最近在学习NIO相关知识,发现需要掌握的知识点非常多,当做笔记记录就下。
在学NIO之前得先去了解IO模型
(1)同步阻塞IO(Blocking IO):即传统的IO模型。
(2)同步非阻塞IO(Non-blocking IO):默认创建的socket都是阻塞的,非阻塞IO要求socket被设置为NONBLOCK。注意这里所说的NIO并非Java的NIO(New IO)库。
(3)多路复用IO(IO Multiplexing):即经典的Reactor设计模式,有时也称为异步阻塞IO,Java中的Selector和Linux中的epoll都是这种模型。
(4)异步IO(Asynchronous IO):即经典的Proactor设计模式,也称为异步非阻塞IO。
这里重点介绍多路复用IO模型(JAVA NIO就是采用此模式)
在多路复用IO模型中,会有一个线程(Java中的Selector)不断去轮询多个socket的状态,只有当socket真正有读写事件时,才真正调用实际的IO读写操作。因为在多路复用IO模型中,只需要使用一个线程就可以管理多个socket,系统不需要建立新的进程或者线程,也不必维护这些线程和进程,并且只有在真正有socket读写事件进行时,才会使用IO资源,所以它大大减少了资源占用。
IO多路复用模型使用了Reactor设计模式实现了这一机制。Reactor模式有三种实现方式:
Reactor单线程

每个客户端发起连接请求都会交给acceptor,acceptor根据事件类型交给线程handler处理,注意acceptor 处理和 handler 处理都在一个线程中处理,所以其中某个 handler 阻塞时, 会导致其他所有的 client 的 handler 都得不到执行, 并且更严重的是, handler 的阻塞也会导致整个服务不能接收新的 client 请求(因为 acceptor 也被阻塞了). 因为有这么多的缺陷, 因此单线程Reactor 模型用的比较少.
Reactor多线程模式
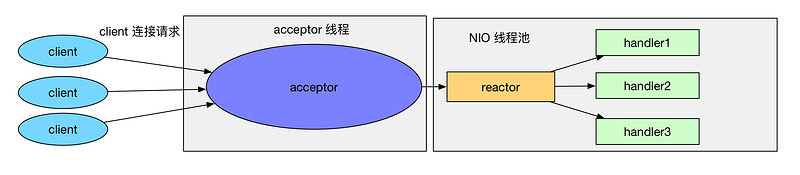
有专门一个线程, 即 Acceptor 线程用于监听客户端的TCP连接请求.
客户端连接的 IO 操作都是由一个特定的 NIO 线程池负责. 每个客户端连接都与一个特定的 NIO 线程绑定, 因此在这个客户端连接中的所有 IO 操作都是在同一个线程中完成的.
客户端连接有很多, 但是 NIO 线程数是比较少的, 因此一个 NIO 线程可以同时绑定到多个客户端连接中.
缺点:如果我们的服务器需要同时处理大量的客户端连接请求或我们需要在客户端连接时, 进行一些权限的检查, 那么单线程的 Acceptor 很有可能就处理不过来, 造成了大量的客户端不能连接到服务器.
Reactor主从模式
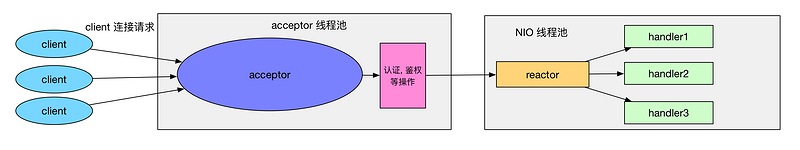
Reactor 的主从多线程模型和 Reactor 多线程模型很类似, 只不过 Reactor 的主从多线程模型的 acceptor 使用了线程池来处理大量的客户端请求.
NIO代码层面是如何实现这三种模式呢?
acceptor :也可以理解为一个Handler,这个Handler只负责创建具体处理IO请求的Handler(负责所有client的连接请求),如果Reactor广播时SelectionKey创建一个Handler负责绑定相应的SocketChannel到Selector中。下次再次有IO事件时会调用对应的Handler去处理
/** * 单独一个线程去处理链接请求 * Created by zhangwentao on 2018/4/12. */ public class Acceptor implements Runnable{ Reactor reactor; public Acceptor(Reactor reactor){ this.reactor=reactor; } public void run() { try { //监听TCP链接请求 SocketChannel socketChannel=reactor.serverSocketChannel.accept(); if(socketChannel!=null)//调用Handler来处理channel new SocketReadHandler(reactor.selector, socketChannel); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Reactor 的作用 :给ServerSocketChannel设置一个Acceptor,接收请求,给每一个一个SocketChannel(代表一个Client)关联一个Handler , 要注意其实Acceptor也是一个Handler(只是与它关联的channel是ServerSocketChannel而不是SocketChannel)
代码如下
/** * Reactor模式有助于理解netty * Created by zhangwentao on 2018/4/12. */ public class Reactor implements Runnable { public final Selector selector; public final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; public Reactor(int port) throws IOException { //用于监控fds selector=Selector.open(); //socket服务器的chanel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open(); InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress=new InetSocketAddress(InetAddress.getLocalHost(),port); // serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress); //不设置阻塞队列 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //向selector注册该channel 返回selectionKey SelectionKey selectionKey=serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //利用selectionKey的attache功能绑定Acceptor 如果有事情,触发Acceptor selectionKey.attach(new Acceptor(this)); } public void run() { try { while(!Thread.interrupted()){ selector.select();//selector 阻塞 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys= selector.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selectionKeys.iterator(); //Selector如果发现channel有OP_ACCEPT或READ事件发生,下列遍历就会进行。 while(it.hasNext()){ //来一个事件 第一次触发一个accepter线程 //以后触发SocketReadHandler SelectionKey selectionKey=it.next(); dispatch(selectionKey); selectionKeys.clear(); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 运行Acceptor或SocketReadHandler * @param key */ void dispatch(SelectionKey key) { Runnable r = (Runnable)(key.attachment()); if (r != null){ r.run(); } } }
hanler线程是具体的事件处理者,例如ReadHandler、SendHandler,ReadHandler负责读取缓存中的数据,然后再调用一个工作处理线程去处理读取到的数据。具体为一个SocketChannel,Acceptor初始化该Handler时会将SocketChannel注册到Reactor的Selector中,同时将SelectionKey绑定该Handler,这样下次就会调用本Handler。代码如下
** * Created by zhangwentao on 2018/4/12. */ public class SocketReadHandler implements Runnable { private SocketChannel socketChannel; public SocketReadHandler(Selector selector, SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException{ this.socketChannel=socketChannel; socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); SelectionKey selectionKey=socketChannel.register(selector, 0); //将SelectionKey绑定为本Handler 下一步有事件触发时,将调用本类的run方法。 //参看dispatch(SelectionKey key) selectionKey.attach(this); //同时将SelectionKey标记为可读,以便读取。 selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ); selector.wakeup(); } /** * 处理读取数据 */ public void run() { ByteBuffer inputBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); inputBuffer.clear(); try { socketChannel.read(inputBuffer); //激活线程池 处理这些request //requestHandle(new Request(socket,btt)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
上述就是用原生的NIO实现reactor模式,我们发现还是有些繁琐的(多线程都没有写进去)
用netty可以很方便的实现三种方式,单线程模式:
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup(1); b.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) .remoteAddress(serverAddress);
我们观察EventLoopGroup的构造方法 EventLoopGroup的参数表示线程池大小(1表示只有一个线程),Bootstrap.group
多线程模式
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); EventLoopGroup acceptorLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup handlerLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup(); b.group(eventLoopGroup,handlerLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) .remoteAddress(serverAddress);
EventLoopGroup acceptorLoopGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup(1);说明acceptor还是单线程的。EventLoopGroup handlerLoopGroup=new EventLoopGrooup();设置线程数量是多核数量的2倍