写在前面
好久没更新公众号和博客了,因为最近在研究新的方向,所以很少发文。
笔者接触编程只有一年,这一年间主要研究启发式算法在运筹学中的应用。但是由于编程基础薄弱,在进一步研究复杂运筹学问题时发现基础算法不过关导致写出的代码运行速度很慢,因此很苦恼。所以决定这个暑假补习一下基础算法,主要是刷一些简单的ACM入门题。偶尔会发一些刷题笔记(偶尔!)。和作者有类似目标的同学可以一起交流共勉!
目前在看的教程:
北京理工大学ACM冬季培训课程
算法竞赛入门经典/刘汝佳编著.-2版可以在这里下载->github
课程刷题点
Virtual Judge
刷题代码都会放在github上,欢迎一起学习进步!
第二章模拟与暴力刷题点,提交密码20202020
昨天有事儿去了,没有刷题,今天多刷一点(多写一点WA)。
D - Crashing Robots
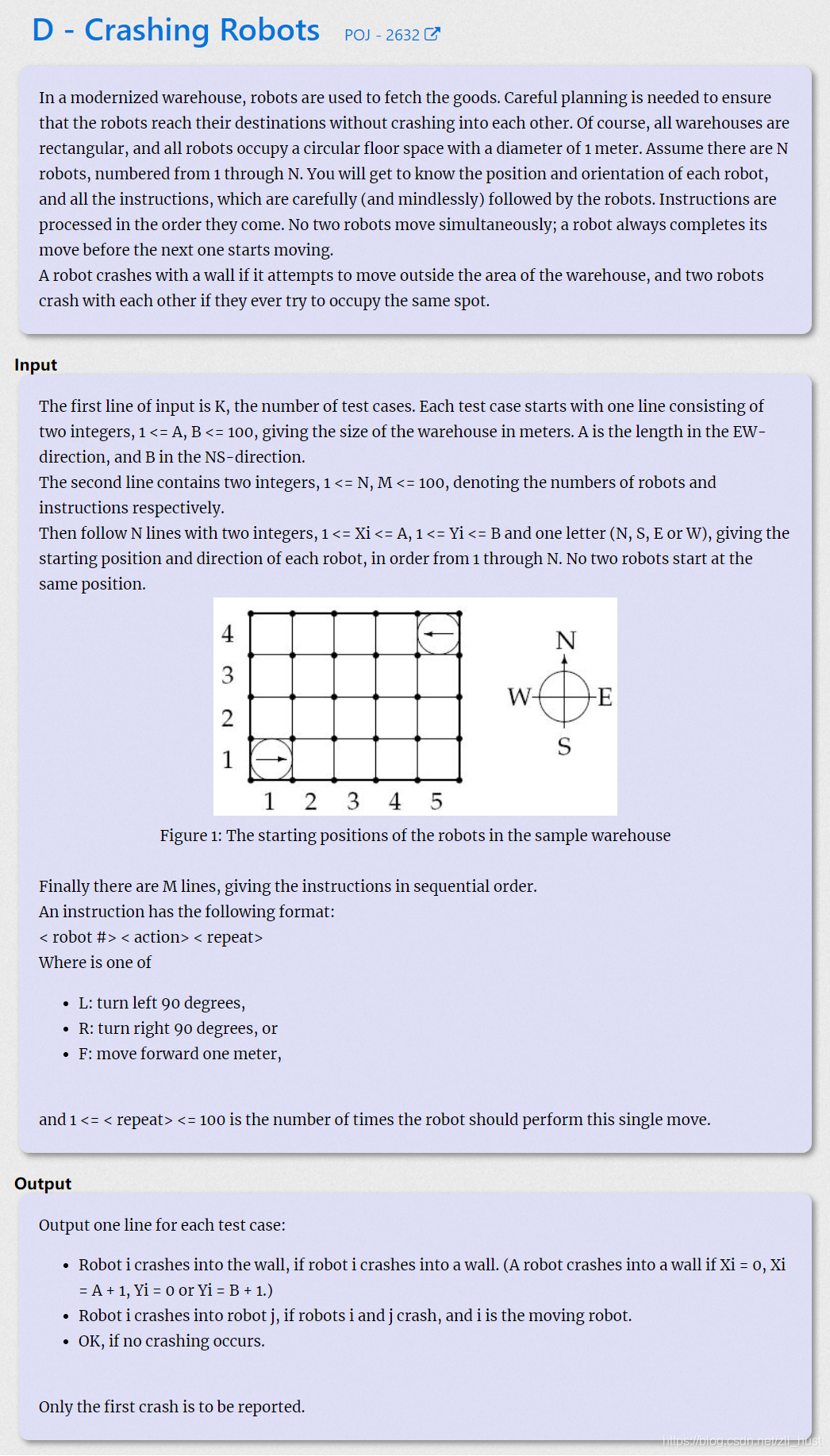
棋盘上有两个机器人,根据指定动作(前进,左转,右转)运动,如果撞到墙或撞到对方则结束,输出第一个撞击动作。(一开始看到题目描述瞬间想到AGV,还以为要规划路径,吓死了)
简单模拟题,没啥好说的。(我已经忘了自己的答案都是WA还是AC了,就不管了,反正看着差不多都是对的…)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define LOCAL
#define E 0
#define N 1
#define W 2
#define S 3
int Id = 0;
struct Robot
{
int id;
int x;
int y;
int dir;
Robot()
{
this->id = Id++;
this->x = -1;
this->y = -1;
this->dir = -1;
}
} robots[105];
int graph[105][105];
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int kase;
scanf("%d", &kase);
while (kase--)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
// 初始化地图
for (int j = 1; j <= a; j++)
graph[0][j] = -1; // -1代表墙体
for (int i = 1; i <= b; i++)
{
graph[i][0] = -1; // -1代表墙体
for (int j = 1; j <= a; j++)
graph[i][j] = 0; // 0代表空地
graph[i][a + 1] = -1;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= a; j++)
graph[b + 1][j] = -1; // -1代表墙体
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
char dir;
cin >> robots[i].x >> robots[i].y >> dir;
if (dir == 'E')
robots[i].dir = 0;
else if (dir == 'N')
robots[i].dir = 1;
else if (dir == 'W')
robots[i].dir = 2;
else
robots[i].dir = 3;
graph[robots[i].y][robots[i].x] = robots[i].id; // 更新graph,graph上的数字表示机器编号
}
int r1 = -1;
int r2 = -1;
while (m--)
{
int robot;
char behave;
int lenth;
cin >> robot >> behave >> lenth;
if (behave == 'L')
robots[robot].dir = (robots[robot].dir + lenth) % 4;
else if (behave == 'R')
robots[robot].dir = (robots[robot].dir - lenth) % 4;
else
{
if (robots[robot].dir == E)
{
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= lenth; j++)
{
if (graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x + j])
{
r1 = robots[robot].id;
r2 = graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x + j];
goto end;
}
}
robots[robot].x += lenth;
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = robots[robot].id;
}
else if (robots[robot].dir == N)
{
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= lenth; j++)
{
if (graph[robots[robot].y + j][robots[robot].x])
{
r1 = robots[robot].id;
r2 = graph[robots[robot].y + j][robots[robot].x];
goto end;
}
}
robots[robot].y += lenth;
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = robots[robot].id;
}
else if (robots[robot].dir == W)
{
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= lenth; j++)
{
if (graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x - j])
{
r1 = robots[robot].id;
r2 = graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x - j];
goto end;
}
}
robots[robot].x -= lenth;
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = robots[robot].id;
}
else
{
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= lenth; j++)
{
if (graph[robots[robot].y - j][robots[robot].x])
{
r1 = robots[robot].id;
r2 = graph[robots[robot].y - j][robots[robot].x];
goto end;
}
}
robots[robot].y -= lenth;
graph[robots[robot].y][robots[robot].x] = robots[robot].id;
}
}
}
end:
if (r1 == -1)
printf("OK
");
else if (r2 == -1)
printf("Robot %d crashes into the wall
", r1);
else
printf("Robot %d crashes into the %d
", r1, r2);
while (m > 0)
{
int robot;
char behave;
int lenth;
cin >> robot >> behave >> lenth;
m--;
}
}
return 0;
}
E - New Year and Buggy Bot

走迷宫。1,2,3,4分别代表向某个方向移动一步,要求根据指定数字找到可以走出迷宫的数字到方向的映射。
暴力枚举,没啥好讲的。这里注意迷宫数组里只有墙体和障碍物是不能碰到的,出发点是可以返回的(Example2亲测)。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
// #define LOCAL
#define E 0
#define N 1
#define W 2
#define S 3
struct Robot
{
int x;
int y;
Robot()
{
this->x = -1;
this->y = -1;
}
};
int graph[55][55];
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
Robot r0;
// 初始化地图
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
graph[0][j] = -1; // -1代表墙体
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
graph[i][0] = -1; // -1代表墙体
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
graph[i][j] = 0; // 0代表空地
graph[i][m + 1] = -1;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
graph[n + 1][j] = -1; // -1代表墙体
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (str[j - 1] == '#')
graph[i][j] = -1; // -1代表墙体
else if (str[j - 1] == 'S')
{
// graph[i][j] = 2; // 2代表入口 可以回到入口!!
r0.y = i;
r0.x = j;
}
else if (str[j - 1] == 'E')
graph[i][j] = 3; // 3代表出口
}
}
string path;
cin >> path;
int d[4];
int ans = 0;
int i = 0, j, k;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
d[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
if (j == i)
continue;
d[j] = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
if (k == i || k == j)
continue;
d[k] = 2;
for (int o = 0; o < 4; o++)
{
if (o == i || o == j || o == k)
continue;
d[o] = 3;
Robot r = r0;
for (int l = 0; l < path.length(); l++)
{
int step = path[l] - '0';
if (d[step] == E)
r.x++;
else if (d[step] == N)
r.y++;
else if (d[step] == W)
r.x--;
else
r.y--;
if (graph[r.y][r.x])
break;
}
if (graph[r.y][r.x] == 3)
ans++;
}
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
F - Maximum Product
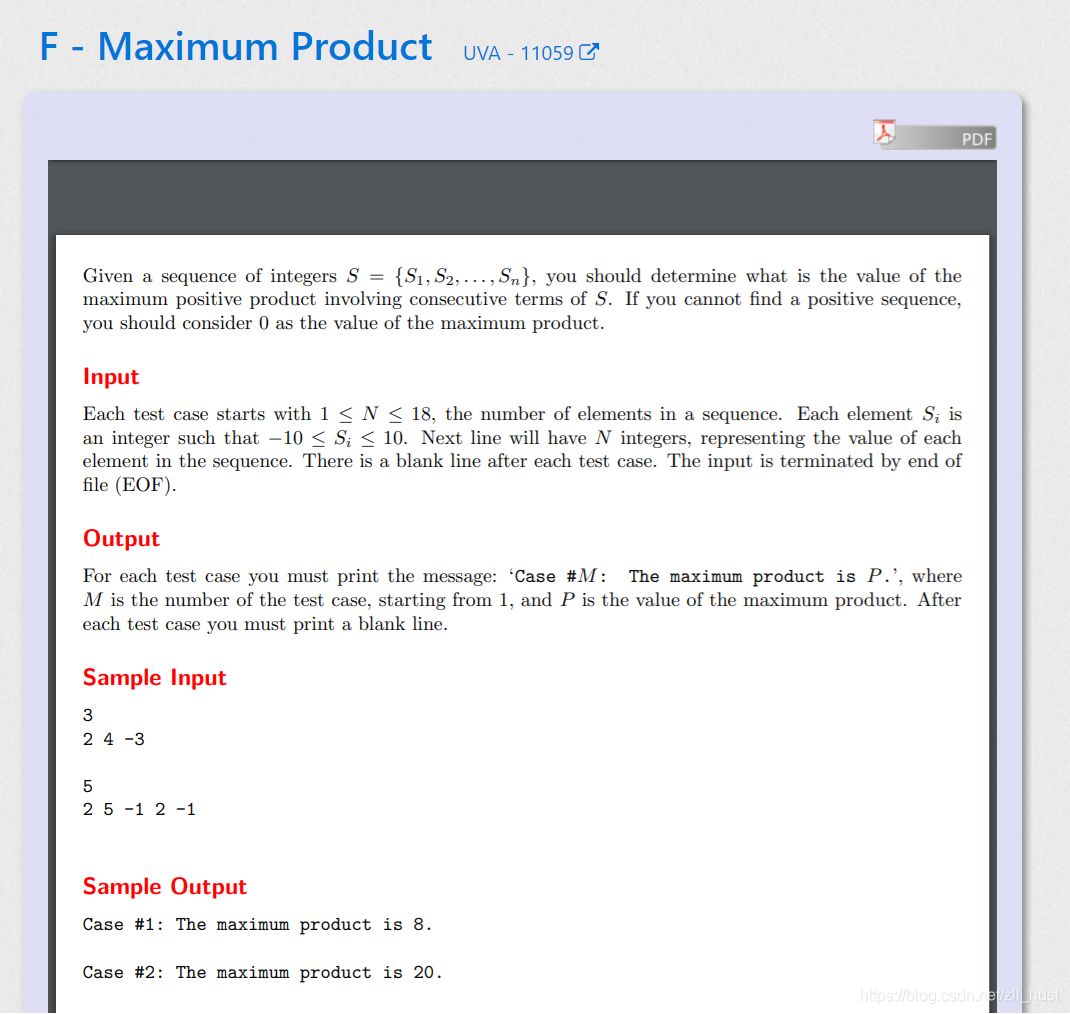
做这题的时候我脑溢血了…
给一串数字,要求找出最大的连续数字串,使得乘积最大(如果小于0,取最大为0)。
我第一反应居然是,遇到奇数个负数的时候标记,遇到偶数个时再累乘。
结果一看别人的答案,直接暴力累乘然后取较大值不就好了吗!!!!
这里的连续数字串好像是从第一个开始的,我把所有都枚举过去了,懒得改了,放个别人的答案吧。
注意数字串中出现0的情况(出现0应该是可以break的)。
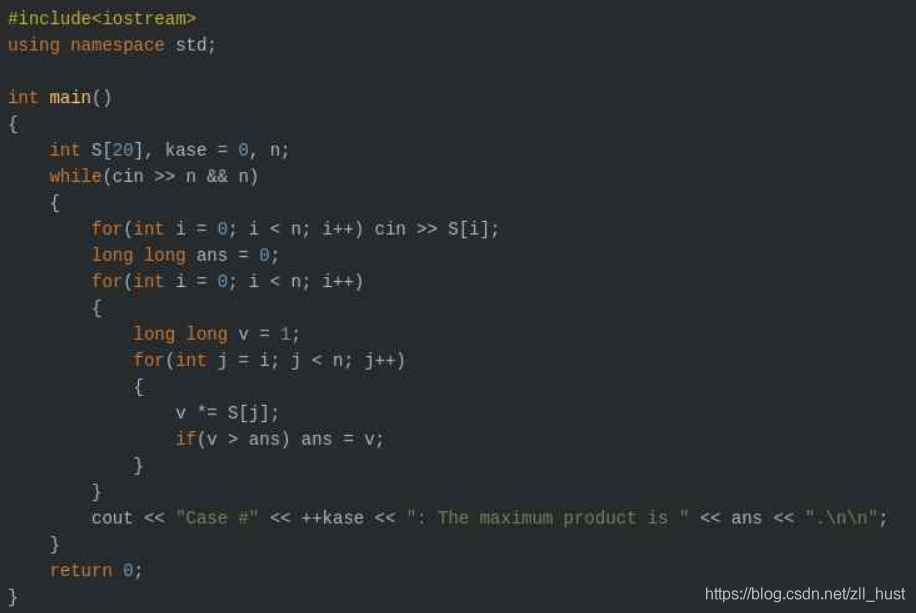
附上愚蠢的标记:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define LOCAL
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int kase = 1;
int lenth;
while (cin >> lenth)
{
int num[20];
for (int i = 0; i < lenth; i++)
cin >> num[i];
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lenth; i++)
{
int ans = 0;
int pos = -1;
bool first = true;
for (int j = i; j < lenth; j++) // 从第i个字符开始查找
{
if (num[j] == 0)
break;
else if (num[j] > 0 && pos == -1) // 如果前面有负数,暂时不乘上
{
if (first)
{
ans = num[j];
first = false;
}
else
ans *= num[j];
}
else if(num[j] < 0)
{
if (pos != -1) // pos代表上一个出现负数的位置,-1代表这是第一个
{
for (int k = pos; k <= j; k++)
ans *= num[k];
pos = -1;
}
else
pos = j;
}
}
if (ans > res)
res = ans;
}
printf("Case #%d: The maximum product is %d.
", kase++, res);
}
return 0;
}
G - NPY and arithmetic progression

女朋友与等差数列(狗头)。
有很多个1,2,3,4,要求把这若干个1,2,3,4划分为好多组等差数列,如果划分的完则yes,划分不完no。
我第一反应是3个相同数字可以为一组,因为公差可以为0,就想什么模3模6,看看能不能化简。但要注意等差数列不一定只有三个数字,那就肯定没戏了。可以考虑用暴力的递归方法求解。针对数量小于3的数不断划分,看看能不能出现无法划分的情况,也就是出现负数个(讲不清楚,具体参见代码注释)。
其实这题单独拿出来当数学题可能比写代码要轻松些。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
// #define LOCAL
typedef long long LL;
bool devide(LL n1, LL n2, LL n3, LL n4)
{
// cout << n1 << " " << n2 << " " << n3 << " " << n4 << endl;
if (n1 < 0 || n2 < 0 || n3 < 0 || n4 < 0)
return false;
if ((n1 >= 3 || n1 == 0) && (n2 >= 3 || n2 == 0) && // 注意等差数列可以为公差为0的任意长数列,因此超过3个也算true
(n3 >= 3 || n3 == 0) && (n4 >= 3 || n4 == 0))
return true;
if (n1 == 1 || n1 == 2) // 剩下的数种肯定有至少一个数为1或2
{
if (devide(n1 - 1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4 - 1)) // 逐步分解让n1减小到0 注意等差数列可以是4个数
return true;
if (devide(n1 - 1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4))
return true;
}
if ((n2 == 1 || n2 == 2) || (n3 == 1 || n3 == 2))
{
if (devide(n1 - 1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4 - 1))
return true;
if (devide(n1 - 1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4))
return true;
if (devide(n1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4 - 1)) // n2、n3比n1多一种分解方法,从后半边分解
return true;
}
if (n4 == 1 || n4 == 2)
{
if (devide(n1 - 1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4 - 1))
return true;
if (devide(n1, n2 - 1, n3 - 1, n4 - 1))
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int kase;
cin >> kase;
while (kase--)
{
LL n1, n2, n3, n4;
cin >> n1 >> n2 >> n3 >> n4;
if (devide(n1, n2, n3, n4))
cout << "Yes
";
else
cout << "No
";
}
return 0;
}
H - Herding

给几个点,找点连成的面积最小的图形。
那应该是找三角形吧。枚举找所有的三角形。坐标就叉乘公式。记得还有Impossible的情况要判断一哈。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
struct Point
{
double x;
double y;
Point()
{
this->x = -1;
this->y = -1;
}
} points[105];
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int kase;
cin >> kase;
while (kase--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> points[i].x >> points[i].y;
double min = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
// 向量叉乘计算面积: S = |x1y2 - x1y3 + x2y3 - x2y1 + x3y1 - x3y2| / 2
double s = abs(points[i].x * points[j].y - points[i].x * points[k].y +
points[j].x * points[k].y - points[j].x * points[i].y +
points[k].x * points[i].y - points[k].x * points[j].y) / 2.0;
if (s < min && s > 0.0) {
min = s;
// cout << i << j << k << endl;
}
}
if(min == INT_MAX) cout << "Impossible" << endl;
else printf("%0.2f
", min);
}
return 0;
}
I - Four Operations
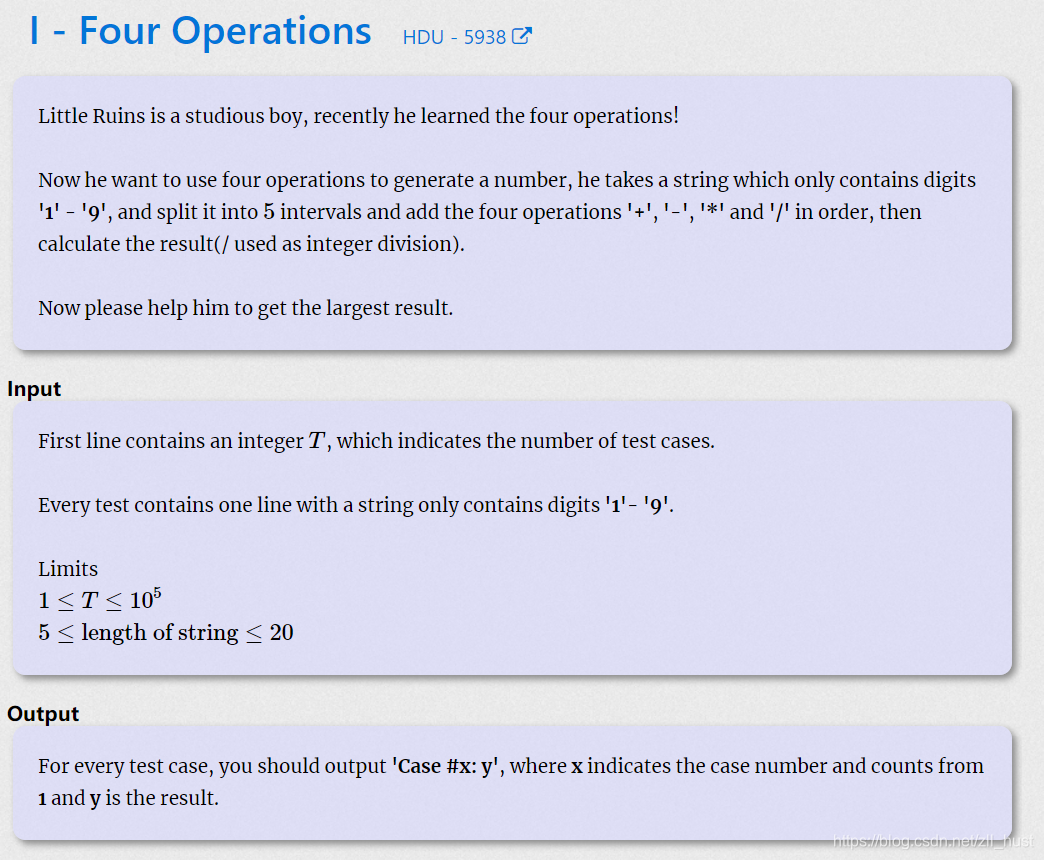
上课讲过的,我直接找课堂的思路做了,放个图吧就。


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int kase;
int x = 1;
cin >> kase;
while (x <= kase)
{
LL res, sum;
string str;
cin >> str;
LL a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0, e = 0;
// case 1: e取一位数字, a取一位数
e = str[str.length() - 1] - '0';
d = str[str.length() - 2] - '0';
c = str[str.length() - 3] - '0';
a = str[0] - '0';
for (int i = 1; i < str.length() - 3; i++)
{
b *= 10;
b += str[i] - '0';
}
res = a + b - c * d / e;
a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0, e = 0;
// case 2: e取一位数字, b取一位数
e = str[str.length() - 1] - '0';
d = str[str.length() - 2] - '0';
c = str[str.length() - 3] - '0';
b = str[str.length() - 4] - '0';
for (int i = 0; i < str.length() - 4; i++)
{
a *= 10;
a += str[i] - '0';
}
sum = a + b - c * d / e;
if(res < sum) res = sum;
a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0, e = 0;
// case 3: e取两位数字, b取一位数
e = (str[str.length() - 2] - '0') * 10 + str[str.length() - 1] - '0';
d = str[str.length() - 3] - '0';
c = str[str.length() - 4] - '0';
b = str[str.length() - 5] - '0';
for (int i = 0; i < str.length() - 5; i++)
{
a *= 10;
a += str[i] - '0';
}
sum = a + b - c * d / e;
if(res < sum) res = sum;
a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0, e = 0;
// case 4: e取两位数字, a取一位数
e = (str[str.length() - 2] - '0') * 10 + str[str.length() - 1] - '0';
d = str[str.length() - 3] - '0';
c = str[str.length() - 4] - '0';
a = str[0] - '0';
for (int i = 1; i < str.length() - 4; i++)
{
b *= 10;
b += str[i] - '0';
}
sum = a + b - c * d / e;
if(res < sum) res = sum;
cout << "Case #" << x++ << ": " << res <<endl;
}
}
J - The Artful Expedient
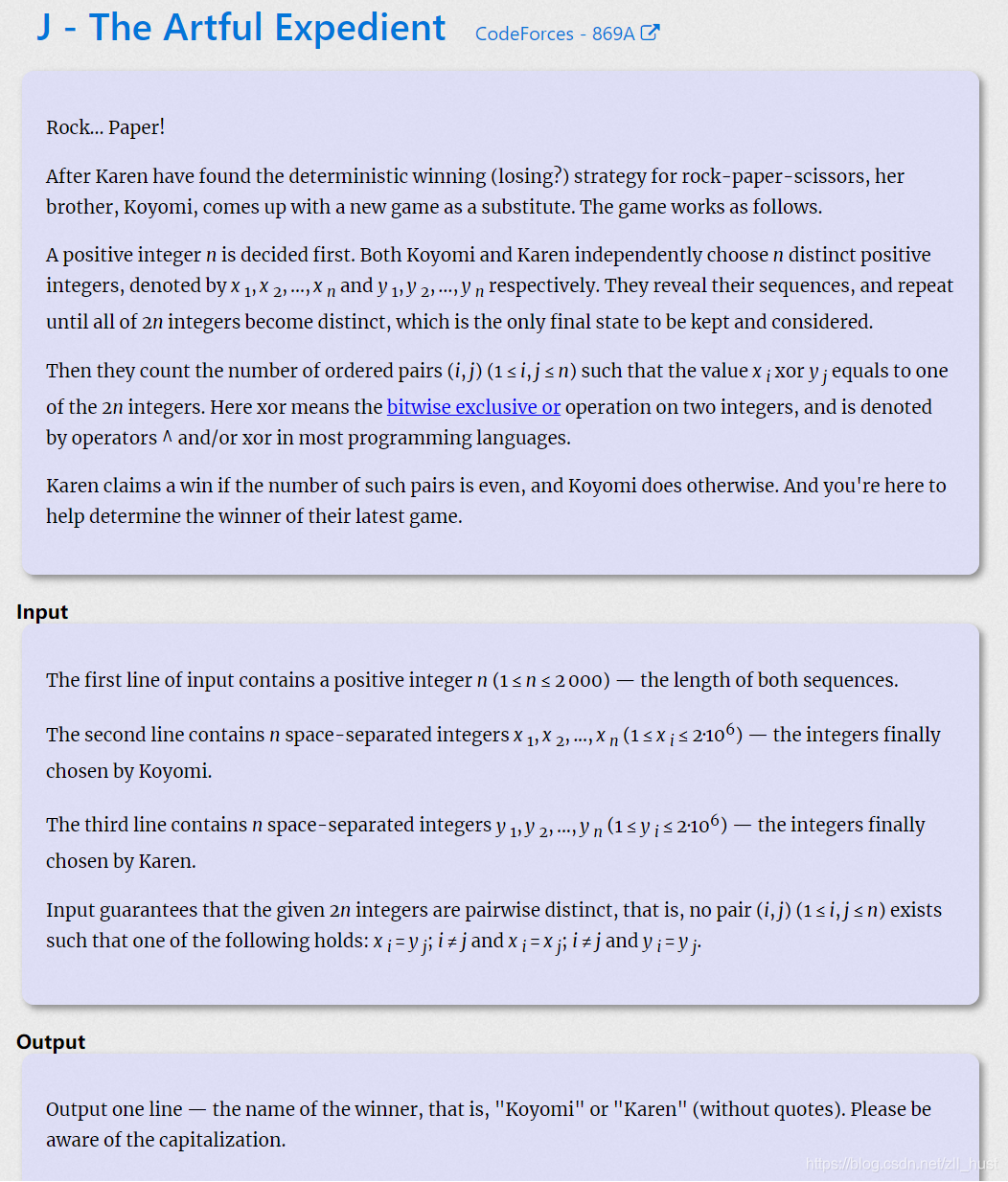
给两串各不相同、相同长度的数字。两串中各取一个,做位取或操作,如果新的数在原来的数中出现过,则sum++,判断sum为偶数还是奇数。
说来惭愧,直到做这题时百度才知道位取或到底啥意思…就是换成二进制之后逐位取或生成一个新的数,C++里用 ^ 表示。
就是遍历咯…一开始我是用set判断是否出现的,后来WA的时候找答案看到一个用bucket才醒悟,又脑溢血了…不过用set也不会TL,bucket也不会超空间,倒是两种做法都在第23WA了,未知原因…
这里分享一个神奇解法:
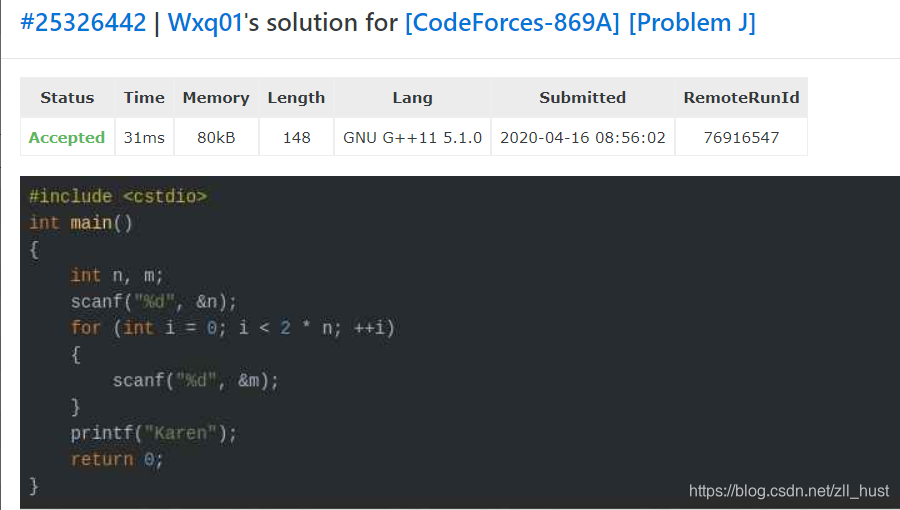
看到lenth比较短就点进去了,不知道是不是确实有数学依据呢…
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
int x[2005];
int y[2005];
int bucket[5000005];
// set<int> num;
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
memset(bucket, 0, sizeof(bucket));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x[i]);
// num.insert(x[i]);
bucket[x[i]] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &y[i]);
// num.insert(y[i]);
bucket[y[i]] = 1;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
// if(num.find(x[i] ^ y[i]) != num.end()) res++;
if(bucket[x[i] ^ y[i]]) res++;
}
}
if(res % 2) cout << "Koyomi" << endl;
else cout << "Karen"<<endl;
return 0;
}
结语
今天的太长了,累了累了…写博客比刷题还累…