https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805346063728640
There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
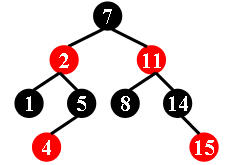 | 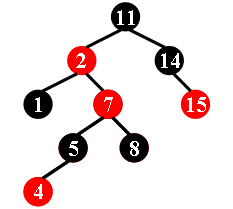 | 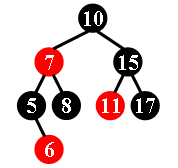 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 500;
int T, n;
int preorder[maxn];
struct Node {
int child[2];
int blackCnt;
int value;
int color;
}s[maxn];
int root, sz, ans;
int AddNode(int valAndcol) {
sz ++;
s[sz].value = abs(valAndcol);
s[sz].color = valAndcol >= 0;
return sz;
}
void Build(int L, int R, int father, bool direction) {
int l1 = -1, r1 = -1;
int l2 = -1, r2 = -1;
for(int i = L + 1; i <= R; i ++) {
if(abs(preorder[i]) < abs(preorder[L])) {
l1 = L + 1, r1 = i;
} else if(abs(preorder[i]) == abs(preorder[L])) {
ans = 0;
return;
} else {
if(l2 == -1) l2 = i, r2 = R;
}
}
if(l1 != -1) {
for(int i = l1; i <= r1; i ++) {
if(abs(preorder[i]) >= abs(preorder[L])) {
ans = 0;
return;
}
}
}
if(l2 != -1) {
for(int i = l2; i <= r2; i ++) {
if(abs(preorder[i]) <= abs(preorder[L])) {
ans = 0;
return;
}
}
}
// left: [l1, r1], right: [l2, r2]
int currentNode = AddNode(preorder[L]);
father != -1 ? s[father].child[direction] = currentNode : root = currentNode;
if(l1 != -1) Build(l1, r1, currentNode, 0);
if(ans == 0) return;
if(l2 != -1) Build(l2, r2, currentNode, 1);
}
void Initialize() {
ans = 1;
root = -1;
sz = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i ++) {
s[i].child[0] = s[i].child[1] = s[i].color = -1;
s[i].blackCnt = s[i].value = 0;
}
}
void dfs(int x) {
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i ++) {
if(s[x].child[i] != -1) {
dfs(s[x].child[i]);
if(ans == 0) return;
}
}
if(s[x].child[0] != -1 &&
s[x].child[1] != -1 &&
s[s[x].child[0]].blackCnt != s[s[x].child[1]].blackCnt) {
ans = 0;
return;
}
if(s[x].child[0] != -1) s[x].blackCnt = s[s[x].child[0]].blackCnt;
if(s[x].child[1] != -1) s[x].blackCnt = s[s[x].child[1]].blackCnt;
s[x].blackCnt += s[x].color;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf("%d", &preorder[i]);
}
Initialize();
Build(1, n, -1, -1);
/*
// Debug Information:
for(int i = 1; i <= sz; i ++) {
printf("Id: %d, L: %d, R: %d, val: %d, col: %d
", i, s[i].child[0], s[i].child[1], s[i].value, s[i].color);
}
*/
// (1) Every node is either red or black.
// (2) The root is black.
if(!s[root].color) ans = 0;
// (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
// (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
for(int i = 1; i <= sz; i ++) {
if(!s[i].color) {
if(s[i].child[0] != -1 && !s[s[i].child[0]].color) ans = 0;
if(s[i].child[1] != -1 && !s[s[i].child[1]].color) ans = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 2; j ++) {
if(s[i].child[j] == -1) {
s[i].child[j] = AddNode(0);
}
}
}
// (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
dfs(root);
printf("%s
", ans ? "Yes" : "No");
}
return 0;
}