1.什么是链表


优点:不需要处理固定容量的问题
缺点:丧失了随机访问的能力
2.数组和链表的对比

3.在链表中添加元素
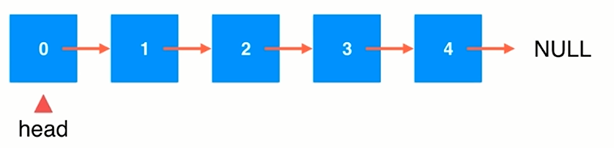
(1)在链表头添加元素
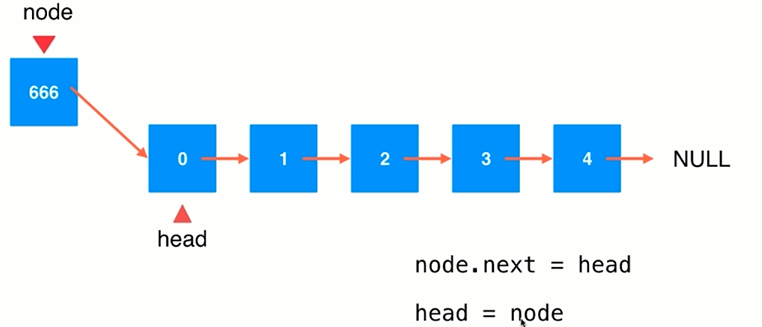
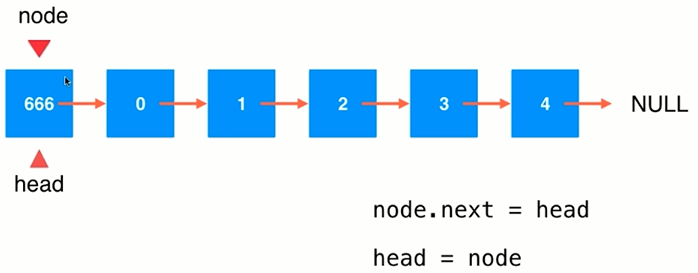

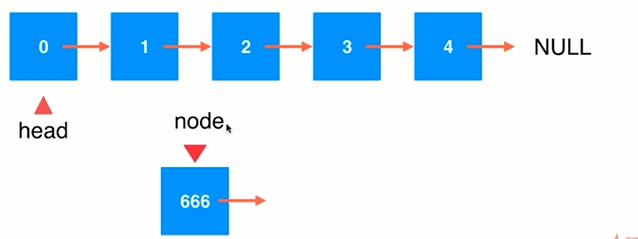
(2)在链表中间添加元素

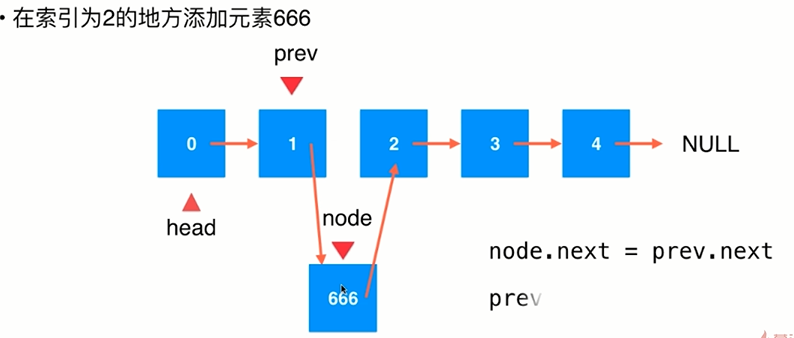
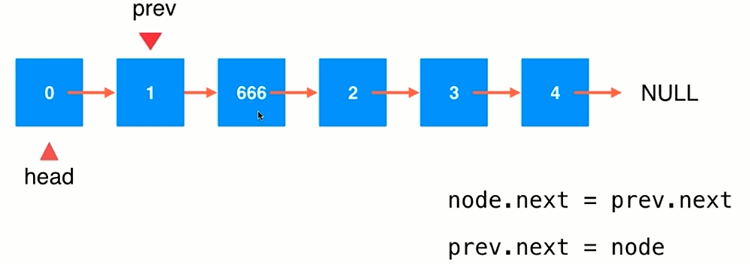
(3)链表中添加节点的代码实现
public class LinkedList<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e,Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node head; int size; public LinkedList(){ head = null; size =0; } //获取链表中的元素个数 public int getSize(){ return size; } //返回链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } //在链表头添加新的元素e public void addFirst(E e){ // Node node = new Node(e); // node.next = head; // head = node; head = new Node(e,head); size ++; } //在链表的index位置添加新元素e public void add(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed.Illegal index."); if(index == 0) addFirst(e); else{ Node prev = head; for(int i = 0;i < index -1;i ++) prev =prev.next; // Node node =new Node(e); // node.next = prev.next; // prev.next = node; prev.next =new Node(e,prev.next); size ++; } } //在链表末尾添加新的元素e public void addLast(E e){ add(size,e); } }
4.使用链表的虚拟头结点
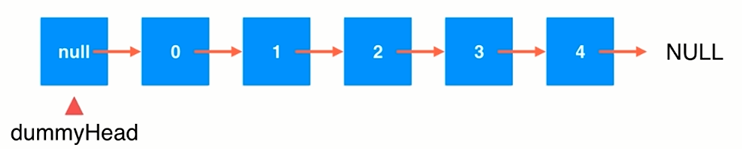
public class LinkedList<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e,Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node dummyHead; private int size; public LinkedList(){ dummyHead = new Node(null,null); size =0; } //获取链表中的元素个数 public int getSize(){ return size; } //返回链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } //在链表的index位置添加新元素e public void add(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed.Illegal index."); Node prev = dummyHead; for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++) prev =prev.next; prev.next =new Node(e,prev.next); size ++; } //在链表头添加新的元素e public void addFirst(E e){ add(0,e); } //在链表末尾添加新的元素e public void addLast(E e){ add(size,e); } }
5.链表的遍历,查询和修改
public class LinkedList<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e,Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node dummyHead; private int size; public LinkedList(){ dummyHead = new Node(null,null); size =0; } //获取链表中的元素个数 public int getSize(){ return size; } //返回链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } //在链表的index位置添加新元素e public void add(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed.Illegal index."); Node prev = dummyHead; for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++) prev =prev.next; prev.next =new Node(e,prev.next); size ++; } //在链表头添加新的元素e public void addFirst(E e){ add(0,e); } //在链表末尾添加新的元素e public void addLast(E e){ add(size,e); } //获得链表的第index位置的元素 public E get(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get Failed.Illegal index."); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++) cur = cur.next; return cur.e; } //获得链表的第一个元素 public E getFirst(){ return get(0); } //获得链表的最后一个元素 public E getLast(){ return get(size - 1); } //修改链表的第index位置的元素e public void set(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed.Illegal index."); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for(int i = 0;i <index;i ++) cur = cur.next; cur.e = e; } //查找链表中是否有元素e public boolean contains(E e){ Node cur = dummyHead.next; while(cur != null){ if(cur.e.equals(e)) return true; cur = cur.next; } return false; } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder res =new StringBuilder(); Node cur =dummyHead.next; while(cur != null){ res.append(cur + "->"); cur =cur.next; } res.append("NULL"); return res.toString(); } }
调用链表实例
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); for(int i = 0;i < 5; i ++){ linkedList.addFirst(i); System.out.println(linkedList); } linkedList.add(2,666); System.out.println(linkedList); // 0->NULL // 1->0->NULL // 2->1->0->NULL // 3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL } }
6.链表元素的删除
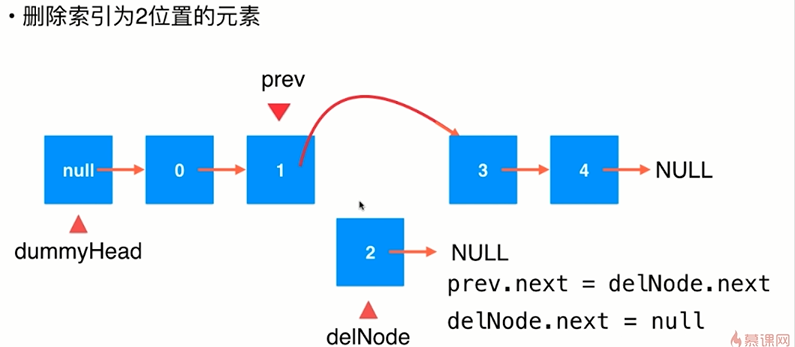
public class LinkedList<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e,Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node dummyHead; private int size; public LinkedList(){ dummyHead = new Node(null,null); size =0; } //获取链表中的元素个数 public int getSize(){ return size; } //返回链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } //在链表的index位置添加新元素e public void add(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index > size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed.Illegal index."); Node prev = dummyHead; for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++) prev =prev.next; prev.next =new Node(e,prev.next); size ++; } //在链表头添加新的元素e public void addFirst(E e){ add(0,e); } //在链表末尾添加新的元素e public void addLast(E e){ add(size,e); } //获得链表的第index位置的元素 public E get(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get Failed.Illegal index."); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for(int i = 0;i < index;i ++) cur = cur.next; return cur.e; } //获得链表的第一个元素 public E getFirst(){ return get(0); } //获得链表的最后一个元素 public E getLast(){ return get(size - 1); } //修改链表的第index位置的元素e public void set(int index,E e){ if(index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed.Illegal index."); Node cur = dummyHead.next; for(int i = 0;i <index;i ++) cur = cur.next; cur.e = e; } //查找链表中是否有元素e public boolean contains(E e){ Node cur = dummyHead.next; while(cur != null){ if(cur.e.equals(e)) return true; cur = cur.next; } return false; } //从链表中删除index位置的元素,返回删除的元素 public E remove(int index){ if(index < 0 || index >=size) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed.Index is illegal"); Node prev = dummyHead; for(int i = 0;i < index; i ++) prev = prev.next; Node retNode = prev.next; prev.next = retNode.next; retNode.next = null; size --; return retNode.e; } //从链表中删除第一个元素,返回删除的元素 public E removeFirst(){ return remove(0); } //从链表中删除最后一个元素,返回删除的元素 public E removeLast(){ return remove(size - 1); } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder res =new StringBuilder(); Node cur =dummyHead.next; while(cur != null){ res.append(cur + "->"); cur =cur.next; } res.append("NULL"); return res.toString(); } }
调用删除链表实例:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); for(int i = 0;i < 5; i ++){ linkedList.addFirst(i); System.out.println(linkedList); } linkedList.add(2,666); System.out.println(linkedList); // 0->NULL // 1->0->NULL // 2->1->0->NULL // 3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL linkedList.remove(2); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeFirst(); System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.removeLast(); System.out.println(linkedList); // 0->NULL // 1->0->NULL // 2->1->0->NULL // 3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->666->2->1->0->NULL // 4->3->2->1->0->NULL // 3->2->1->0->NULL // 3->2->1->NULL } }
7.链表的时间复杂度分析
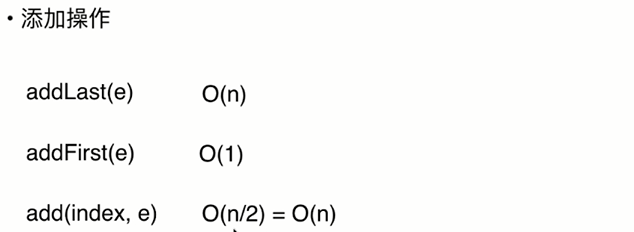


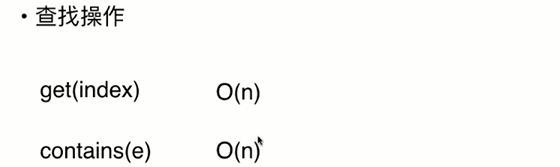
8.使用链表实现栈
public class LinkedListStack<E> implements Stack<E>{ private LinkedList<E> list; public LinkedListStack(){ list = new LinkedList<>(); } @Override public int getSize(){ return list.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty(){ return list.isEmpty(); } @Override public void push(E e){ list.addFirst(e); } @Override public E pop(){ return list.removeFirst(); } @Override public E peek(){ return list.getFirst(); } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); res.append("Stack: top "); res.append(list); return res.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedListStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedListStack<>(); for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++){ stack.push(i); System.out.println(stack); } stack.pop(); System.out.println(stack); // Stack: top 0->NULL // Stack: top 1->0->NULL // Stack: top 2->1->0->NULL // Stack: top 3->2->1->0->NULL // Stack: top 4->3->2->1->0->NULL // Stack: top 3->2->1->0->NULL } }
9.数组栈和链表栈比较
import java.util.Random; public class Main {//测试使用q运行opCount个enqueue和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒 private static double testStack(Stack<Integer> stack,int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random(); for(int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) stack.push(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); for(int i = 0;i < opCount; i++) stack.pop(); long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 10000000; //数组栈 ArrayStack<Integer> arrayStack = new ArrayStack<>(); double time1 = testStack(arrayStack,opCount); System.out.println("ArrayStack, time:" + time1 + "s"); // ArrayStack, time:4.220762637s //链表栈 LinkedListStack<Integer> linkedListStack = new LinkedListStack<>(); double time2 = testStack(linkedListStack,opCount); System.out.println("LinkedListStack, time:" + time2 + "s"); // LinkedListStack, time:6.295457665s } }
10.改进我们的链表来实现队列
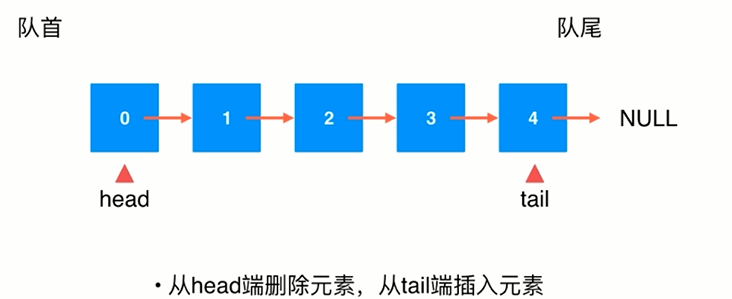
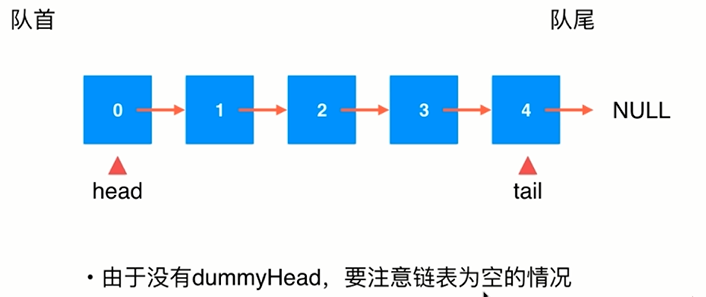
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> { private class Node{ public E e; public Node next; public Node(E e,Node next){ this.e = e; this.next = next; } public Node(E e){ this(e,null); } public Node(){ this(null,null); } @Override public String toString(){ return e.toString(); } } private Node head , tail; private int size; public LinkedListQueue(){ head = null; tail = null; size = 0; } @Override public int getSize(){ return size; } @Override public boolean isEmpty(){ return size == 0; } @Override public void enqueue(E e){ if(tail == null){ tail = new Node(e); head = tail; }else{ tail.next = new Node(e); tail = tail.next; } size ++; } @Override public E dequeue(){ if(isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("cannot dequeue from an empty queue"); Node retNode = head; head = head.next; retNode.next = null; if(head == null) tail = null; size --; return retNode.e; } @Override public E getFront(){ if(isEmpty()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty."); return head.e; } @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); res.append("Queue: front "); Node cur = head; while(cur != null){ res.append(cur + "->"); cur = cur.next; } res.append("NULL tail"); return res.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue<>(); for(int i = 0;i < 10;i ++){ linkedListQueue.enqueue(i); System.out.println(linkedListQueue); if(i % 3 == 2){ linkedListQueue.dequeue(); System.out.println(linkedListQueue); } } // Queue: front 0->NULL tail // Queue: front 0->1->NULL tail // Queue: front 0->1->2->NULL tail // Queue: front 1->2->NULL tail // Queue: front 1->2->3->NULL tail // Queue: front 1->2->3->4->NULL tail // Queue: front 1->2->3->4->5->NULL tail // Queue: front 2->3->4->5->NULL tail // Queue: front 2->3->4->5->6->NULL tail // Queue: front 2->3->4->5->6->7->NULL tail // Queue: front 2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL tail // Queue: front 3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL tail // Queue: front 3->4->5->6->7->8->9->NULL tail } }
11.链表队列和数组队列、循环队列进行比较
import java.util.Random; public class Main {//测试使用q运行opCount个enqueue和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒 private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q,int opCount){ long startTime = System.nanoTime(); Random random = new Random(); for(int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); for(int i = 0;i < opCount; i++) q.dequeue(); long endTime = System.nanoTime(); return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int opCount = 100000; //数组队列 ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>(); double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue,opCount); System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time:" + time1 + "s"); //ArrayQueue, time:4.859302024s //循环队列 LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>(); double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue,opCount); System.out.println("LoopQueue, time:" + time2 + "s"); //LoopQueue, time:0.019878675s //链表队列 LinkedListQueue<Integer> linkedListQueue = new LinkedListQueue<>(); double time3 = testQueue(linkedListQueue,opCount); System.out.println("LinkedListQueue, time:" + time3 + "s"); //LinkedListQueue, time:0.015294216s } }
12.删除链表中的结点(https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/)
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6 输出: 1->2->3->4->5
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { //删除头结点 while(head != null && head.val == val){ ListNode delNode = head; head = head.next; delNode.next = null; } if(head == null) return null; ListNode prev = head; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val){ ListNode delNode = prev.next; prev.next = delNode.next; delNode.next = null; }else{ prev = prev.next; } } return head; } }
进一步优化,增加虚拟头结点
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode prev = dummyHead; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val){ ListNode delNode = prev.next; prev.next = delNode.next; delNode.next = null; }else{ prev = prev.next; } } return dummyHead.next; } }
调用实例:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6}; ListNode head = new ListNode(nums); System.out.println(head); //1->2->6->3->4->5->6->NULL ListNode res = (new Solution()).removeElements(head , 6); System.out.println(res); //1->2->3->4->5->NULL } }