
" "balance":666255.32,
" +
" "hobbyDesc": {
" +
" "subject": "数学",
" +
" "score":25,
" +
" "sport_desc":"跑步有益健康"
" +
" }
" +
"
" +
"}";
JsonObject jsonObject = (JsonObject) new JsonParser().parse(jsonStr);
System.out.println("id <getAsInt> = "+jsonObject.get("id").getAsInt());//id <getAsInt> = 84041462
System.out.println("id <getAsString> = "+jsonObject.get("id").getAsString());//id <getAsString> = 84041462
System.out.println("position = "+ jsonObject.get("hobbyDesc").getAsJsonObject().get("sport_desc").getAsString());//position = 跑步有益健康
参照jsonObject结构,可以了解Gson这种封装对象的方式,如果仅仅是取某值的话,可以采用这种方式,可以节约大量时间