Kvm基本命令
一、查询命令
1.列出所有的虚拟机
virsh list –all
2.显示虚拟机信息
virsh dominfo kvm-1
3.显示虚拟机内存和cpu的使用情况
yum install virt-top -y
virt-top
4.显示虚拟机分区信息
virt-df kvm-1
5.关闭虚拟机(shutodwn)
virsh shutdown kvm-1
6.启动虚拟机
virsh start kvm-1
7.设置虚拟机(kvm-1)跟随系统自启
virsh autostart kvm-1
8. 关闭虚拟及自启
virsh autostart --disable kvm-1
9.删除虚拟机
(当在安装虚拟机中系统过程中,没有安装成功,必须是删除了才能重新安装,不然会一直调用系统、驱动、空磁盘文件)
virsh undefine kvm-1
9.1. 查看列表定位要删除的虚拟机
virsh list –all
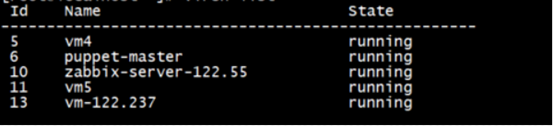
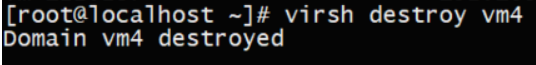
9.2.强制停止虚拟机
virsh destroy vm4
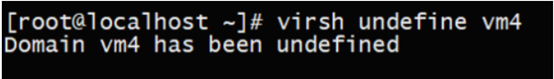
9.3. 删除虚拟机
virsh undefined vm4
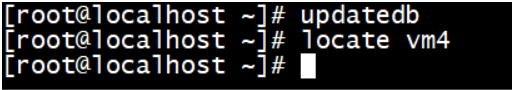
9.4. 更新当前文件,并查找包含虚拟机vm4的所有内容
updatedb

9.5. 删除和vm4一切相关的内容

9.6. 更新本机文件后继续查找,确保vm4相关文件彻底删除
10.通过控制窗口登录虚拟机
virsh console kvm-1
二、给虚拟机添加硬盘
1.添加硬盘(lvm卷)或者USB到虚拟机上
virsh attach-disk kvm-1 /dev/sdb vbd --driver qemu --mode shareable
使用完成之后可以卸载usb
virsh detach-disk kvm vdb
2. 添加lvm卷,并挂载
[root@sh-kvm-1 ~]# lvcreate -n kvm-1-data -L 50G vg_shkvm1
[root@sh-kvm-1 ~]# virsh attach-disk kvm-1 /dev/vg_shkvm1/kvm-1-data vdb --driver qemu --mode shareable
Disk attached successfully
# 登录到kvm-1上查看lvm是否已经被挂载
[root@sh-kvm-1 ~]# virsh console kvm-1 # 输入kvm-1的用户和密码
[root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# fdisk -l # 查看硬盘挂载情况
Disk /dev/vda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 41610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 1008 * 512 = 516096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00058197
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vda1 * 3 1018 512000 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/vda2 1018 41611 20458496 8e Linux LVM
Partition 2 does not end on cylinder boundary.
Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root: 18.8 GB, 18798870528 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2285 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 261 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/vdb: 53.7 GB, 53687091200 bytes # 新添加的硬盘
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 104025 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 1008 * 512 = 516096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
3. 格式化新添加的vdb,并添加到lvm组中
# 对新添加的硬盘分区
[root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xf04b6807.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): m # 查看帮助
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n #添加一个分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p #选择添加一个扩展分区
Partition number (1-4):
Value out of range.
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-104025, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-104025, default 104025):
Using default value 104025
Command (m for help): t #改变分区的格式
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e #改成lvm
Changed system type of partition 1 to 8e (Linux LVM)
Command (m for help): w # 保存更改
root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1 # 格式化分区
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
3276800 inodes, 13107142 blocks
655357 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=4294967296
400 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 28 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# pvc reate /dev/vdb1 # 创建pv
vdb vdb1
[root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# vgextend VolGroup /dev/vdb # 扩展lvm vg
vdb vdb1
[root@sh-kvm-1-1 ~]# vgs
VG #PV #LV #SN Attr VSize VFree
VolGroup 2 2 0 wz--n- 69.50g 50.00g
# 从上面能看出,新添加的 已经加到lvm组中
三、改变虚拟机的参数
1.通过命令行更改创建之后虚拟机的内存,cpu等信息
1.1更改内存
1. 查看虚拟机当前内存
[root@sh-kvm-1 ~]# virsh dominfo kvm-1 | grep memory
Max memory: 4194304 KiB
Used memory: 4194304 KiB
# 2、动态设置内存为512MB,内存减少
virsh setmem kvm-1 524288
# 注意单位必须是KB
# 3、查看内存变化
# virsh dominfo kvm-1 | grep memory
Max memory: 14194304 KiB
Used memory: 524288 kiB
# 4、内存增加
virsh shutdown kvm-1
virsh edit kvm-1 # 直接更改memory
virsh create /etc/libvirt/demu/kvm-1/xml
# 之后操作1,2,3步骤增加内存
2. 更改CPU
需要修改配置文件,因此需要停止虚拟机
virsh shutdown kvm-1
virsh edit kvm-1
# <vcpu>2</vcpu> # 4 > 2
virsh create /etc/libvirt/demu/kvm-1/xml
3. 硬盘扩容
1. Create a 10-GB non-sparse file:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/vm-images/vm1-add.img bs=1M count=10240
2. Shutdown the VM:
# virsh shutdown vm1
3. Add an extra entry for ‘disk’ in the VM's XML file in /etc/libvirt/qemu. You can look copy & paste
the entry for your mail storage device and just change the target and address tags. For example:
# virsh edit vm1
<disk type='file' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw' cache='none' io='threads'/>
<source file='/vm-images/vm1.img'/>
<target dev='vda' bus='virtio'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x04'
function='0x0'/>
</disk>
Add:
<disk type='file' device='disk'>
<driver name='qemu' type='raw' cache='none' io='threads'/>
<source file='/vm-images/vm1-add.img'/>
<target dev='vdb' bus='virtio'/>
<address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x06'
function='0x0'/>
</disk>
# 这里建议使用上面的添加硬盘的方式添加