- HashMap 如何实现?
- put 做了什么?
- get 做了什么?
- 初始化容量,满载率,扩展?
- hash?
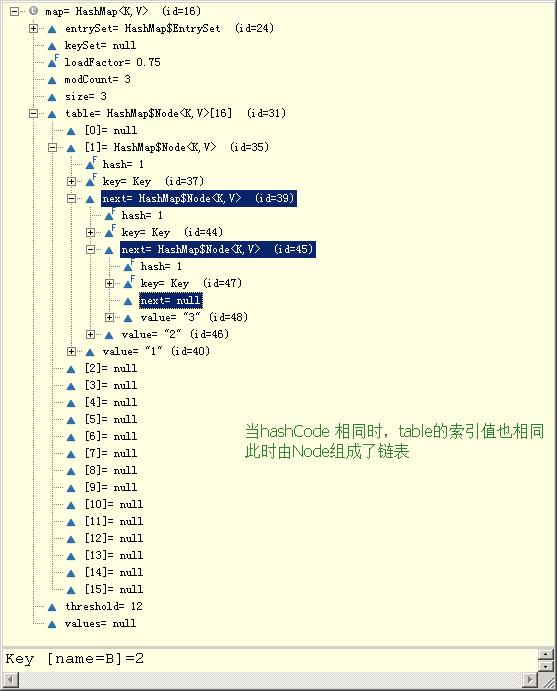
- 类似的结构及相似处,不同点?
load factor 满载率
capacity 容量
threshold 临界值
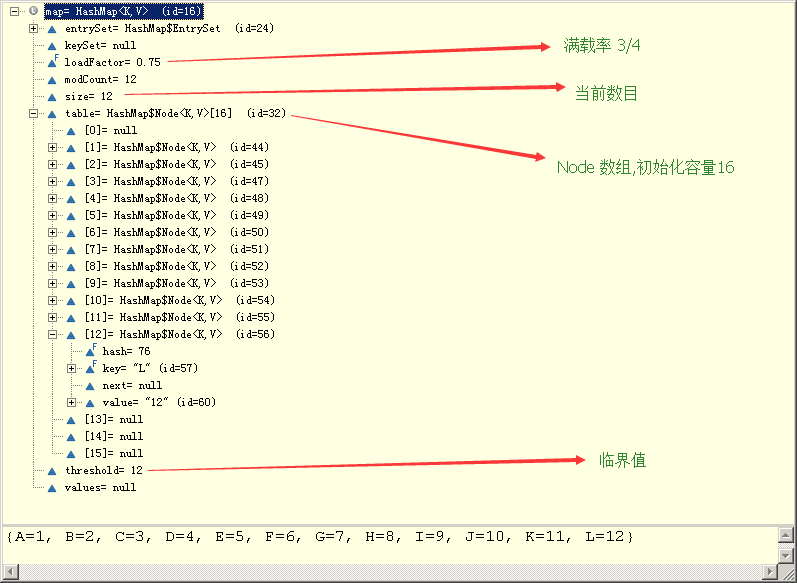
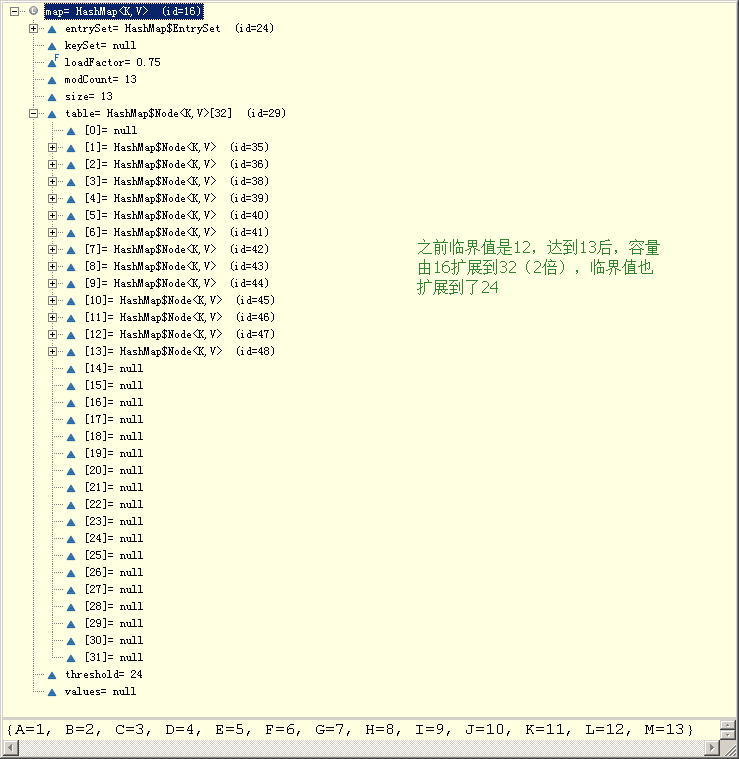
import java.util.Map; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Key, String> map = new HashMap<Key, String>(); map.put(new Key("A"), "1"); map.put(new Key("B"), "2"); map.put(new Key("C"), "3"); System.out.println(map); } } class Key { private String name; Key(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; } @Override public String toString() { return "Key [name=" + name + "]"; } }
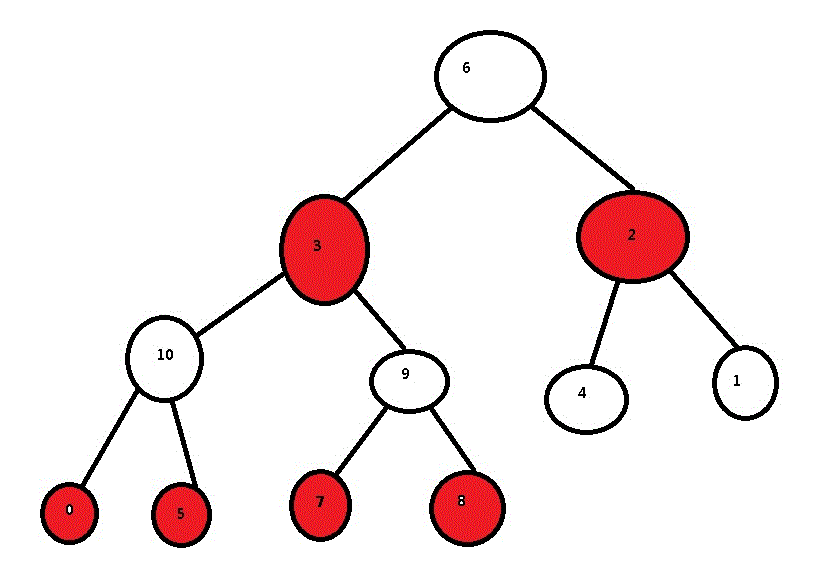
import java.util.Map; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<Key, Integer> map = new HashMap<Key, Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) { map.put(new Key(System.nanoTime()), i); } System.out.println(map); } } class Key { private long name; Key(long name) { this.name = name; } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; } @Override public String toString() { return "Key [name=" + name + "]"; } }
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
控制treeify的临界值是8 ,当bin中链大于8时,则尝试treeify
- 1)如果此时表容量不足64,则会扩表。因此添加第9个元素时,由16->32 ,添加第10个元素时,由32->64
- 2)添加第11个元素时,此时转为了TreeNode

==============================================
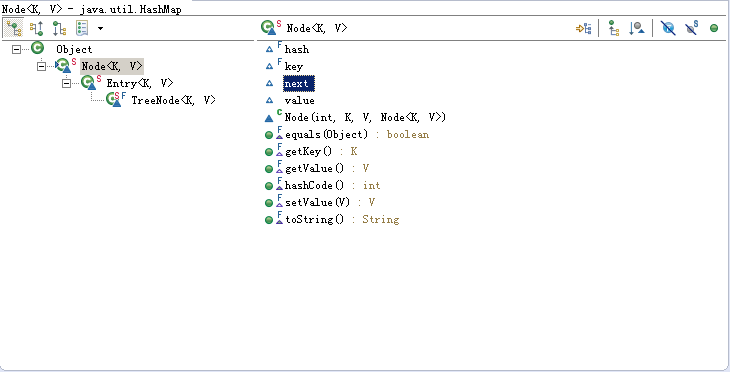
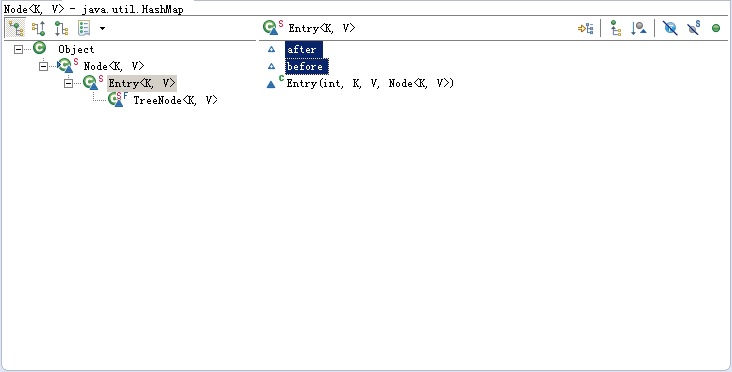
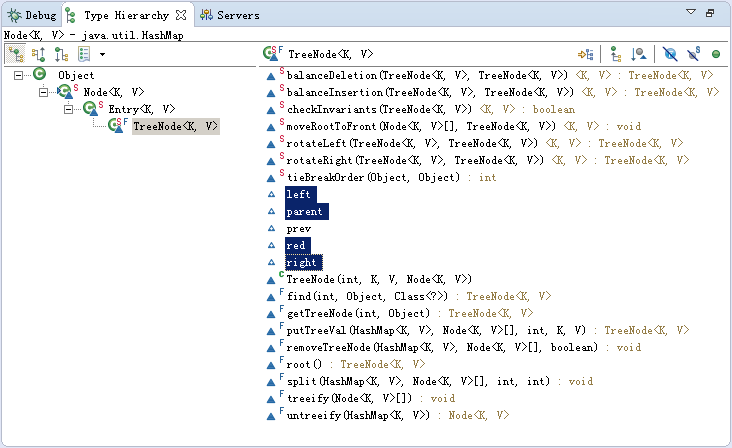
put
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K, V>[] tab; Node<K, V> p; int n, i; // 1 table 为空时重置大小 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; // 2 落到空bin 直接添加节点 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 3 落到非空bin ,判断 a , b ,c, else { Node<K, V> e; K k; // a) header与入参key相同,替换旧值 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; // b) header是红黑树去添加树节点 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K, V>) p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); // c) header是链 else { // 遍历链,逐项检查 ,判断 I ,II for (int binCount = 0;; ++binCount) { // I) 末尾追加节点并检查是否需要转为红黑树 if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } // II) key相同则替换旧值 返回 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; // 表中元素个数大于临界值时,扩展表X2 if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
get
final Node<K, V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K, V>[] tab; Node<K, V> first, e; int n; K k; // table 存在,header节点存在 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { // 与 header 节点key相同,返回header 节点 if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; // 如果存在header的子节点 if ((e = first.next) != null) { // 如果 header 是红黑树去取树节点 if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K, V>) first).getTreeNode(hash, key); // 如果 header 是链 do { // 遍历节点,找到相同key返回 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } // 未查到相同key return null; }
treeify
final void treeifyBin(Node<K, V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K, V> e; // 如果table达不到最小treeify 容量(64)则扩容X2 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); // header 节点存在时 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K, V> hd = null, tl = null; // 遍历链将 Node -> TreeNode do { TreeNode<K, V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) // 绘制红黑树 hd.treeify(tab); } }
resize
/** * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold. * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move * with a power of two offset in the new table. * * @return the table */ final Node<K, V>[] resize() { ... return newTab; }
hash
/** * Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash * to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of * hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will * always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys * holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we * apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits * downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and * quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes * are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from * spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of * collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the * cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as * to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise * never be used in index calculations because of table bounds. */ static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
关于编写方法时使用的缩略词猜想
- mc = modCount
- tab = table
- bin = table[i]
- tl = tree left
- hd = header
- p = present
- i = index
- prev = previous
- next = next
- k = key
- val = value
- v = value
- n = length
- e = entry
- simple -> simplify
- tree -> treeify
- do -> undo
- untreeify -> untreeify