(1) 在树莓派中安装opencv库
参考教程:关于opencv的编译安装,可以参考Adrian Rosebrock的Raspbian Stretch: Install OpenCV 3 + Python on your Raspberry Pi。
步骤一:拓展SD卡内存
sudo raspi-config #打开树莓派配置
#选择Advanced Options——>Expand fileSystem
sudo reboot #重启
df -h #查看内存使用情况,如果内存占用过多建议卸载LibreOffice和 Wolfram engine来释放空间
#卸载
sudo apt-get purge wolfram-engine
sudo apt-get purge libreoffice*
sudo apt-get clean
sudo apt-get autoremove
步骤二:安装依赖库(建议先换国内源,否则你就痛苦吧)
更新和升级软件包
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
安装一些开发者工具
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake pkg-config
安装image I/O所需的包
sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev libtiff5-dev libjasper-dev libpng12-dev
安装video I/O所需的包
sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libv4l-dev
sudo apt-get install libxvidcore-dev libx264-dev
安装编译highgui所需包
sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev libgtk-3-dev
安装一些扩展包
sudo apt-get install libatlas-base-dev gfortran
安装python
sudo apt-get install python2.7-dev python3-dev
安装pip
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
sudo python get-pip.py
sudo python3 get-pip.py
python2安装opencv
python2 -m pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
python3安装opencv
sudo pip3 install opencv_python-3.4.3.18-cp37-cp37m-linux_armv7l.whl #这里是把所需的包事先下载到本地,进行本地安装。
sudo apt install libqt4-test #安装缺少的依赖包
sudo apt install libqtgui4
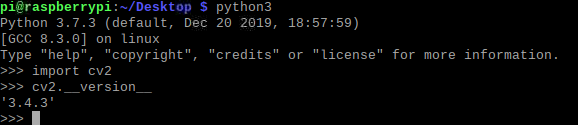
测试是否编译成功
python2
import cv2
cv2.__version__

python3
import cv2
cv2.__version__
(2) 使用opencv和python控制树莓派的摄像头
参考教程:还是可以参考Adrian Rosebrock的Accessing the Raspberry Pi Camera with OpenCV and Python
跑通教程的示例代码(有可能要调整里面的参数)
安装picamare
pip install "picamera[array]"

很好,我们已经有了picamera了,不需要安装了。
拍照这部分上次作业有做过,这里就不再重复了。
拍视频示例代码(test_video.py)
# import the necessary packages
from picamera.array import PiRGBArray
from picamera import PiCamera
import time
import cv2
# initialize the camera and grab a reference to the raw camera capture
camera = PiCamera()
camera.resolution = (640, 480)
camera.framerate = 32
rawCapture = PiRGBArray(camera, size=(640, 480))
# allow the camera to warmup
time.sleep(0.1)
# capture frames from the camera
for frame in camera.capture_continuous(rawCapture, format="bgr", use_video_port=True):
# grab the raw NumPy array representing the image, then initialize the timestamp
# and occupied/unoccupied text
image = frame.array
# show the frame
cv2.imshow("Frame", image)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
# clear the stream in preparation for the next frame
rawCapture.truncate(0)
# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loop
if key == ord("q"):
break
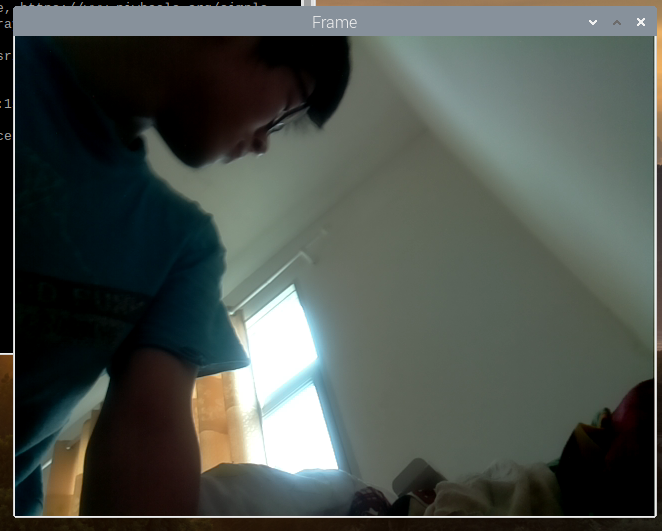
视频截图
(3) 利用树莓派的摄像头实现人脸识别
人脸识别有开源的python库face_recognition,这当中有很多示例代码
要求:跑通face_recognition的示例代码facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py以及facerec_from_webcam_faster.py
参考教程:树莓派上使用python实现人脸识别
安装dlib、facerecognition
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package --default-timeout=100 dlib
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple some-package --default-timeout=100 face_recognition
示例一代码
# coding = utf-8
import face_recognition
import picamera
import numpy as np
# 创建视频对象
camera = picamera.PiCamera()
# 设置分辨率
camera.resolution = (320, 240)
# 初始化一个空的ndarray类型的数据
rgb_frame = np.empty((240, 320, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 加载当前目录下名为'test.jpg'的照片,照片里需要有且仅有一张脸,这张脸将作为认识的脸
print('loading...')
image = face_recognition.load_image_file('test.jpg')
face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(image)[0]
while True:
print('Capturing image.')
# 用Picamera读取一帧照片
camera.capture(rgb_frame, format='rgb')
# 获取这一帧图片里所有人脸的位置和特征值
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_frame)
print('Found {} faces in image.'.format(len(face_locations)))
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_frame, face_locations)
# 对获取的每张脸进行循环,判断是否是认识的脸
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# 判断当前的脸是否与认识的脸匹配
match = face_recognition.compare_faces([face_encoding], face_encoding)
name = '<Unknown Person>'
if match[0]:
name = 'test' # test为'test.jpg'里面人脸的名字
print('I see someone named {}!'.format(name))
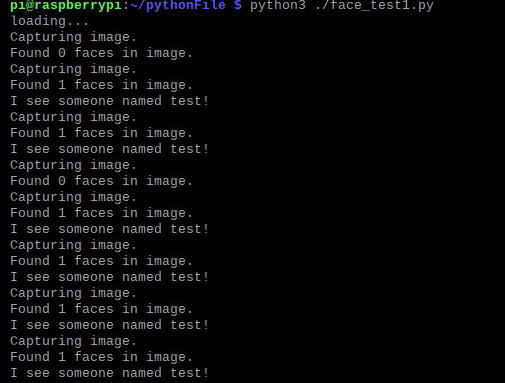
在代码目录下添加一张test.jpg
结果如下
示例二代码
import face_recognition
import cv2
import numpy as np
# This is a demo of running face recognition on live video from your webcam. It's a little more complicated than the
# other example, but it includes some basic performance tweaks to make things run a lot faster:
# 1. Process each video frame at 1/4 resolution (though still display it at full resolution)
# 2. Only detect faces in every other frame of video.
# PLEASE NOTE: This example requires OpenCV (the `cv2` library) to be installed only to read from your webcam.
# OpenCV is *not* required to use the face_recognition library. It's only required if you want to run this
# specific demo. If you have trouble installing it, try any of the other demos that don't require it instead.
# Get a reference to webcam #0 (the default one)
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# Load a sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
obama_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("obama.jpg")
obama_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(obama_image)[0]
# Load a second sample picture and learn how to recognize it.
biden_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("biden.jpg")
biden_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(biden_image)[0]
# Create arrays of known face encodings and their names
known_face_encodings = [
obama_face_encoding,
biden_face_encoding
]
known_face_names = [
"Barack Obama",
"Joe Biden"
]
# Initialize some variables
face_locations = []
face_encodings = []
face_names = []
process_this_frame = True
while True:
# Grab a single frame of video
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# Resize frame of video to 1/4 size for faster face recognition processing
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Convert the image from BGR color (which OpenCV uses) to RGB color (which face_recognition uses)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1]
# Only process every other frame of video to save time
if process_this_frame:
# Find all the faces and face encodings in the current frame of video
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
# See if the face is a match for the known face(s)
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
name = "Unknown"
# # If a match was found in known_face_encodings, just use the first one.
# if True in matches:
# first_match_index = matches.index(True)
# name = known_face_names[first_match_index]
# Or instead, use the known face with the smallest distance to the new face
face_distances = face_recognition.face_distance(known_face_encodings, face_encoding)
best_match_index = np.argmin(face_distances)
if matches[best_match_index]:
name = known_face_names[best_match_index]
face_names.append(name)
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame
# Display the results
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# Scale back up face locations since the frame we detected in was scaled to 1/4 size
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
# Draw a box around the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Draw a label with a name below the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, bottom - 35), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), cv2.FILLED)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX
cv2.putText(frame, name, (left + 6, bottom - 6), font, 1.0, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# Display the resulting image
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
# Hit 'q' on the keyboard to quit!
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release handle to the webcam
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
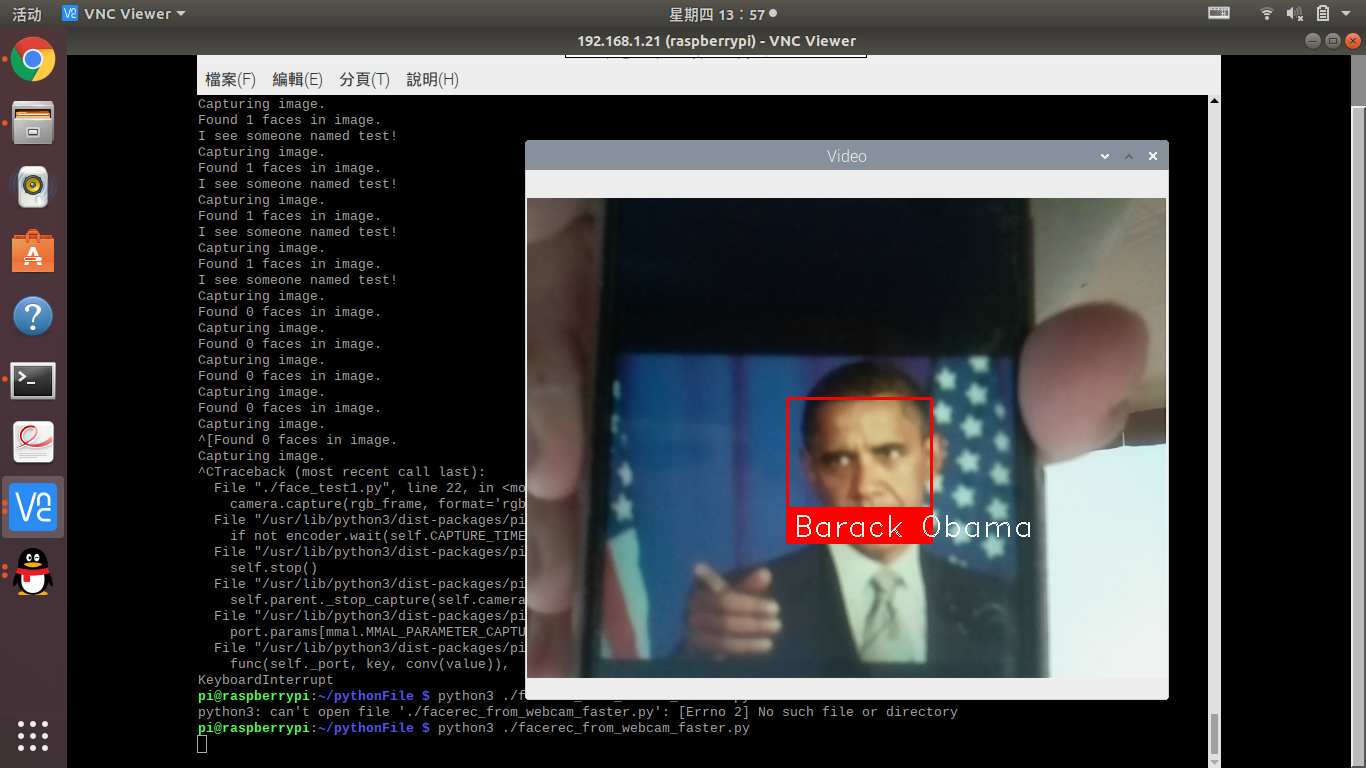
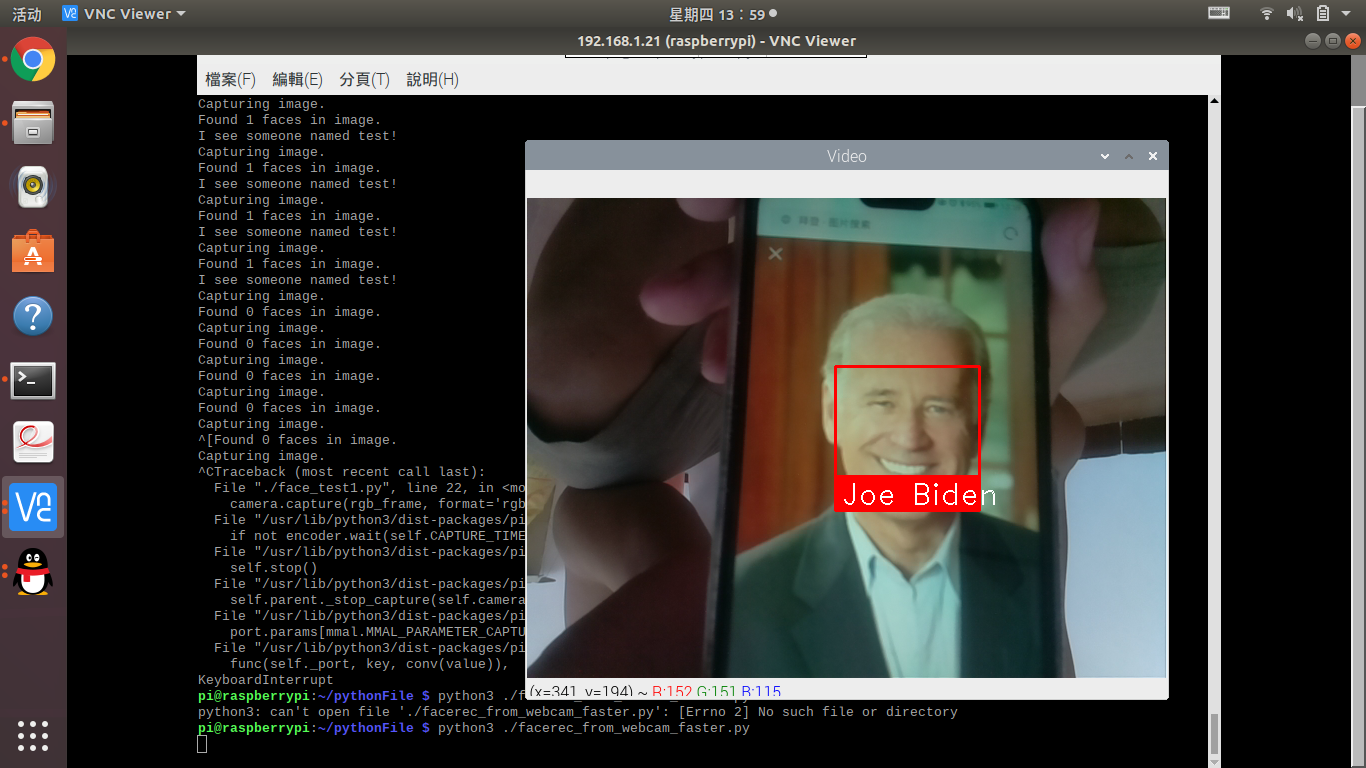
在工作目录下存放Obama和biden的图片

结果如下
(4) 结合微服务的进阶任务
使用微服务,部署opencv的docker容器(要能够支持arm),并在opencv的docker容器中跑通(3)的示例代码facerec_on_raspberry_pi.py
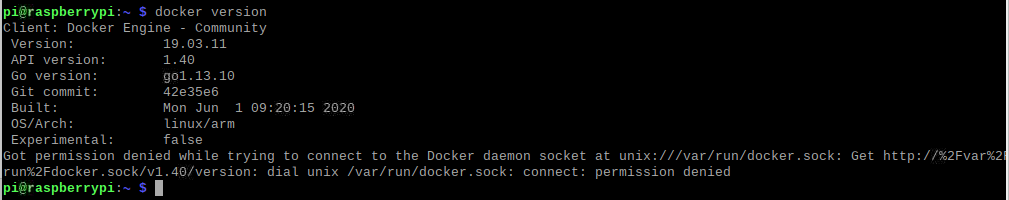
首先,先在树莓派上安装docker
sudo curl -sSL https://get.docker.com | sh
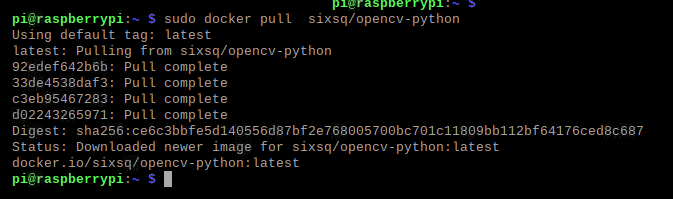
然后,拉取opencv镜像
sudo docker pull sixsq/opencv-python
建一个工作目录,编写dockerfile,将所需文件放进来
dockerfile
FROM sixsq/opencv-python
MAINTAINER gg
WORKDIR /usr/local/opencv
COPY ./face_recognition-1.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl /usr/local/opencv
COPY ./face_recognition_models-0.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl /usr/local/opencv
RUN sudo pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --upgrade pip &&
pip install --upgrade -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --default-timeout=500 "picamera[array]" dlib &&
python3 -m pip install wheel face_recognition_models-0.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl &&
python3 -m pip install wheel face_recognition-1.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
EXPOSE 80

构建镜像
sudo docker build -t myopencv .
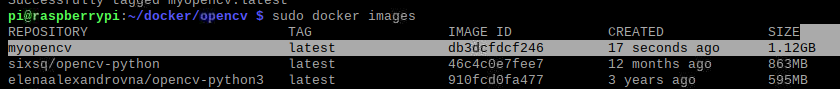
用该镜像创建容器
#创建并运行容器
docker run -it --rm --name myopencv -v /home/pi/docker/opencv:/usr/local/opencv --device=/dev/vchiq --device=/dev/video0 myopencv /bin/bash
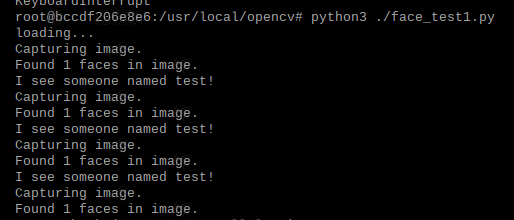
#在容器内部运行人脸识别代码
python3 ./face_test1.py
结果:
选做:在opencv的docker容器中跑通步骤(3)的示例代码facerec_from_webcam_faster.py
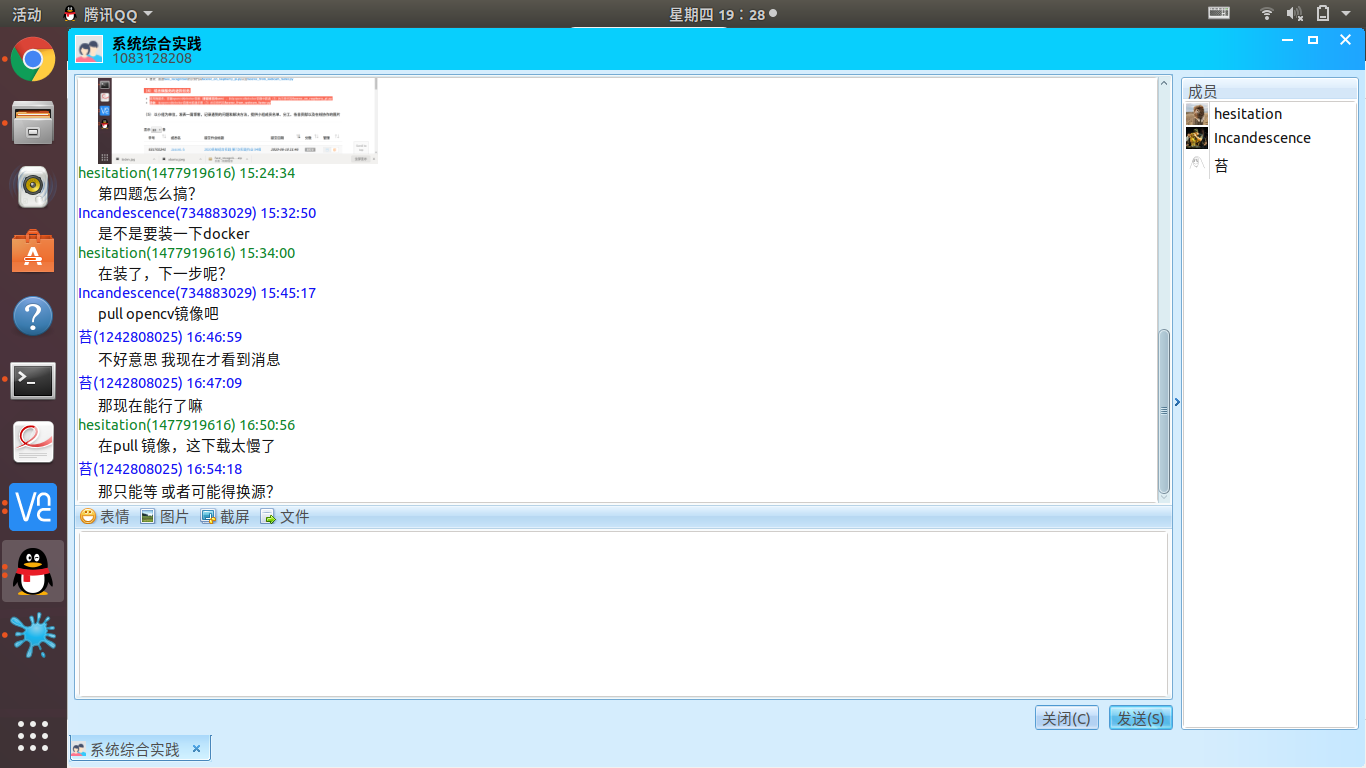
(5) 以小组为单位,发表一篇博客,记录遇到的问题和解决方法,提供小组成员名单以及在线协作的图片
小组成员
031702518 吴长星
031702526 周华
031702103 朱雅珊
遇到的问题
一、安装OpenCV时提示缺少boostdesc_bgm.i文件
解决方案:参考安装OpenCV时提示缺少boostdesc_bgm.i文件的问题解决方案(附带资源)
二、安装opencv时提示没有找到cuda.hpp文件
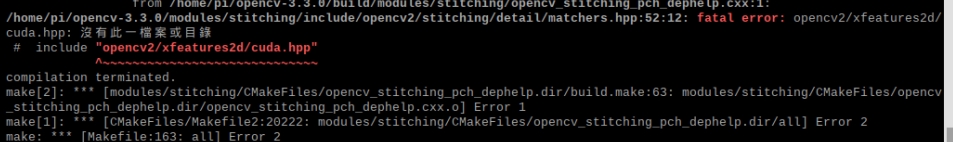
解决方案:找到cuda.hpp,记下它的绝对路径,找到报错的文件(这里是matchers.hpp),用文本编辑器打开,找到出错的语句(这里是" # include "opencv/..." "),将
引号中的路径改为绝对路径。
后来也遇到多次相同的错误,也是同样的处理:找到缺失的文件的绝对路径,在找到并修改出错的文件。
三、编译时遇到内存不足的情况

解决方案:参考linux问题记录
四、编译时

啧,这个问题没解决,我们决定换成用pip安装opencv。(明明用pip安装那么方便,为什么百度上一堆都是用make编译的勒?)
五、在pip install 时经常出现read timeout
解决方案:1、使用-i 参数换成国内源;2、使用--default-timeout=100参数避免下载速度过慢导致的timeout
协作截图