1.Sigmoid Gradient

function g = sigmoidGradient(z) %SIGMOIDGRADIENT returns the gradient of the sigmoid function %evaluated at z % g = SIGMOIDGRADIENT(z) computes the gradient of the sigmoid function % evaluated at z. This should work regardless if z is a matrix or a % vector. In particular, if z is a vector or matrix, you should return % the gradient for each element. g = zeros(size(z)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the gradient of the sigmoid function evaluated at % each value of z (z can be a matrix, vector or scalar). g=sigmoid(z).*(1-sigmoid(z)); % ============================================================= end
2.nnCostFunction
这是一道综合问题;
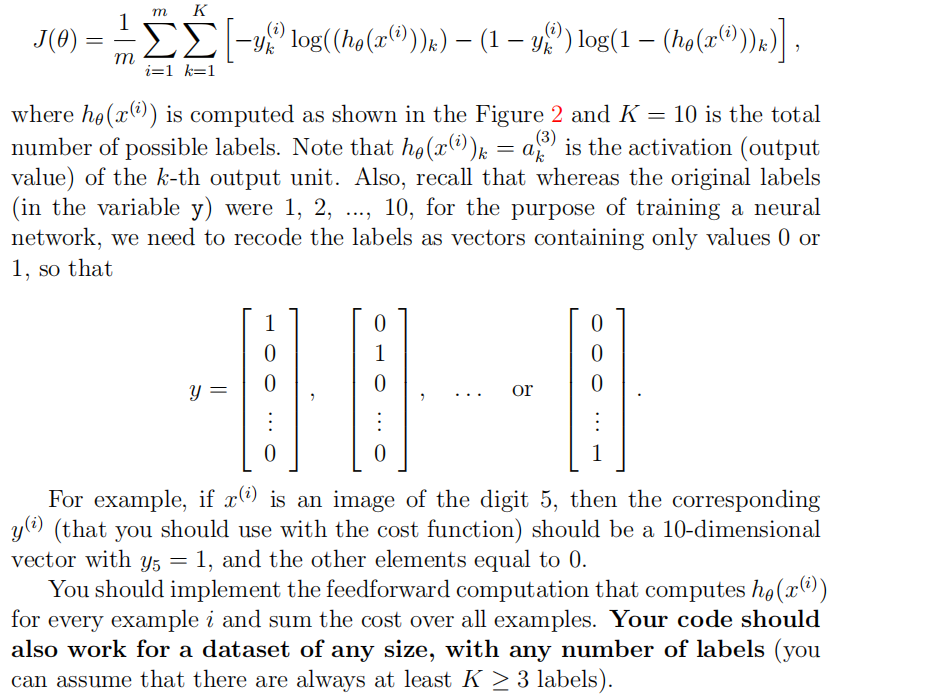
Ⅰ:计算代价函数J(前向传播)
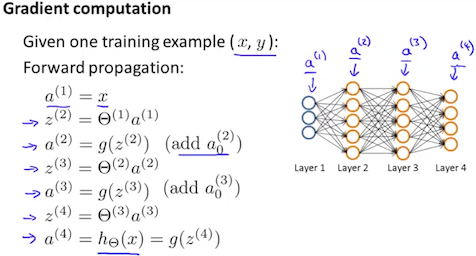
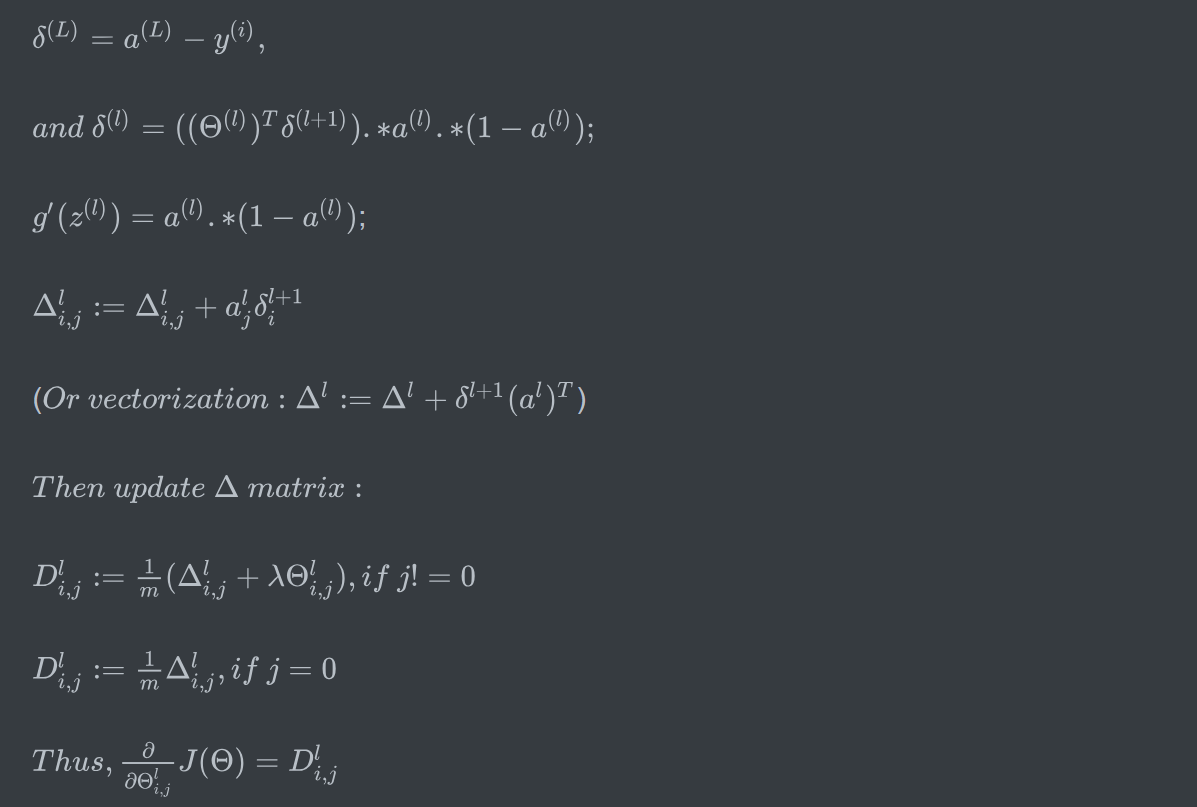
Ⅱ:BackPropagation
Ⅲ:正则化;


function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda)
%NNCOSTFUNCTION Implements the neural network cost function for a two layer
%neural network which performs classification
% [J grad] = NNCOSTFUNCTON(nn_params, hidden_layer_size, num_labels, ...
% X, y, lambda) computes the cost and gradient of the neural network. The
% parameters for the neural network are "unrolled" into the vector
% nn_params and need to be converted back into the weight matrices.
%
% The returned parameter grad should be a "unrolled" vector of the
% partial derivatives of the neural network.
%
% Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
% for our 2 layer neural network
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
% Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the code by working through the
% following parts.
%
% Part 1: Feedforward the neural network and return the cost in the
% variable J. After implementing Part 1, you can verify that your
% cost function computation is correct by verifying the cost
% computed in ex4.m
%
% Part 2: Implement the backpropagation algorithm to compute the gradients
% Theta1_grad and Theta2_grad. You should return the partial derivatives of
% the cost function with respect to Theta1 and Theta2 in Theta1_grad and
% Theta2_grad, respectively. After implementing Part 2, you can check
% that your implementation is correct by running checkNNGradients
%
% Note: The vector y passed into the function is a vector of labels
% containing values from 1..K. You need to map this vector into a
% binary vector of 1's and 0's to be used with the neural network
% cost function.
%
% Hint: We recommend implementing backpropagation using a for-loop
% over the training examples if you are implementing it for the
% first time.
%
% Part 3: Implement regularization with the cost function and gradients.
%
% Hint: You can implement this around the code for
% backpropagation. That is, you can compute the gradients for
% the regularization separately and then add them to Theta1_grad
% and Theta2_grad from Part 2.
%
X=[ones(m,1) X];
a1=Theta1*X';
z1=[ones(m,1),sigmoid(a1)'];
a2=Theta2*z1';
h=sigmoid(a2);
yy=zeros(m,num_labels);
for i=1:m,
yy(i,y(i))=1;
endfor
J=1/m*sum( sum( (-yy).*log(h')-(1-yy).*log(1-h') ) );
J=J+lambda/(2*m)*( sum(sum(Theta1(:,2:end).^2))+sum(sum(Theta2(:,2:end).^2)));
for i=1:m,
a1=X(i,:)';
z2=Theta1*a1;
a2=[1;sigmoid(z2)];
z3=Theta2*a2;
a3=sigmoid(z3);
tmpy=yy(i,:);
dlt3=a3-tmpy';
dlt2=(Theta2(:,2:end)'*dlt3.*sigmoidGradient(z2));
Theta1_grad=Theta1_grad+dlt2*a1';
Theta2_grad=Theta2_grad+dlt3*a2';
endfor
Theta1_grad=Theta1_grad./m;
Theta2_grad=Theta2_grad./m;
Theta1(:,1)=0;
Theta2(:,1)=0;
Theta1_grad=Theta1_grad+lambda/m*Theta1;
Theta2_grad=Theta2_grad+lambda/m*Theta2;
% -------------------------------------------------------------
% =========================================================================
% Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];
end