1、Zoo1
public class Zoo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Feeder f = new Feeder("小李");
// 饲养员小李喂养一只狮子
f.feedLion(new Lion());
// 饲养员小李喂养十只猴子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
f.feedMonkey(new Monkey());
}
// 饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
f.feedPigeon(new Pigeon());
}
}
}
class Feeder
{
public String name;
public Feeder(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void feedLion(Lion l)
{
l.eat();
}
public void feedPigeon(Pigeon p)
{
p.eat();
}
public void feedMonkey(Monkey m)
{
m.eat();
}
}
class Lion
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!");
}
}
class Monkey
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。");
}
}
class Pigeon
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。");
}
}

2、Zoo2
public class Zoo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Feeder f = new Feeder("小李");
//饲养员小李喂养一只狮子
f.feedAnimal(new Lion());
//饲养员小李喂养十只猴子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
f.feedAnimal(new Monkey());
}
//饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
f.feedAnimal(new Pigeon());
}
}
}
class Feeder
{
public String name;
Feeder(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void feedAnimal(Animal an)
{
an.eat();
}
}
abstract class Animal
{
public abstract void eat();
}
class Lion extends Animal
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!");
}
}
class Monkey extends Animal
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。");
}
}
class Pigeon extends Animal
{
public void eat()
{
System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。");
}
}
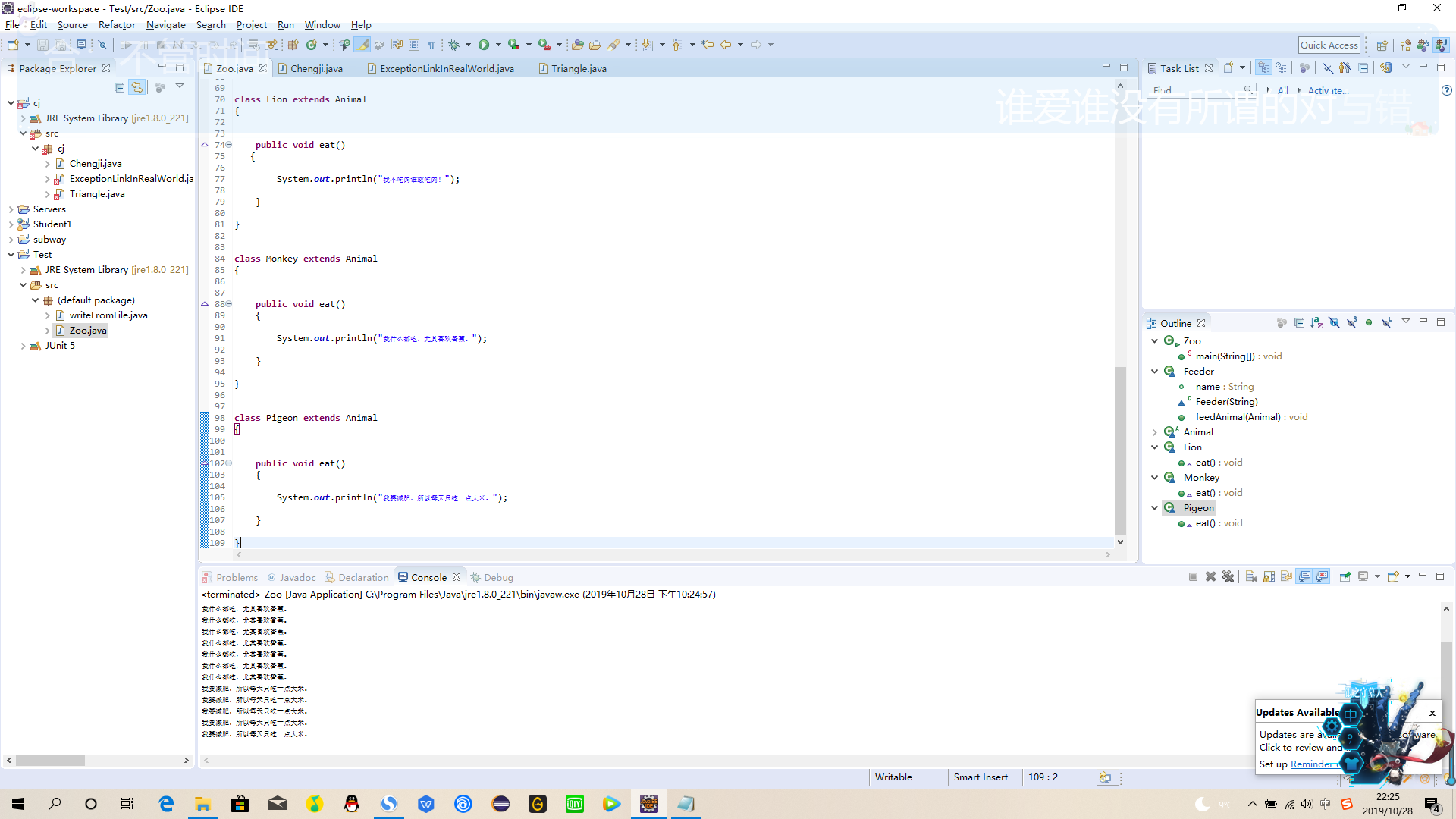
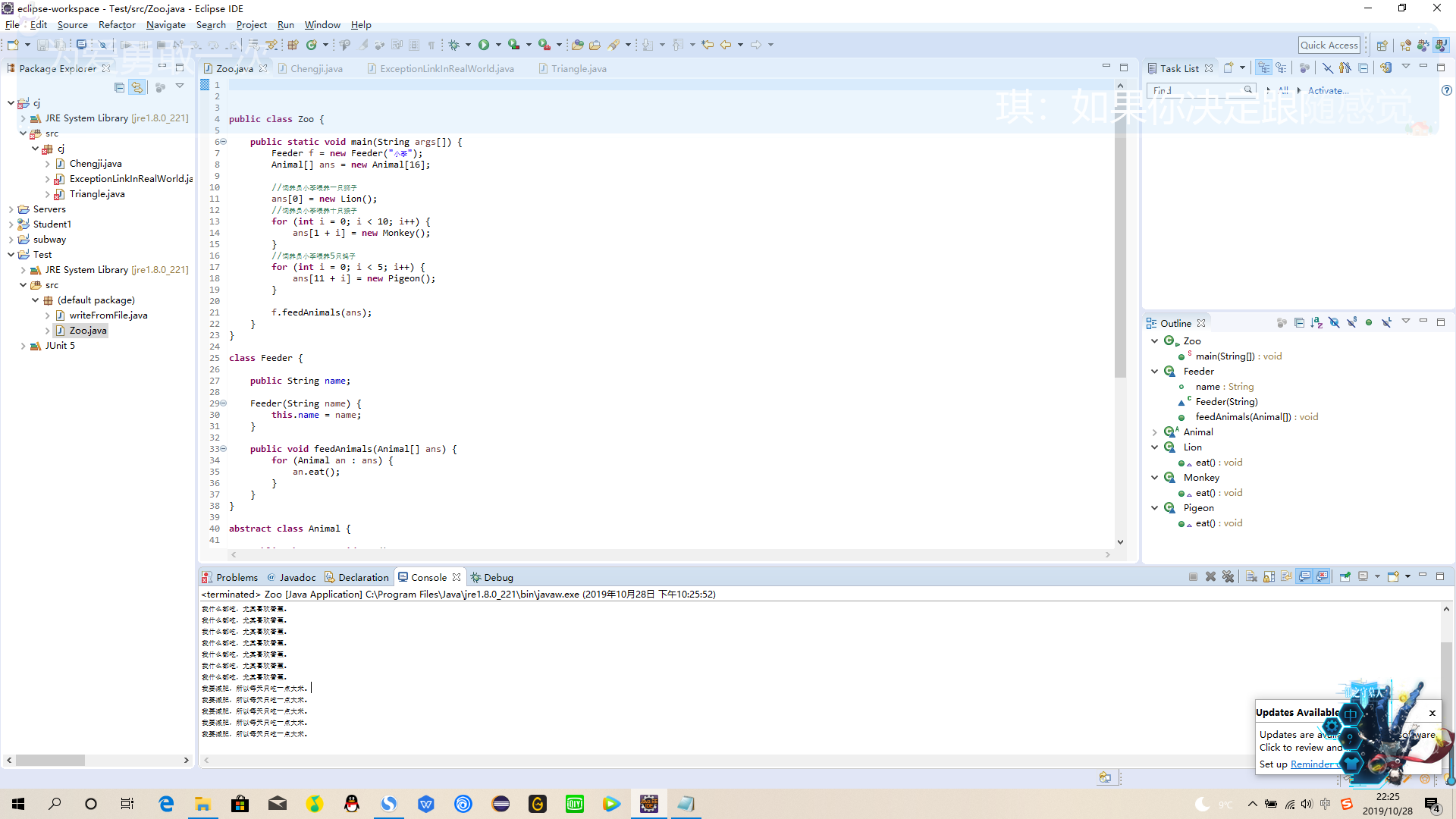
3、Zoo3
package zoo3;
public class Zoo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Feeder f = new Feeder("小李");
Animal[] ans = new Animal[16];
//饲养员小李喂养一只狮子
ans[0] = new Lion();
//饲养员小李喂养十只猴子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ans[1 + i] = new Monkey();
}
//饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
ans[11 + i] = new Pigeon();
}
f.feedAnimals(ans);
}
}
class Feeder {
public String name;
Feeder(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void feedAnimals(Animal[] ans) {
for (Animal an : ans) {
an.eat();
}
}
}
abstract class Animal {
public abstract void eat();
}
class Lion extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!");
}
}
class Monkey extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。");
}
}
class Pigeon extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。");
}
}
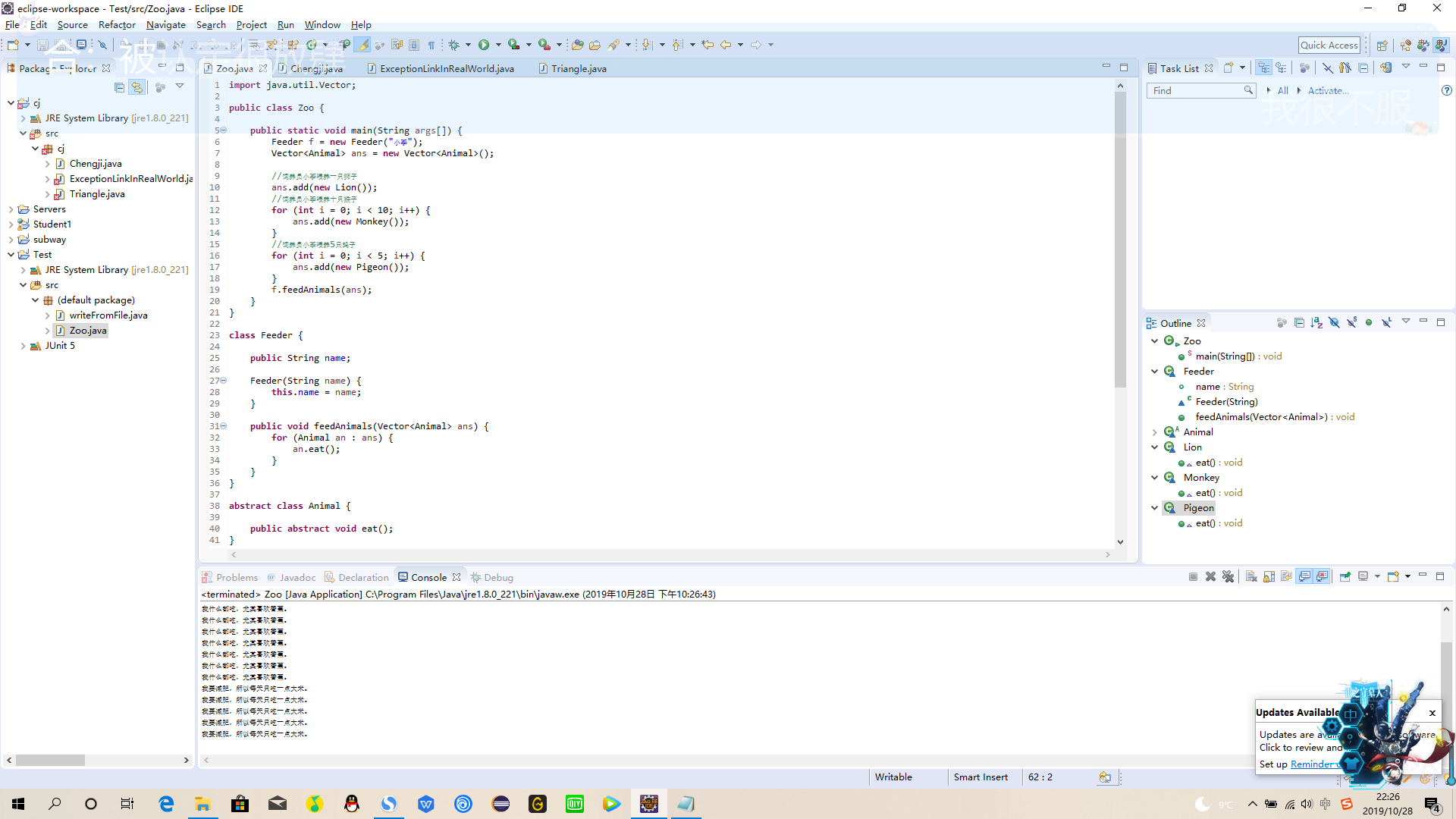
4、Zoo4
import java.util.Vector;
public class Zoo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Feeder f = new Feeder("小李");
Vector<Animal> ans = new Vector<Animal>();
//饲养员小李喂养一只狮子
ans.add(new Lion());
//饲养员小李喂养十只猴子
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ans.add(new Monkey());
}
//饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
ans.add(new Pigeon());
}
f.feedAnimals(ans);
}
}
class Feeder {
public String name;
Feeder(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void feedAnimals(Vector<Animal> ans) {
for (Animal an : ans) {
an.eat();
}
}
}
abstract class Animal {
public abstract void eat();
}
class Lion extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!");
}
}
class Monkey extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。");
}
}
class Pigeon extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。");
}
}
5、Address
public final class Address
{
private final String detail;
private final String postCode;
//在构造方法里初始化两个实例属性
public Address()
{
this.detail = "";
this.postCode = "";
}
public Address(String detail , String postCode)
{
this.detail = detail;
this.postCode = postCode;
}
//仅为两个实例属性提供getter方法
public String getDetail()
{
return this.detail;
}
public String getPostCode()
{
return this.postCode;
}
//重写equals方法,判断两个对象是否相等。
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (obj instanceof Address)
{
Address ad = (Address)obj;
if (this.getDetail().equals(ad.getDetail()) && this.getPostCode().equals(ad.getPostCode()))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int hashCode()
{
return detail.hashCode() + postCode.hashCode();
}
}

6、ExplorationJDKSource
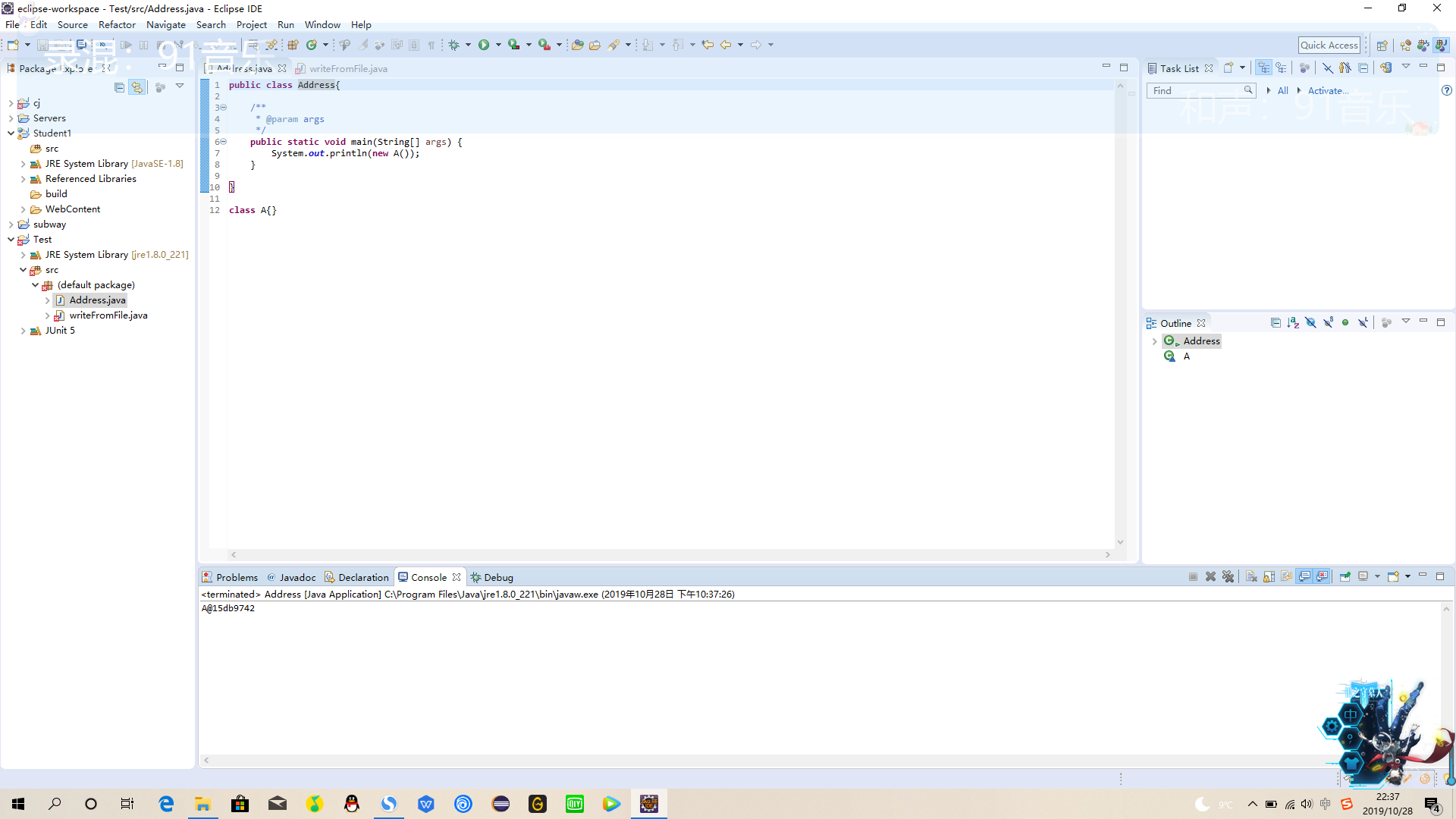
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
7、Fruit
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}

8、ParentChildTest
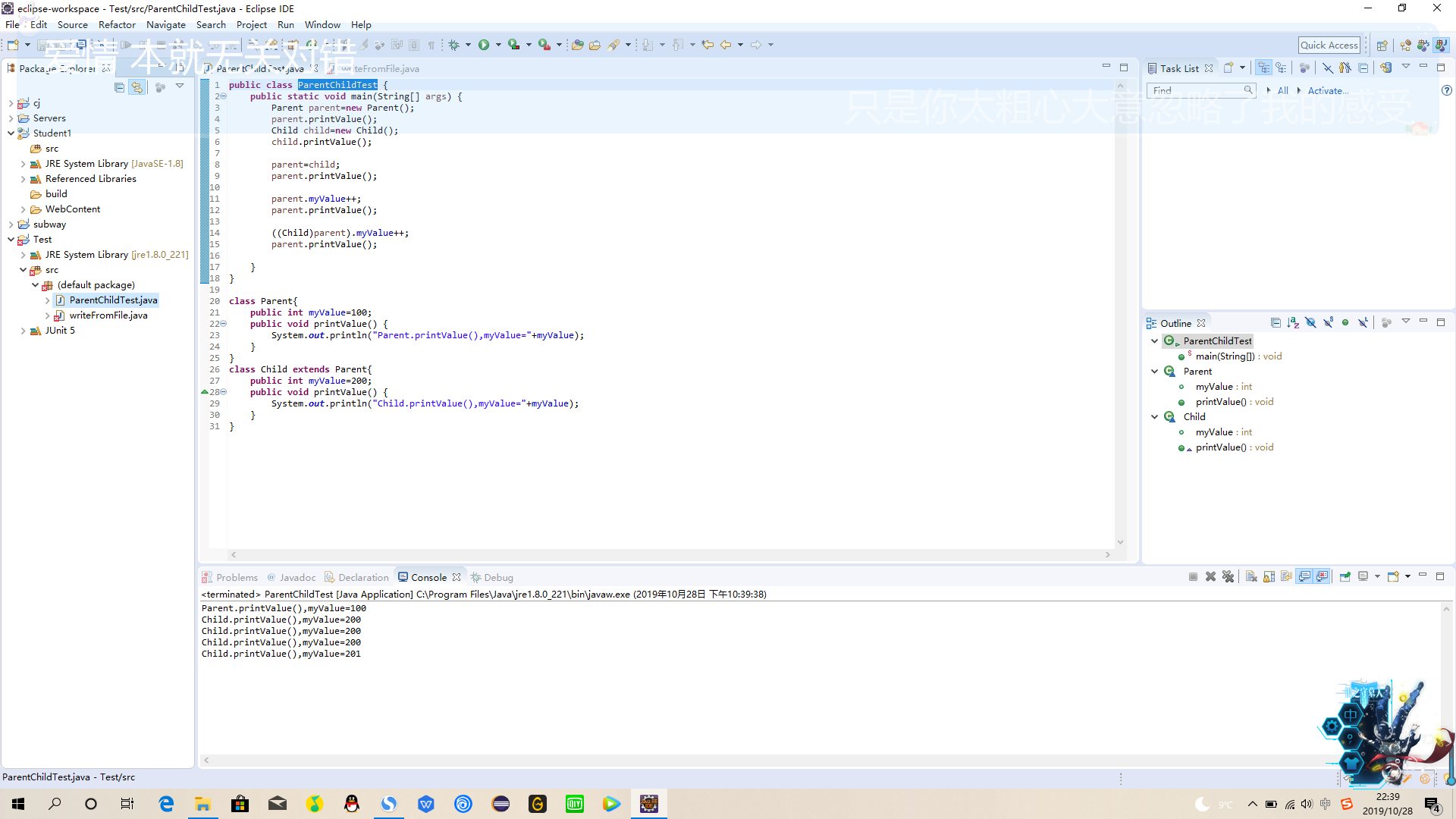
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
9、TestCast
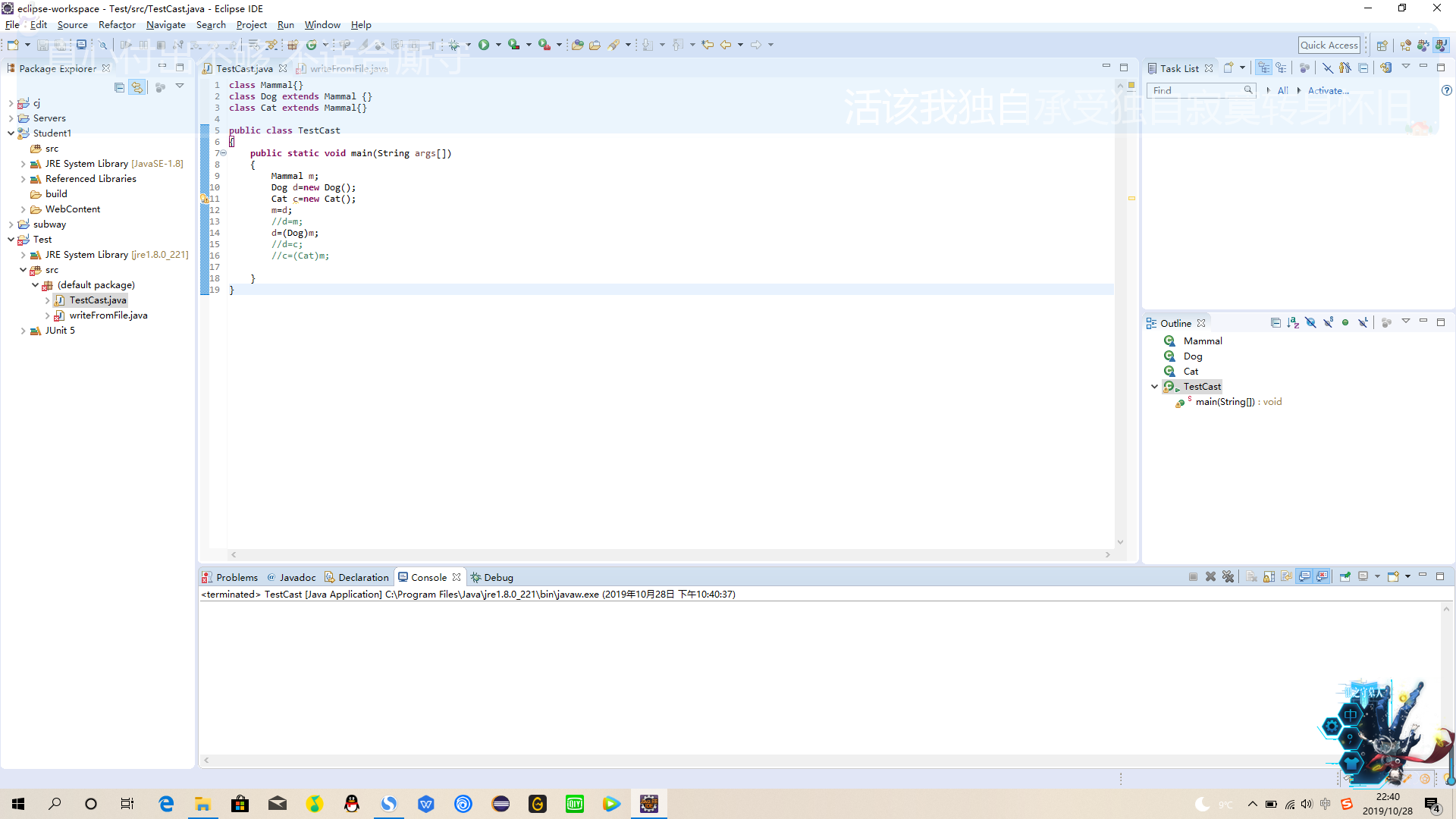
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
//c=(Cat)m;
}
}
10、TestInherits
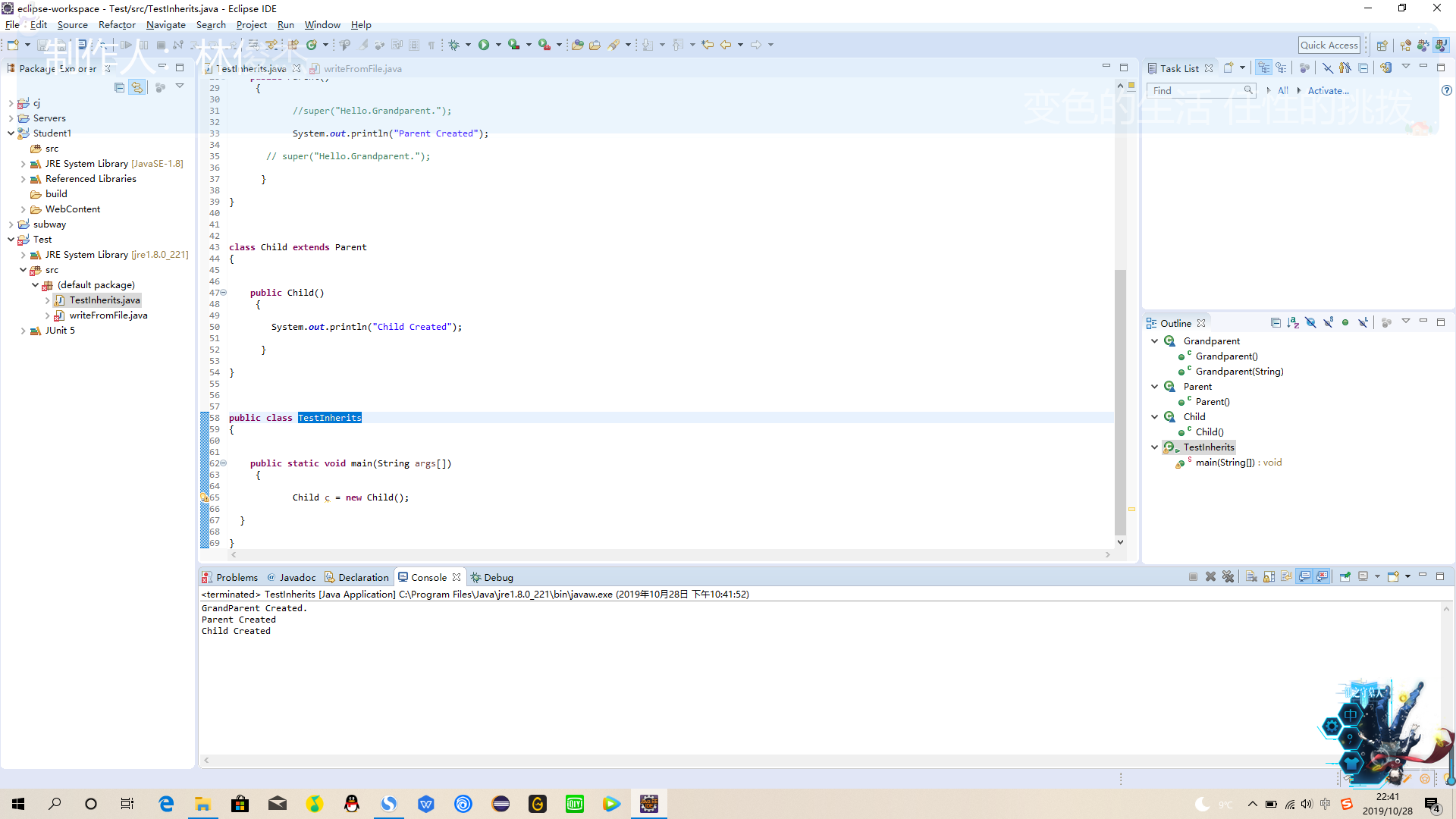
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}
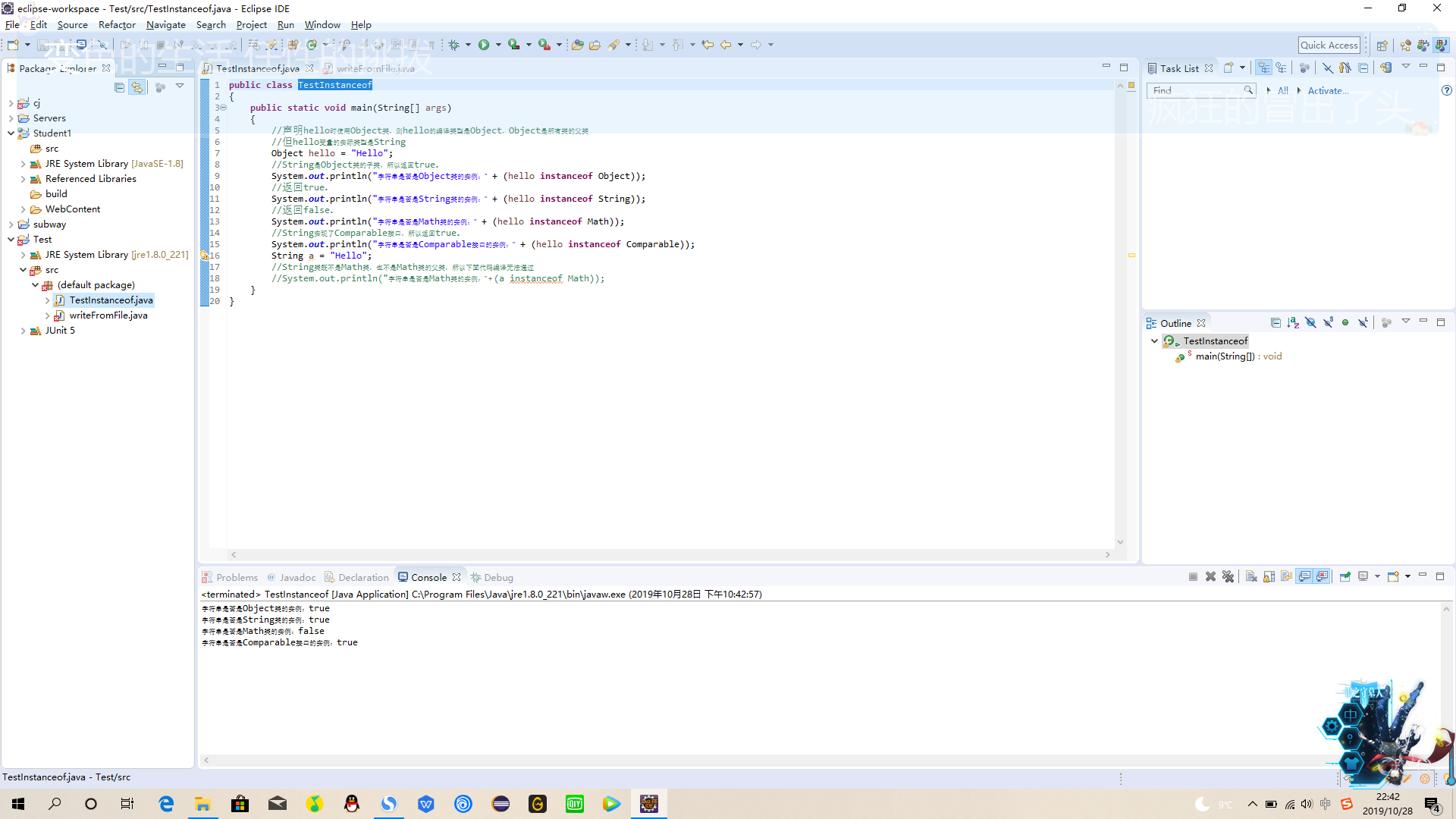
11、TestInstanceof
public class TestInstanceof
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类
//但hello变量的实际类型是String
Object hello = "Hello";
//String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object));
//返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String));
//返回false。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math));
//String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable));
String a = "Hello";
//String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过
//System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math));
}
}
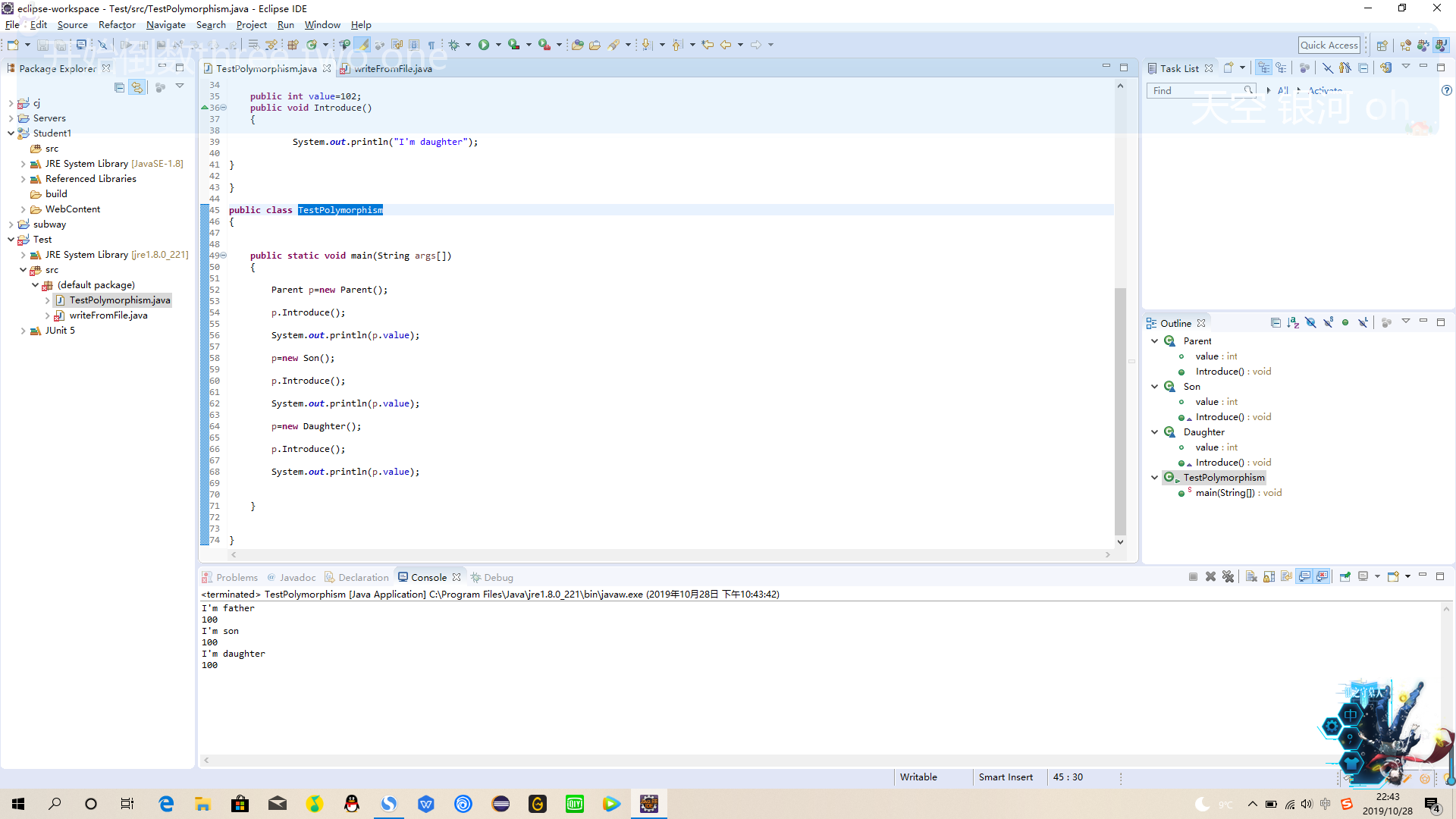
12、TestPolimorphism
class Parent
{
public int value=100;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm father");
}
}
class Son extends Parent
{
public int value=101;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm son");
}
}
class Daughter extends Parent
{
public int value=102;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm daughter");
}
}
public class TestPolymorphism
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Parent p=new Parent();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Son();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Daughter();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
}
}