实验一 线性表的应用,实现和分析
0.目录
- [线性结构-1 Java中的线性表的测试](#1) - [线性结构-2 Java中的线性表的应用](#2) - [线性结构-3 顺序表的实现](#3) - [线性结构-4 链表的实现](#4) - [线性结构-5 源码分析](#5)线性结构-1 线性表的测试
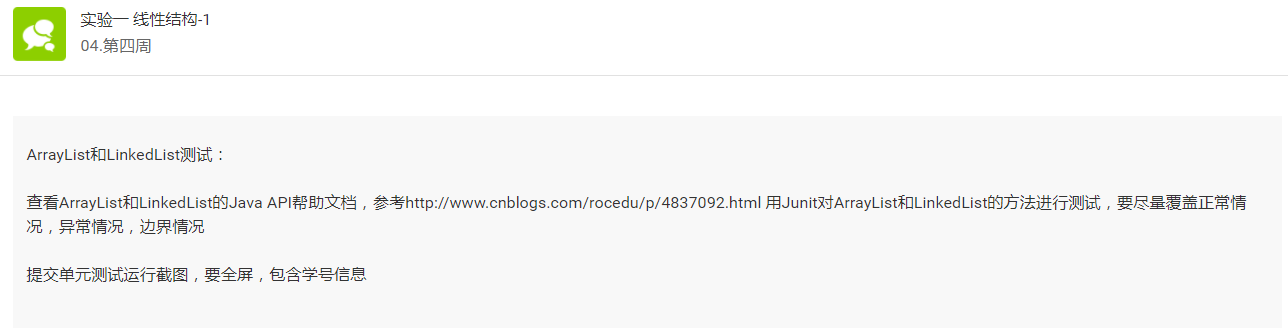
实验过程
- 首先,我先认真学习帮助文档中ArrayList和LinkedList部分,重点关注其方法的使用。
- 其次,我复习了在IDEA中用JUnit测试的方法。
- 写测试代码进行测试。
实验结果

线性结构-2 线性表的应用
实验过程
- 与同学们讨论,得到了两种解决方案。第一种,比较两个List比较第一个元素,并将俩元素依次add进新的List中,之后再删去各自的第一项,再比较下一项...依次类推。第二种,直接将两个List合并到一起,再进行排序。
- 选择第一种,写产品代码
- 写测试代码
实验结果

线性结构-3 顺序表的实现
实验过程
- 我先研究ArrayList的源码,看看大佬如何通过数组实现顺序表
- 写伪代码、产品代码
- 使用Junit进行测试
代码实现
// 1. 定义线性表的默认长度空间(DEFAULT_SIZE)、实际分配数组长度(capacity)、当前元素个数及线性表的长度(size)
private int DEFAULT_SIZE = 16;
private int capacity;
private int size = 0;
private Object[] element;// 数据元素封装一个数组
// 2. 初始化
// 无参构造线性表
public MyArrayList() {
this.element = new Object[DEFAULT_SIZE];// 初始化列表的空间
this.capacity = DEFAULT_SIZE;// 实际分配数组长度
}
// 初始化含有一个元素的线性表
public MyArrayList(T elem) {
this();// 调用空参数构造函数
this.element[size++] = elem;
}
// 指定长度并初始化一个元素创建线性表
public MyArrayList(T elem, int size) {
this.capacity = 1;// 初始化
// 扩充数组空间使得capicity的size且是2的n次方
while (this.capacity < size) {
this.capacity <<= 1;
}
this.element = new Object[this.capacity];
this.element[size++] = elem;
}
// 3. 求长度
public int length() {
return this.size;
}
// 获取线性表的索引为i处的元素(i介于0~size-1)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getelem(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i > size - 1) {// 检测是否越界
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("线性表的索引越界:" + i);
}
return (T) this.element[i];
}
// 4. 取元素
// 查找元素在线性表中的索引
public int findindex(T elem) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (this.element[i].equals(elem))
return i;// 找到返回对应的索引
}
return -1;// 若没有找到返回-1
}
// 5. 插入
// 插入一个元素到线性表的第i个索引处
public void insert(T elem, int i) {
if (i < 0 || i > size) {// 插入位置非法
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("插入元素线性表索引位置越界:" + i);
}
// 是否需要扩充容量
this.ensureCapicty(size + 1);
// 插入元素第i个位置空出来从i位置开始所有元素后移一个位置
System.arraycopy(this.element, i, this.element, i + 1, size - i);
// 将元素插入到指定位置
this.element[i] = elem;
// 当前容量增加1
this.size++;
}
// 在线性表末尾插入元素
public void add(T elem) {
this.insert(elem, this.size);
}
// 6. 删除
// 删除线性表中第i个元素并返回该处的值
public T delete(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i > size - 1) {// 检测删除位置对不对
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("删除位置索引越界:" + i);
}
// 获得i处的元素值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T del = (T) this.element[i];
// 删除元素后从i+1位置开始元素要前移
int moved = this.size - i - 1;// 需要移动元素的个数
if (moved > 0) {
System.arraycopy(this.element, i + 1, this.element, i, moved);
}
// 清空最后一个元素
this.element[--size] = null;
return del;
}
// 移除线性表中最后一个元素
public T remove() {
return this.delete(size - 1);
}
实验结果

线性结构-4 链表的实现
实验过程
- 研究LinkedList的源码,看看大佬如何通过链表实现顺序表
- 写伪代码、产品代码
- 使用Junit进行测试
代码实现
private Node<E> header = null;// 头结点
int size = 0;// 表示数组大小的指标
public MyLinkedList() {
this.header = new Node<E>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
if (size == 0) {
header.e = e;
} else {
// 根据需要添加的内容,封装为结点
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
// 得到当前最后一个结点
Node<E> last = getNode(size-1);
// 在最后一个结点后加上新结点
last.addNext(newNode);
}
size++;// 当前大小自增加1
return true;
}
public boolean insert(int index, E e) {
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
// 得到第N个结点
Node<E> cNode = getNode(index);
newNode.next = cNode.next;
cNode.next = newNode;
size++;
return true;
}
private Node<E> getNode(int index) {
// 先判断索引正确性
if (index > size || index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引值有错:" + index);
}
Node<E> tem = new Node<E>();
tem = header;
int count = 0;
while (count != index) {
tem = tem.next;
count++;
}
return tem;
}
public E get(int index) {
// 先判断索引正确性
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引值有错:" + index);
}
Node<E> tem = new Node<E>();
tem = header;
int count = 0;
while (count != index) {
tem = tem.next;
count++;
}
E e = tem.e;
return e;
}
public E get(int index) {
// 先判断索引正确性
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引值有错:" + index);
}
Node<E> tem = new Node<E>();
tem = header;
int count = 0;
while (count != index) {
tem = tem.next;
count++;
}
E e = tem.e;
return e;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean set(int index, E e) {
// 先判断索引正确性
if (index > size || index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引值有错:" + index);
}
Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
// 得到第x个结点
Node<E> cNode = getNode(index);
cNode.e = e;
return true;
}
class Node<e> {
private E e;// 结点中存放的数据
Node<E> next;// 用来指向该结点的下一个结点
Node() { }
Node(E e) {
this.e = e;
}
// 在此结点后加一个结点
void addNext(Node<E> node) {
next = node;
}
}
线性结构-5 源码分析
学习之前的思考和疑问:
之前在学习Java集合类的时候已经了解到ArrayList类和LinkedList类均是List的实现类,是线性、有序的存储容器,可通过索引访问元素的类。那么,在Java源码中,ArrayList类和LinkedList类究竟是怎么实现List的呢?ArrayList类和LinkedList类之间又有什么区别呢?以下是问题解答:
ArrayList
- 定义
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
从`ArrayList<E>`可以看出它是支持泛型的,它继承自AbstractList,实现了List、RandomAccess、Cloneable、java.io.Serializable接口。
AbstractList提供了List接口的默认实现(个别方法为抽象方法)。List接口定义了列表必须实现的方法。RandomAccess是一个标记接口,接口内没有定义任何内容。
实现了Cloneable接口的类,可以调用Object.clone方法返回该对象的浅拷贝。通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化。序列化接口没有方法或字段,仅用于标识可序列化的语义。
2. 属性
private transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
关于transient:
java语言的关键字,变量修饰符,如果用transient声明一个实例变量,当对象存储时,它的值不需要维持。换句话来说就是,用transient关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程。
LinkedList
- 定义
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
LinkedList继承自AbstractSequenceList、实现了List及Deque接口。其实AbstractSequenceList已经实现了List接口,这里标注出List只是更加清晰而已。AbstractSequenceList提供了List接口骨干性的实现以减少实现List接口的复杂度。Deque接口定义了双端队列的操作。
- 属性
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
private transient int size = 0;
size肯定就是LinkedList对象里面存储的元素个数了。LinkedList既然是基于链表实现的,那么这个header肯定就是链表的头结点了,Entry就是节点对象了。一下是Entry类的代码。
ArrayList和LinkedList
因为ArrayList底层由数组实现,在0号位置插入时将移动list的所有元素,在末尾插入元素时不需要移动。LinkedList是双向链表,在任意位置插入元素所需时间均相同。所以在List中有较多插入和删除操作的情况下应使用LinkedList来提高效率,而有较多索引查询的时候使用ArrayList(使用增强型的for循环或Iterator遍历LinkedList效率将提高很多)。