线性表的链式表示
不要求逻辑上相邻的元素在物理存储上相邻,使用指针来表示元素之间的逻辑关系。
优点:
对线性表进行插入删除操作时不需要移动大量的元素,只需要修改对应元素的指针域即可,方便省时;
不需要为整个线性链表提前分配足够的存储空间;
当节点不再使用时,可以将存储空间进行及时的回收。
抽象链式类的定义
链式表使用指针来表示前后元素之间的关系,因此每个元素节点除了包含自身数据的相关信息外,还包括存储后续元素地址的指针。节点类的定义如下:
template <class type> class ListNode {//链表节点类定义
public:
ListNode();
{ next = nullptr;}//默认构造函数
ListNode(ListNode(const type &item, ListNode<type> *next1 = nullptr))
{
data = item;
next = next1;
} //带参数的构造函数
type data; //节点数据域
ListNode<type> *next; //节点指针域
};
节点类的两个数据成员:data用于存储数据元素值,next用于指向下一个节点。两个构造函数用于给数据成员设置初值。其链表结构如下:
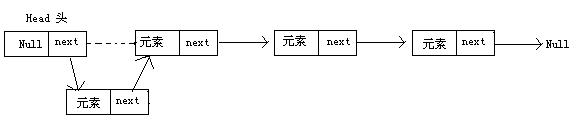
指示链表的第一个结点的指针称为头指针head,最后一个结点没有后继结点,指针域为空NULL或^,对于仅含有表头元素的链表为空表。

链表有三种类型,单链表、循环链表与双向链表三种。
抽象链表类的定义如下:
template <class type>
class ablinklist :public ablist<type> { //继承线性表抽象类
public:
ListNode<type> *GetHead() { //获得节点头指针
return head;
}
ListNode<type> *GetNext(ListNode<type> &n) { //获得节点n下一节点位置
return n.next == head ? n.next->next : n.next; //这句不是很明白
}
type Get(int i); //获得第i元素
bool Set(type x, int i); //设置i处元素
ListNode<type> *Find(int i); //获得i处元素位置
ListNode<type> *Find1(type value); //获得元素value位置
void MakeEmpty();
virtual bool Insert(type value, int i) = 0;
virtual bool Remove(int i) = 0;
virtual bool Remove1(type value) =0;
protected:
ListNode<type> *head;
};
抽象链表类各成员函数的实现
设置函数
//节点元素设置函数
template <class type>
bool ablinklist<type>::Set(type x, int i)
{
ListNode<type> *p = Find(i); //找到节点
if (p == NULL || p == head) //链表不存在或空表
return false;
else
p->data = x; //设置元素
return true;
}
取值函数
//获得第i元素值函数
template <class type>
type ablinklist<type>::Get(int i)
{
LinkNode<type> *p = Find(i); //确定节点位置
assert(p && p != head);
return p->data; //返回节点元素
}
清空链表函数
//清空链表函数
template<class type>
void ablinklist<type>::MakeEmpty() {
LinkNode<type> *q = head->next; //表头
int i = 0;
while (i++ < length) {
head->next = q->next; //删除第一个元素
delete q; //回收空间
q = head->next; //后移
}
length = 0;
}
搜索数据元素值为value的结点
//获得元素value位置
template<class type>
ListNode<type> *ablinklist<type>::Find1(type value) {
ListNode<type> *p = heda->next; //表头
int i = 1;
while (i++ <= length && p->data != value) //i有效且为找到元素时
p = p->next; //后移
return p;
}
定位函数
//获得i处元素位置
template<class type>
ListNode<type> *ablinklist<type>::Find(int i) {
ListNode<type> *p = head->next; //表头
if (i<0 || i>length) return NULL; //i无效,返回空
if (i == 0) return head; //空表
int j = 1;
while (p != NULL && j < i) //遍历找元素
{
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}
用C语言描述:
插入操作:在值为a的结点前面插入值为x的结点,若链表为空,则x为其头结点,若表中无a元素,在将x插入链表末尾。
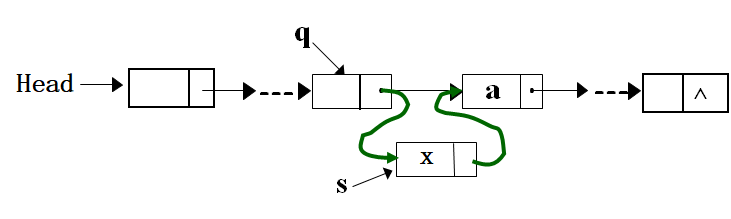
//将元素x对应为链表格式
NODE *GetListNode(int x)
{
NODE *s;
s=(NODE *)malloc(NODESIZE);
if (s)
{ s->data=x; s->next=NULL; }//数据域x,指针域空
return(s);
}
NODE *InsertList(NODE *head,int a,int x)
{
NODE *s,*q;
s=GetListNode(x); if (!s) return(head);//没有元素指针时
if (head==NULL){ //表为空时
head=s; return(head);
}
if (head->data==a){ //第一个结点满足
s->next=head; head=s; return(head);
//不是很明白这一句----------------------
}
q=head;//其它情况,进行查找
while (q->next!=NULL && q->next->data!=a)
q=q->next;
s->next=q->next; //插入
q->next=s;
return(head); //返回头指针
}
删除操作:在头指针为head的链表中将值为a的结点删除
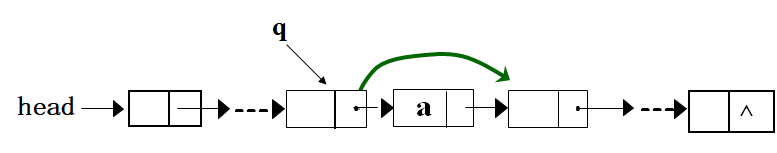
NODE *DeleteList(NODE *head,int a)
{
NODE *p,*q;
if (head==NULL) return(NULL);
if (head->data==a) //第一个结点满足
{ p=head; head=head->next; free(p);
return(head);
}
q=head; //其它情况,进行查找
while (q->next!=NULL && q->next->data!=a)
q=q->next;
if (q->next!=NULL);//找到,删除
{ p=q->next; q->next=p->next; free(p);}
return(head); //返回头指针
}