SELECT篇
这是products表然后执行下面操作进行实验
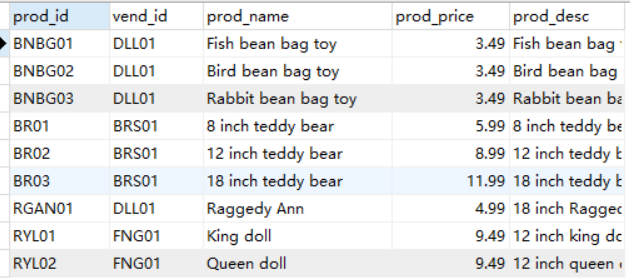
这个是vendors表
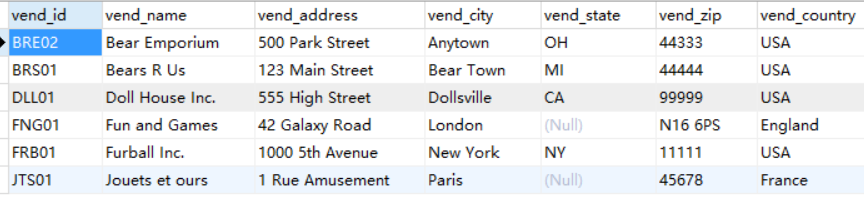
检索数据:
1.检索所有的列 select * from products;
2.检索不同的值 select distinct vend_id from products;
3.检索限制结果 select prod_name from products limit 5;
排序检索数据:order by
1.排序数据 select prod_name from products order by prod_name;
2.多个列排序select prod_id,prod_price,prod_name from products order by prod_price,prod_name;
3.列位置排序select prod_id,prod_price,prod_name from products order by 2,3;
4.降序排列select prod_id,prod_price,prod_name from products order by prod_price DESC;
过滤数据:
1.使用WHERE子句
select prod_name,prod_price from products where prod_price=3.49;
以下为WHERE子句的操作符:
(1)检查单个值:where prod_price<=10;
(2)不匹配检查:SELECT vend_id, prod_name FROM Products WHERE vend_id <> 'DLL01';
(3)范围值检查:SELECT prod_name, prod_price FROM Products WHERE prod_price BETWEEN 5 AND 10;
(4)空值检查:
高级过滤:
1.组合的where子句
(1)AND操作符:select prod_id,prod_price,prod_name from products where vend_id='DLL01' and prod_price<=4 order by prod_id DESC;
(2)OR操作符:SELECT prod_name, prod_price FROM Products WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01' OR vend_id = ‘BRS01’;
(3)求值顺序,and的优先级高于or;
2.IN操作符
(1)指定语句执行范围:SELECT prod_name, prod_price FROM Products WHERE vend_id IN ( 'DLL01', 'BRS01' ) ORDER BY prod_name;
IN的优点:1.清楚直观,2.求值顺序易管理3.执行速度比where or更快4.最大优点可以动态建立where子句
3.NOT操作符
SELECT prod_name FROM Products WHERE NOT vend_id = 'DLL01' ORDER BY prod_name;
通配符过滤:
LIKE操作符:
(1).%(%表示任何字符出现任意次数)
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '%bean bag%';
注意:a.%可以匹配null之外的所有东西.b.很多DBMS都用空格填补字段的内容
(2)._(_和%区别是只匹配单个字符)
select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name like '__ inch teddy bear';
函数:略
汇总数据:
(1).COUNT()函数:确定表中行的数目:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS num_cust FROM products;
注意:如果指定列名,则COUNT()函数会忽略指定列的值为空的行,但如果COUNT()函数中用的是星号(*),则不忽略。
如:SELECT COUNT(cust_email) AS num_cust FROM Customers;
(2).MIN(),AVG(),MAX(),SUM()函数:SELECT MIN(prod_price) AS min_price FROM Products;
(3).聚集不同的值:
SELECT AVG(DISTINCT prod_price) AS avg_price FROM Products WHERE vend_id = 'DLL01';
(4).组合聚集函数:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS num_items,
MIN(prod_price) AS price_min,
MAX(prod_price) AS price_max,
AVG(prod_price) AS price_avg
FROM Products
数据的分组
1.group by创建分组
select vend_id, count(*) as count from products group by vend_id;
注意:a.GROUP BY子句必须出现在WHERE子句之后,ORDER BY子句之前
2.having过滤分组(where只可以过滤行不可以过滤分组)
select vend_id, count(*) as count from products group by vend_id having count(*)>2;
3.组排序
SELECT order_num, COUNT(*) AS items FROM OrderItems GROUP BY order_num HAVING COUNT(*) >= 3 ORDER BY items, order_num;
子查询:就是嵌套select语句
mysql> select cust_id
-> from orders
-> where order_num IN(select order_num from orderitems where prod_id='RGAN01');
(从里到外)
先执行select order_num from orderitems where prod_id='RGAN01'得到(20007,20008)
之后执行
SELECT cust_id
FROM Orders
WHERE order_num IN (20007,20008);
联结表:
为什么用联结表?
将数据分解为多个表能更有效地存储,更方便地处理,并且可伸缩性更好
例子:看上面两个表
一个存储供应商信息,另一个存储产品信息。Vendors表包含所有供应商信息,每个供应商占一行,具有唯一的标
识。此标识称为主键,可以是供应商 ID 或任何其他唯一值。
Products表只存储产品信息,除了存储供应商 ID (Vendors表的主键)外,它不存储其他有关供应商的信息。Vendors表的主键将Vendors表
与Products表关联,利用供应商 ID 能从Vendors表中找出相应供应商的详细信息。
好处:
1.供应商信息不重复,不会浪费时间和空间;
2.如果供应商信息变动,可以只更新Vendors表中的单个记录,相关表中的数据不用改动;
3.由于数据不重复,数据显然是一致的,使得处理数据和生成报表更简单。
关系数据可以有效地存储,方便地处理,可伸缩性更强
用法:
1.创建联结
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from vendors,products where vendors.vend_id = products.vend_id;
2.内联结
SELECT vend_name, prod_name, prod_price FROM Vendors INNER JOIN Products ON Vendors.vend_id = Products.vend_id;(效果以上面相同)
3.联结多个表(联结的表约多性能越差,所以要减少不必要的表)
创建高级联结
1.给表也可以取别名
2.自联结
mysql> select cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact
-> from customers
-> where cust_name=(select cust_name from customers where cust_contact='JIM Jones')
-> ;
+------------+-----------+------------------+
| cust_id | cust_name | cust_contact |
+------------+-----------+------------------+
| 1000000003 | Fun4All | Jim Jones |
| 1000000004 | Fun4All | Denise L. Stephens |
+------------+-----------+------------------+
2 rows in set
mysql> select c1.cust_id,c1.cust_name,c1.cust_contact
-> from customers as c1,customers as c2
-> where c1.cust_name=c2.cust_name
-> and c2.cust_contact='Jim Jones'
-> ;
+------------+-----------+------------------+
| cust_id | cust_name | cust_contact |
+------------+-----------+------------------+
| 1000000003 | Fun4All | Jim Jones |
| 1000000004 | Fun4All | Denise L. Stephens |
+------------+-----------+------------------+
2 rows in set
自然联结
外联结
使用带聚集函数联结
mysql> SELECT Customers.cust_id, COUNT(Orders.order_num) AS num_ord FROM Customers INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id GROUP BY Customers.cust_id; +------------+---------+ | cust_id | num_ord | +------------+---------+ | 1000000001 | 2 | | 1000000003 | 1 | | 1000000004 | 1 | | 1000000005 | 1 | +------------+---------+ 4 rows in set mysql> SELECT Customers.cust_id, COUNT(Orders.order_num) AS num_ord FROM Customers LEFT OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id GROUP BY Customers.cust_id; +------------+---------+ | cust_id | num_ord | +------------+---------+ | 1000000001 | 2 | | 1000000002 | 0 | | 1000000003 | 1 | | 1000000004 | 1 | | 1000000005 | 1 | +------------+---------+ 5 rows in set mysql> SELECT Customers.cust_id, COUNT(Orders.order_num) AS num_ord FROM Customers right OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id GROUP BY Customers.cust_id; +------------+---------+ | cust_id | num_ord | +------------+---------+ | 1000000001 | 2 | | 1000000003 | 1 | | 1000000004 | 1 | | 1000000005 | 1 | +------------+---------+ 4 rows in set
组合查询
1.使用union
mysql> SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_state IN ('IL','IN','MI') UNION SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_name = 'Fun4All'; +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | cust_name | cust_contact | cust_email | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | Village Toys | John Smith | sales@villagetoys.com | | Fun4All | Jim Jones | jjones@fun4all.com | | The Toy Store | Kim Howard | NULL | | Fun4All | Denise L. Stephens | dstephens@fun4all.com | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ 4 rows in set
union的使用规则
1.UNION必须由两条或两条以上的SELECT语句组成,语句之间用关键字UNION分隔(因此,如果组合四条SELECT语句,将要使用三个UNION关键字)。
2.UNION中的每个查询必须包含相同的列、表达式或聚集函数(不过,各个列不需要以相同的次序列出)。
3.列数据类型必须兼容:类型不必完全相同,但必须是 DBMS 可以隐含转换的类型(例如,不同的数值类型或不同的日期类型)。
包含或取消重复的行,更上面的作比较
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_state IN ('IL','IN','MI') UNION ALL SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_name = 'Fun4All'; +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | cust_name | cust_contact | cust_email | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | Village Toys | John Smith | sales@villagetoys.com | | Fun4All | Jim Jones | jjones@fun4all.com | | The Toy Store | Kim Howard | NULL | | Fun4All | Jim Jones | jjones@fun4all.com | | Fun4All | Denise L. Stephens | dstephens@fun4all.com | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+
对组合的结果排序
SELECT语句的输出用ORDER BY子句排序。在用UNION组合查询时,只能使用一条ORDER BY子句,它必须位于最后一条SELECT语句之后。对于结果
集,不存在用一种方式排序一部分,而又用另一种方式排序另一部分的情况,因此不允许使用多条ORDER BY子句。
mysql> SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_state IN ('IL','IN','MI') UNION SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email FROM Customers WHERE cust_name = 'Fun4All' ORDER BY cust_name, cust_contact; +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | cust_name | cust_contact | cust_email | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ | Fun4All | Denise L. Stephens | dstephens@fun4all.com | | Fun4All | Jim Jones | jjones@fun4all.com | | The Toy Store | Kim Howard | NULL | | Village Toys | John Smith | sales@villagetoys.com | +--------------+------------------+----------------------+ 4 rows in set
INSERT(数据插入)
这个是customers表
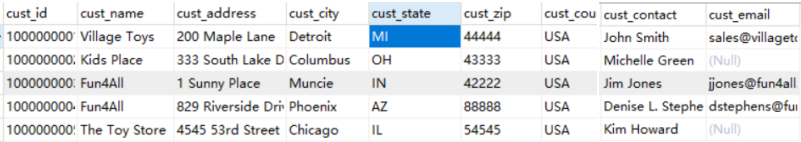
下面进行插入操作
如果这样插入,就一定要按照表头的顺序插入
mysql> INSERT INTO Customers VALUES('199808041011', 'zoulingjin', '123 Any Street', 'HUNAN', 'ZZ', '11111', 'CHINA', NULL, NULL); Query OK, 1 row affected

下面的操作具有稳定性
mysql> INSERT INTO Customers(cust_id, cust_contact, cust_email, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip) VALUES('1000000006', NULL, NULL, 'Toy Land', '123 Any Street', 'New York', 'NY', '11111'); Query OK, 1 row affected

插入检索的数据
INSERT INTO Customers(cust_id, cust_contact, cust_email, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country) SELECT cust_id, cust_contact, cust_email, cust_name, cust_address, cust_city, cust_state, cust_zip, cust_country FROM CustNew;
将一个表复制到另个新表中
mysql> create table zoutable as -> select * from customers; Query OK, 7 rows affected Records: 7 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0

UPDATE AND DELETE
update语法
mysql> UPDATE customers -> set cust_email='zou@qq.com' -> where cust_id='1000000005' -> ; Query OK, 1 row affected Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0

在更新多个列时,是需要一个set命令.每个"列=值"对之间用逗号分割
要删除一个值时,可以设置set 为null
delete语法
mysql> delete from customers -> where cust_id='1000000006' -> ; Query OK, 1 row affected
表的操作
step1:创建表
CREATE TABLE Persons ( Id int(4) NOT NULL, Name varchar(255) NOT NULL, Password varchar(255), PRIMARY KEY (Id) );
![]()
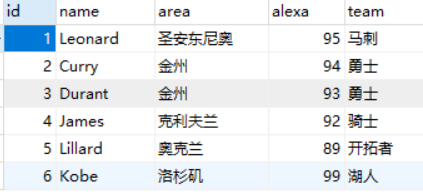
CREATE TABLE `player` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` char(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '站点名称', `area` varchar(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', `alexa` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT 'Alexa 排名', `team` char(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '国家', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `player` VALUES ('1', 'Leonard', '美国圣安东尼奥', '95', '马刺'), ('2', 'Curry', '美国金州', '94', '勇士'), ('3', 'Durant', '美国金州', '93', '勇士'), ('4', 'James', '美国克利夫兰', '92', '骑士'), ('5', 'Lillard', '美国奥克兰', '89', '开拓者');
高级SQL特性