When you employ a new expression (i.e., dynamic creation of an object via a use of new), two things happen. First, memory is allocated (via a function named operator new — see Items 49 and 51). Second, one or more constructors are called for that memory.
When you employ a delete expression (i.e., use delete), two other things happen: one or more destructors are called for the memory, then the memory is deallocated (via a function named operator delete — see Item 51).
The big question for delete is this: how many objects reside in the memory being deleted? The answer to that determines how many destructors must be called.
In particular, the memory for an array usually includes the size of the array, thus making it easy for delete to know how many destructors to call. The memory for a single object lacks this information. You can think of the different layouts as looking like this, where n is the size of the array:
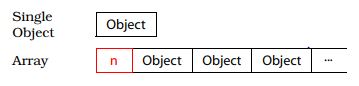
This is just an example, of course. Compilers aren't required to implement things this way, though many do.
If you use brackets in your use of delete, delete assumes an array is pointed to. Otherwise, it assumes that a single object is pointed to:
std::string *stringPtr1 = new std::string; std::string *stringPtr2 = new std::string[100]; // ... delete stringPtr1; // delete an object delete [] stringPtr2; // delete an array of objects
If you used the "[]" form on stringPtr1? The result is undefined,
If you didn't use the "[]" form on stringPtr2? The result is undefined.
This rule is also noteworthy for the typedef-inclined, because it means that a typedef’s author must document which form of delete should be employed when new is used to conjure up objects of the typedef type. For example, consider this typedef
delete pal; // undefined! delete [] pal; // fine
To avoid such confusion, abstain from typedefs for array types. That’s easy, because the standard C++ library (see Item 54) includes string and vector, and those templates reduce the need for dynamically allocated arrays to nearly zero.
Things to Remember:
- If you use [] in a new expression, you must use [] in the corresponding delete expression. If you don't use [] in a new expression, you mustn't use [] in the corresponding delete expression.