一、内容总结
本次打卡任务主要记录自己不熟的知识点,为后续学习pandas做准备!
1.python基础
比较关键的几个点:
-
条件赋值语句
基本形式为:values = a if 某个条件 else b,例如:
values = 1 if 100>99 else 0 values Out[2]: 1 -
匿名函数
之所以采用匿名函数,是因为用户并不关心函数的名字,只是关心函数的映射关系,使语法更加简洁~
基本形式:lambda x:x的表达式,自变量用x表示,因变量用关于x的表达式表示。例如:
In [6]: [(lambda x:x**2)(i) for i in range(3)] Out[6]: [0, 1, 4] -
map函数
map函数传入一个函数和一个对象,然后返回一个对象。大致过程如下图:
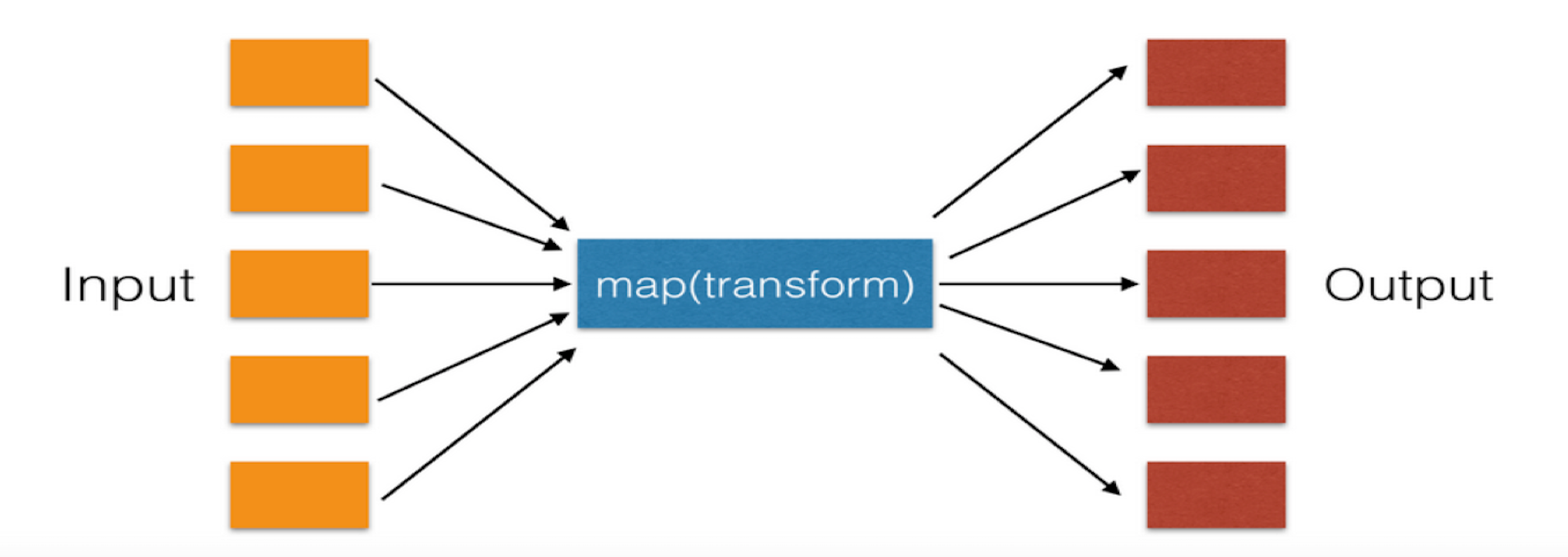
基本形式为:map(func,iterable),对于上面的例子,用map函数可以写作:
list(map(lambda x:x**2,range(3))) Out[11]: [0, 1, 4] -
zip对象
zip主要在循环时使用,可以帮助我们在使用循环时调用多个变量,例如:
L1, L2, L3 = list('abc'), list('def'), list('hij')
for i,j,k in zip(L1,L2,L3):
...: print(i,j,k)
...:
a d h
b e i
c f j
2.numpy基础
-
生成随机整数:randint
用法:np.random.randint(low,high,size),其中不包括high。
示例:
np.random.randint(1,10,5) %生成5个在[1,9]的整数 Out[17]: array([3, 1, 9, 8, 1]) -
常用函数:where
where函数有两种调用形式:
1.np.where(condition,x,y),即满足条件condition输出x,不满足输出y。例如:
x = np.arrat([1,2,3,4,5]) np.where(x>2,x,1) #x大于2时输出x,小于2时输出1 Out[19]: array([1, 1, 3, 4, 5])2.np.where(x),输出x为真时的坐标。拿上面的例子举例:
np.where(x>2) #输出x大于2的坐标 Out[20]: (array([2, 3, 4], dtype=int64),)
二、练习
1.题目:利用列表推导式写矩阵乘法
解答:由最内层的循环开始,逐层使用列表推导式:
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
M1 = np.random.rand(2,3)
M2 = np.random.rand(3,4)
res = [[sum([M1[i][k]* M2[k][j] for k in range(M1.shape[1])]) for j in range(M2.shape[1])] for i in range(M1.shape[0])]
print(((M1@M2-res)<1e-15).all())
2.更新矩阵
解答:先求1/A,然后按行求和,之后将其转换为列向量,最后相乘。
import numpy as np
A = np.arange(1,10).reshape(3,3)
B = A*(np.sum(1/A,1).reshape(-1,1))
3.卡方统计量
解答:先求出B,然后根据公式求就行。
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
A = np.random.randint(10, 20, (8, 5))
B = A.sum(0)*(A.sum(1).reshape(-1,1))/A.sum()
res = ((A-B)**2/B).sum()
4.改进矩阵计算性能
暂时没时间做
5.连续整数的最大长度
思路:先用diff函数计算,若为连续整数,则得到结果为1。题目转换为:连续1的最大长度+1
a = np.diff(x)!=1
然后再在两个端点间插入1,保持位置的不变
b = np.r_[1,a,1]
相当于记录位置
c = np.nozero(b)
得到连续整数的长度,取最大值
res = np.diff(c).max()