工具类JdbuUtils
用于获取连接已经关闭相关资源
package JDBCutils; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.util.Properties; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * @author ztr * @version 创建时间:2021年3月29日 上午10:20:16 类说明 */ /* * 获取连接 * @return Connection * */ public class JdbcUtils { public JdbcUtils() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception { // 读取配置文件的基本信息 // 获取连接 InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(is); String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String password = properties.getProperty("password"); String url = properties.getProperty("url"); String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass"); // 加载驱动 Class.forName(driverClass); Connection connection = DriverManager .getConnection(url, user, password); return connection; }
/*
* 关闭资源
* */
public static void closeResource(Connection connection,PreparedStatement ps){
try {
if (ps != null)
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (connection != null)
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} /* * 关闭资源 * */ public static void closeResource1(Connection connection,PreparedStatement ps,ResultSet rs){ try { if (ps != null) ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (connection != null) connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (rs != null) rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
配置文件jdbc.properties
user=root
password=xxx//换成所连接数据库的密码
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school//school是所连接的database
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
向数据库中添加数据
@Test public void testinsertinfo() { // 读取配置文件的基本信息 // 获取连接 Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; try { // 读取配置文件的基本信息 // 获取连接 InputStream is = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(is); String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String password = properties.getProperty("password"); String url = properties.getProperty("url"); String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass"); // 加载驱动 Class.forName(driverClass); connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); // 预编译sql语句,返回prepareStatement实例 // ?占位符 String sql = "insert into student(sname,gender,class_id)values(?,?,?)"; prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 填充占位符
//需要注意的是setString()方法的下标是从1开始
prepareStatement.setString(1, "哪炸"); prepareStatement.setString(2, "男"); prepareStatement.setInt(3, 3); // 执行sql prepareStatement.execute(); // 资源的关闭 } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (prepareStatement != null) prepareStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (connection != null) connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
修改数据库数据
@Test public void updatedate() { // 获取连接 Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); // 预编译sql语句,返回preparesStatement String sql = "update student set sname = ? where sid = ? "; prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 填充占位符 prepareStatement.setString(1, "宋江"); prepareStatement.setInt(2, 1); // 执行 prepareStatement.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 资源的关闭 JdbcUtils.closeResource(connection, prepareStatement); } // 资源的关闭 JdbcUtils.closeResource(connection, prepareStatement); }
删除数据库数据
// 删除数据库数据 @Test public void droptest() { // 获取连接 Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); // 预编译sql语句,返回preparesStatement String sql = "delete from student where sid = ? "; prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 填充占位符 prepareStatement.setObject(1, 4); // 执行 prepareStatement.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 资源的关闭 JdbcUtils.closeResource(connection, prepareStatement); } // 资源的关闭 JdbcUtils.closeResource(connection, prepareStatement); }
至此我们发现增删改操大部分都相同这时我们可以写一个对增删改操作都通用的方法,是代码更具有有复合性。
我们可以发现增删改操作其实差异就在sql语句中,我们不但要考虑sql还要考虑sql语句中需要我们去填充多少个占位符,这时我们可以通过传入可变参数来解决这个问题。
增删改的通用操作
// 通用的增删改操作 public void update(String sql, Object... args) { // 获取数据连接 Connection connection = null; // 预编译sql语句返回preparedStatement PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); // 填充占位符 // prepareStatement.setObject的下标从1开始 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { prepareStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } // 执行 prepareStatement.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 资源的关闭 JdbcUtils.closeResource(connection, prepareStatement); } }
@Test
public void testcommonupdate() {
String sql = "delete from student where sid = ?";
update(sql, 1);
}
查询操作和增删改操作不同的是,查询需要返回查询的结果,对所查询到的数据进行处理并且显示出来
@Test public void QueryTest() { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; // 执行返回结果集 ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select * from student where sid = 2"; prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); resultSet = prepareStatement.executeQuery(); // 处理结果集 if (resultSet.next()) {// 判断结果集下一条是否有数据,若有则指针下移,若返回为false则指针不下移 int id = resultSet.getInt(1); String sname = resultSet.getString(2); String gender = resultSet.getString(3); int class_id = resultSet.getInt(4); // //方式一 // System.out.println("id "+id+"sname="+sname+"gender="+gender+"calss_id"+class_id); // //方式二 // Object[] objects = new Object[]{id,sname,gender,class_id}; // //方式三,将数据封装成一个对象 Student student = new Student(id, sname, gender, class_id); System.out.println(student); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源 JdbcUtils.closeResource1(connection, prepareStatement, resultSet); } }
这个方发大家可以很容易的发现它的局限性,只能实现对一个表的固定查询操作,如果我们需要的字段不同时,则此方法就失去了意义。
迭代--我们可以通过反射动态的获取sql语句的查询的列数以及对应的列名。
查询的迭代代码
public static Student quaryStudent(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
prepareStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
resultSet = prepareStatement.executeQuery();
// 获取结果即的元数据metaData
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
// 通过metaData获取结果集中的列数
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
if (resultSet.next()) {
Student student = new Student();
// 处理一行数据中的每一个列
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Object colunmValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
// 获取每个列的列名
// String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i + 1);
/*
* 使用getClumnlabel代替getColumnName
* 因为可能锁对应的类的属性和数据表的列名不一致
* 需要注意的是此时sql需要为列名取别名
* eg:select sid 类对应的属性名 from where sid =?
* getClumnLabel当为列名取别名时其返回的是别名,没有别名时返回的是列名
* */
String columnName = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
// 给student对象指定的columName属性,赋值为columValue,通过反射
Field field = Student.class.getDeclaredField(columnName);
// 考虑其属性为私有属性
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(student, colunmValue);
}
return student;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 进行资源的关闭
JdbcUtils.closeResource1(connection, prepareStatement, resultSet);
}
return null;
}
@Test
public void qurytest2() {
String sql = "select * from student";
Student student = PreparedStamentTest.quaryStudent(sql);
System.out.println(student);
}
可能大家会对元数据有疑惑,元数据就是修饰数据的数据。
接受数据类-Student
package bean; /** * @author ztr * @version 创建时间:2021年3月30日 下午3:22:09 * 类说明 */ public class Student { private int sid; private String sname; private String gender; private int class_id; public Student() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Student(int sid, String sname, String gender, int class_id) { super(); this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.gender = gender; this.class_id = class_id; } public int getSid() { return sid; } public void setSid(int sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public int getClass_id() { return class_id; } public void setClass_id(int class_id) { this.class_id = class_id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [sid=" + sid + ", sname=" + sname + ", gender=" + gender + ", class_id=" + class_id + "]"; } }
图解查询流程
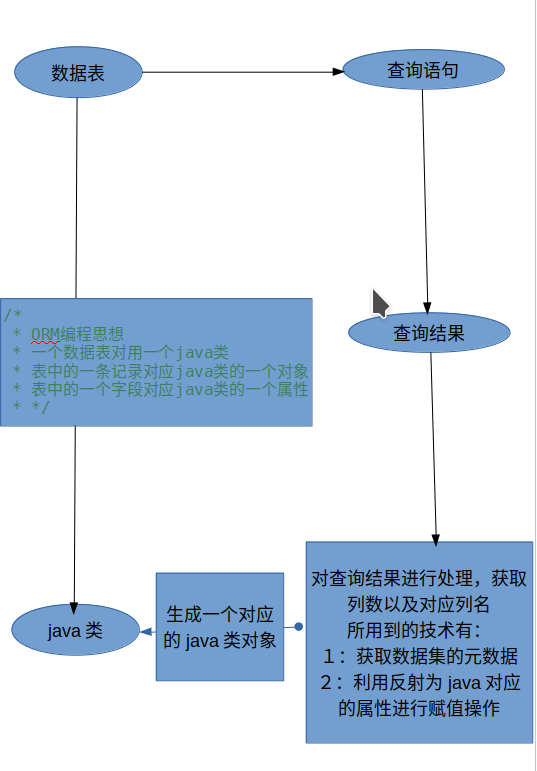
迭代2:实现对全部表格的通用查询
package preparedStament; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData; import org.junit.Test; import JDBCutils.JdbcUtils; import bean.Student; /** * @author ztr * @version 创建时间:2021年3月31日 下午5:10:19 * 类说明:针对不同表的通用查询操作 */ public class QueryCommon { public <T> T GetInstance(Class<T> clazz,String sql,Object ...args){ Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; // 获取结果集 ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { prepareStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } resultSet = prepareStatement.executeQuery(); // 获取元数据 ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 通过metaData获取结果集中的列数 int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); if (resultSet.next()) { T newInstance = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { //获取列值 Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1); // 获取每列的列名 String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i + 1); // 利用反射 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 考虑该属性是否为私有 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(newInstance, columnValue); } return newInstance; } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源 JdbcUtils.closeResource1(connection, prepareStatement, resultSet); } return null; } @Test public void test(){ String sql = "select sid,sname from student where sid=?"; Student getInstance = GetInstance(Student.class, sql, 9); System.out.println(getInstance); } }
以上的查询方法都只适用与查询一条数据
迭代2:查询多条数据
/** * * @param clazz * @param sql * @param args * @return List<T> */ public <T> List<T> getList(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement prepareStatement = null; // 获取结果集 ResultSet resultSet = null; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); prepareStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { prepareStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } resultSet = prepareStatement.executeQuery(); // 获取元数据 ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); // 通过metaData获取结果集中的列数 int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); // 创建集合对象 ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); while (resultSet.next()) { T newInstance = clazz.newInstance(); for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) { // 获取列值 Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1); // 获取每列的列名 String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i + 1); // 利用反射 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); // 考虑该属性是否为私有 field.setAccessible(true); field.set(newInstance, columnValue); } list.add(newInstance); } return list; } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭资源 JdbcUtils.closeResource1(connection, prepareStatement, resultSet); } return null; } @Test public void test1(){ String sql = "select sid,sname from student where sid < ?"; List<Student> list = getList(Student.class, sql, 10); list.forEach(System.out::println); }
运行截图

至此,JDBC对数据库的CURD就全部完成。此博文只是对自己学习得到阶段性总结,若有错误之处,请谅解!