本文主要总结一下spring的所有用法,更多原理篇在后续章节。涵盖内容如下所列:
- 什么是Ioc/DI、AOP、Spring容器
- Ioc/DI基于xml、xml和注解混合、以及纯注解的不同实现
- AOP基于xml、xml和注解混合、以及纯注解的不同实现
- 声明式事务基于xml、xml和注解混合、以及纯注解的不同实现
emmm.........That's All , let's go.
一、spring简介
老规矩,甭管啥,先上图:
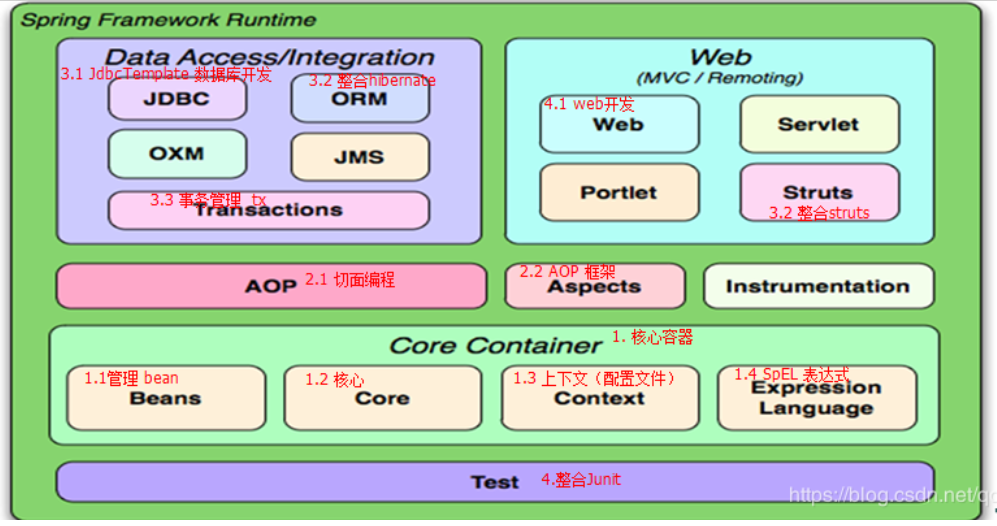
Ioc(核心中的核心):Inverse of control,控制反转。对象的创建权利由程序反转给Spring框架。
DI:Dependency Injection,依赖注入。在Spring框架负责创建对象Bean时,动态的将依赖度的对象注入到Bean组件中!
AOP:Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程。在不修改目标对象的源代码情况下,增强Ioc容器中Bean的功能。
Spring容器:指的就是Ioc容器,装载Bean对象的容器。底层就是一个BeanFactory。
二、Ioc、DI
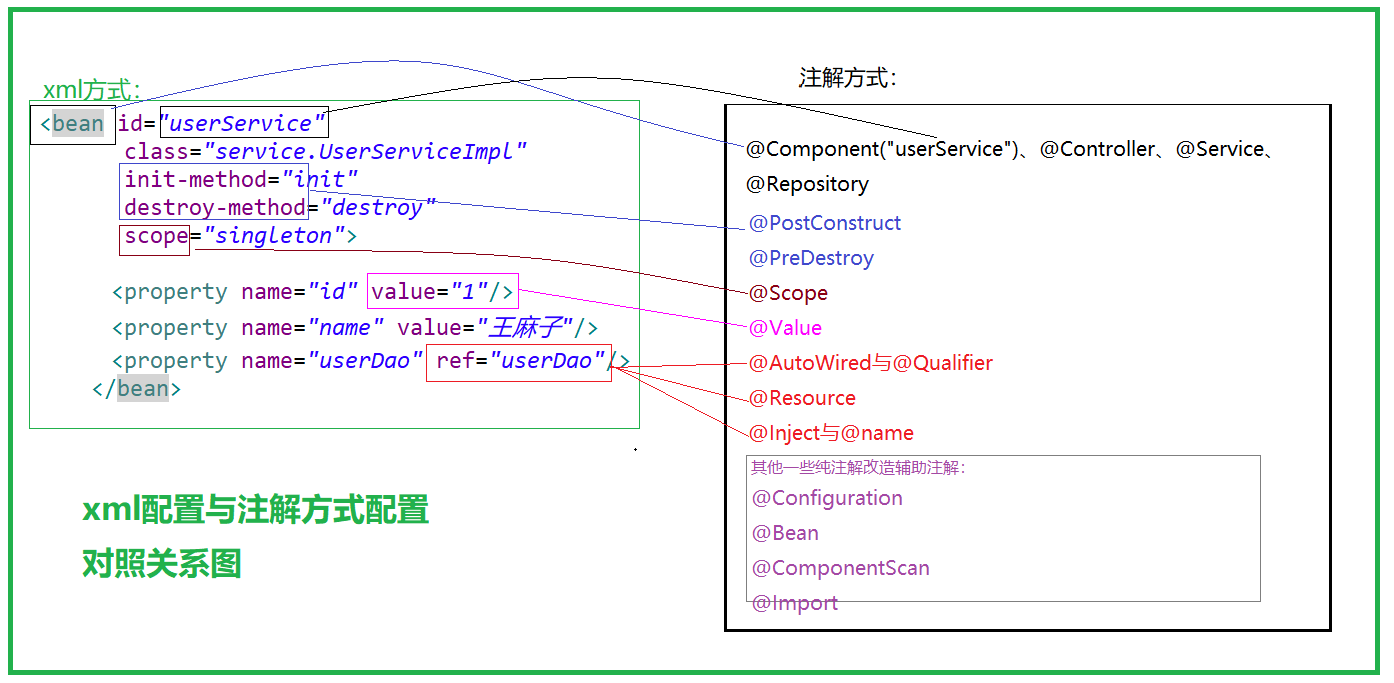
A、Bean的基础使用方式(无参数版本)
spring容器默认通过无参构造方法创建Bean对象。
1、applicationContext.xml配置(多余的命名空间不必在意o(* ̄︶ ̄*)o):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- id是Bean的名称,class是类全限定名,init-method是初始化对象前执行的方法,destroy-method是销毁对象后执行的方法(容器销毁对象就销毁),还有未罗列的scope代表作用域--> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy" /> </beans>
2、Bean类定义如下:
package service; public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ //无参构造 public UserServiceImpl() { } @Override public void saveUser() { System.out.println("保存用户成功!"); } public void init() { System.out.println("初始化操作"); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁操作:释放资源等"); } }
3、测试代码:
@org.junit.Test public void xmlTest() { //一般使用ApplicationContext,由于需要关闭容器使用了AbstractApplicationContext // ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // UserService us = (UserService)context.getBean("userService");//也可以通过bean的名称实例化 UserService us = context.getBean(UserService.class); us.saveUser(); context.close();//关闭容器才会销毁对象,测试destroy()方法 }
4、输出结果为:
初始化操作
保存用户成功!
销毁操作:释放资源等
B、Bean的基础使用方式(有基础类型参数版本)
1、xml配置:(此时值是必传的,否则会报错)

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 1、通过构造器注入属性值 --> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <constructor-arg name="id" value="1" /> <constructor-arg name="name" value="王麻子"/> </bean> <!-- 2、通过setter方法注入属性值 <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <property name="id" value="1" /> <property name="name" value="2" /> </bean> --> </beans>
2、Bean类:

package service;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private String id ;
private String name ;
//构造方法
public UserServiceImpl(String id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//setter
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void saveUser() {
System.out.println("保存用户User[id="+id+",name="+name+"]成功!");
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化操作");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁操作:释放资源等");
}
}
3、测试代码不变(同上)。
4、测试结果:
初始化操作 保存用户User[id=1,name=王麻子]成功! 销毁操作:释放资源等
C、xml方式的Ioc、DI(有引用类型参数版本)
1、xml配置:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 通过setter方法注入属性值 --> <bean id="userService" class="service.UserServiceImpl" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <property name="id" value="1" /> <property name="name" value="王麻子" /> <property name="userDao" ref="userDao" /><!-- 通过ref动态注入userDao --> </bean> <!-- 注入对象 --> <bean id="userDao" class="dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean> </beans>
2、Bean类(增加引用类型):

package service; import dao.UserDao; public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ private String id ; private String name ; private UserDao userDao ;//通过spring容器动态注入值 //setter public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } @Override public void saveUser() { userDao.saveUser(id, name);//调用注入对象的方法 } public void init() { System.out.println("初始化操作"); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁操作:释放资源等"); } }
3、测试代码不变。
4、测试结果:
初始化操作 UserDao=>保存用户User[id=1,name=王麻子]成功! 销毁操作:释放资源等
D、xml与注解混合方式的Ioc、DI
1、配置类:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 开启注解并扫描指定包中带有注解的类 --> <context:component-scan base-package="dao;service" /> </beans>
2、Bean类:
注:此处使用@@PropertySource注入基础类型的值

@Service @PropertySource("classpath:other.properties") public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Value("${id}") private String id ; @Value("${name}") private String name ; @Resource private UserDao userDao ;//通过spring容器动态注入值 //setter public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } @Override public void saveUser() { userDao.saveUser(id, name);//调用注入对象的方法 } @PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("初始化操作"); } @PreDestroy public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁操作:释放资源等"); } }
3、other.properties文件内容:
id=1
name=Jhon
4、测试代码不变
5、测试结果:
初始化操作 UserDao=>保存用户User[id=1,name=Jhon]成功! 销毁操作:释放资源等
Controller&Service&Repository注解:
他们三个都是针对@Component的衍生注解。
@Controller:一般用于表现层。
@Service:一般用于业务层。
@Repository:一般用于持久层。
Autowired&Resource&Inject注解:
三个都是动态装配引用对象的注解。一般使用@Resource即可。
@Autowired是Spring自带的注解,默认是按照类型(byType)装配。如果需要按照名称(byName)装配,需要结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。
@Resource是属于J2EE JSR250的注解,默认是按照名称装配。可以通过@Resource的name属性指定名称,如果没有指定name属性,以字段名首字母小写按照名称查找,当找不到与名称匹配的bean时会自动按照类型进行装配。如果name一旦指出,则只按照名称查找。
@Inject是属于J2EE JSR330的注解。默认按照类型进行装配。如果需要按照名称进行装配,则需要配合@Named注解一起使用。
E、纯注解方式的Ioc、DI
有点饿,想吃饭了,省点时间直接盗用别人的一张图吧。如下(主要讲的是纯注解方式需要面对的问题。也就是纯注解方式相较注解和xml混合方式主要解决了哪些事):

基于以上问题,新引入了几个注解:
@Configuration
@Bean
@ComponentScan
@Import
具体使用,直接看代码吧。
1、配置文件直接干掉。
2、新增配置类:

package configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; @Configuration @ComponentScan("dao;service")//扫描包 @Import({OtherConfiguration.class})//导入其他配置类,可以有多个。和允许有多个xml一个道理 public class SpringConfiguration { public SpringConfiguration() { System.out.println("spring 容器开始启动。。。。"); } // @Bean // @Scope("prototype") // public SqlSessionFactory userService() { // //pass 这里边主要负责实例化spring容器本身需要的一些对象。 // } } @PropertySource("classpath:other.properties") class OtherConfiguration { public OtherConfiguration() { System.out.println("OtherConfiguration构造方法:负责加载其他配置信息。。。"); } }
3、Bean类:

@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Value("${id}") private String id ; @Value("${name}") private String name ; @Resource private UserDao userDao ;//通过spring容器动态注入值 //setter public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } @Override public void saveUser() { userDao.saveUser(id, name);//调用注入对象的方法 } @PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("初始化操作"); } @PreDestroy public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁操作:释放资源等"); } }
4、测试代码:

@org.junit.Test public void annotationTest() { //此处使用注解类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实例化容器 AbstractApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); UserService us = context.getBean(UserService.class); us.saveUser(); context.close(); }
5、测试结果:
spring 容器开始启动。。。。 初始化操作 OtherConfiguration构造方法:负责加载其他配置信息。。。 UserDao=>保存用户User[id=1,name=Jhon]成功! 销毁操作:释放资源等
总结:
虽然使用注解看起来很方便,但是很明显它的缺点是配置与业务代码存在严重耦合。但也不是说注解就是个笑话。总有一些时候,注解使用会更好一些,比如在spring boot中注解就扮演着很重要的角色。(具体情况具体考量,老铁)
二、AOP的使用
通常情况下,程序扩展功能需要修改原有的代码,这样很不方便。而且也使得代码内容显得不够纯粹,比如:业务代码中夹杂有日志统计、柜员复核等一些无关的代码。
解决这一问题:一个很常用的解决方案就是使用动态代理。
spring中的AOP就是使用动态代理技术,来实现代码功能的横向增强。
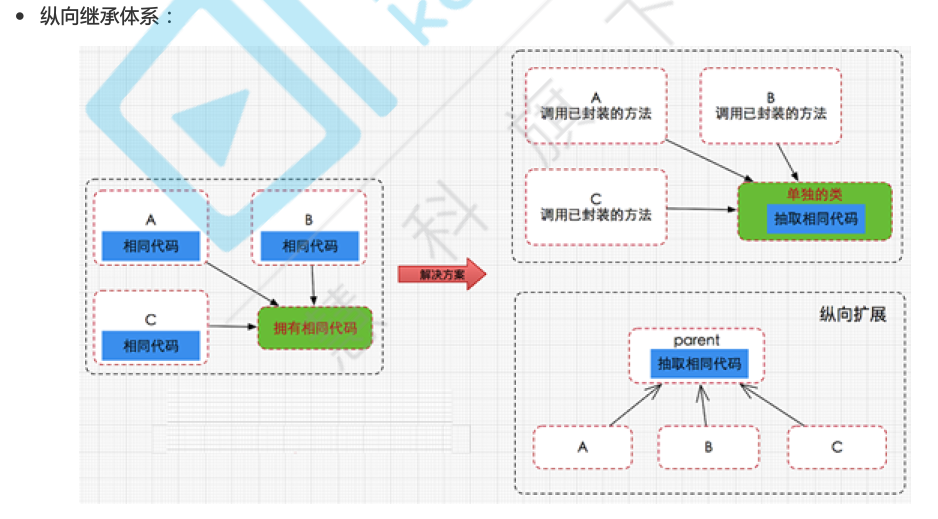
纵向抽取机制:
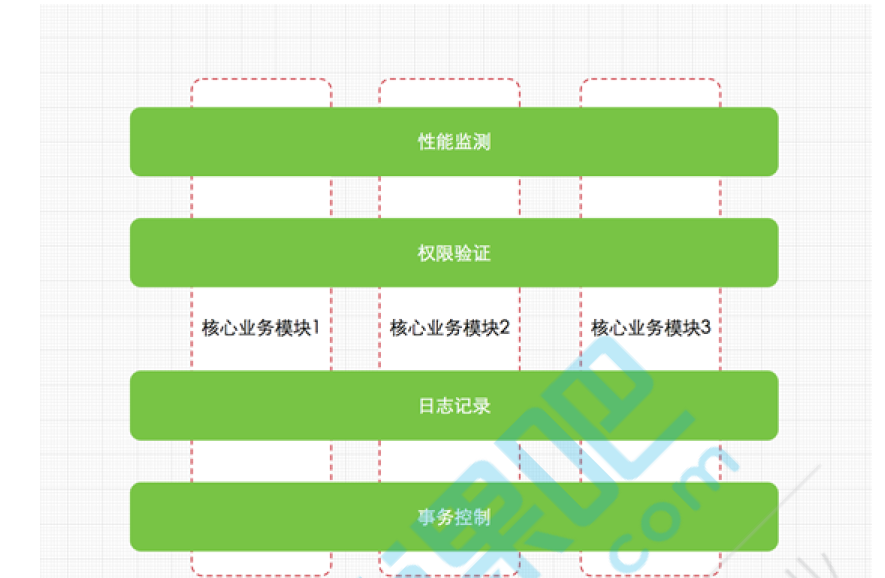
名词解释:
- JoinPoint(连接点)
- 所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点。在spring中,这些点值的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点。
- PointCut(切入点)
- 所谓切入点是指我们要对那些JoinPoint进行拦截的定义。
- Advice(通知/增强)
- 所谓通知是指拦截到JoinPoint后所要做的事情。通知分为前置通知、后置通知、环绕通知、最终通知、异常通知。(切面要完成的功能)
- Introduction(引介)
- 引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下,Introduction可以在运行期间动态的为类添加一些方法或Field。
- Target(目标对象)
- 代理的目标对象。
- Weaving(织入)
- 把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。
- Proxy(代理)
- 被AOP织入增强后产生的代理类。
- Aspect(切面)
- 切入点和通知的结合。
- Advisor(通知器、顾问)
- 和Aspect很相似。
A:使用xml实现AOP
1、编写通知类:

package advice; public class LogAdvice { public void log() { System.out.println("记录日志。。。。。。"); } }
2、AOP配置:
其中切入点的配置使用表达式表示,格式为:
execution([修饰符] 返回值类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数))
①修饰符可省略
②返回值可以用*表示所有。或者使用具体值如:void,int,User等
③包名:
包名可以用*代替。如果是多级包名,想省略中间的*,可以使用..。如*..*可以表示com.a.service,也可以表示com.a.b.service
④类名:
类名可以使用*,表示任意;*Service,表示已Service结尾的类。
⑤参数:
也可以使用*表示,如果是多个参数可以用..表示。

<!-- 配置通知、增强 --> <bean id="logAdvice" class="advice.LogAdvice"></bean> <!-- AOP切面配置 --> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="logAdvice"> <aop:after method="log" pointcut="execution (* service.*.*(..))"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
3、其他不变。测试结果为:
初始化操作
UserDao=>保存用户User[id=1,name=Jhon]成功!
记录日志。。。。。。
销毁操作:释放资源等
B:使用xml与注解混合方式实现AOP
1、配置文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 开启注解并扫描指定包中带有注解的类 --> <context:component-scan base-package="dao;service;advice" /> <!-- 开启切面自动扫描功能 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> </beans>
2、切面类。(此时是切面类而不是通知类)

@Component//注意这个注解不要漏了 @Aspect//注解此类为一个切面(所以里边会定义切入点与通知) public class LogAspect { @After("execution(* *.*.*())")//值为切入点表达式 public void log() { System.out.println("记录日志。。。。。。"); } @Around("LogAspect.fn()")//环绕通知测试 public Object testAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) { try { System.out.println("环绕前....."); Object obj = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后....."); return obj ; } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Before(value="LogAspect.fn()")//引用如下定义的通用切入点 public void testBefore() { System.out.println("方法执行前。。。"); } @Pointcut("execution(void service.UserServiceImpl.saveUser())")//定义一个通用的切入点 public void fn() {} }
3、其他不变。测试结果:
环绕前..... 方法执行前。。。 UserDao=>保存用户User[id=1,name=Jhon]成功! 环绕后..... 记录日志。。。。。。
C:纯注解方式实现AOP
配置类上加入如下注解即可:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class SpringConfiguration { ....... }
三、声明式事务的配置
由于事务的测试需要数据库的支撑,所以在没有整合Mybatis之前无法直接测试事务。
Spring中的事务也只是做个配置,最终还是交由数据库管理事务。因此,此章节仅仅写下示例配置:

<!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="......."> <property name="driverClass" value="..."></property> <property name="url" value="..."></property> <property name="username" value="..."></property> <property name="password" value="..."></property> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DatasourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 注入数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 事务通知 --> <tx:advice id="advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!-- 配置事务相关属性 --> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="query" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="add" propagation="REQUIRED"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置aop --> <aop:config> <aop:advisor advice-ref="advice" pointcut="execution(* *.service.*(..))"/> </aop:config>
