Problem:
Analysis:
I gave up and saw other's solution when I had nearly thought of the method ... What a pity
Let's define a border of string (s) as a prefix (p) of (s) that (p) is also a suffix of (s), and (p) is not longer than half of (s). What the problem asked us to look for is a number (L), that the prefix of length (L) can be divided into two string (s1) and (s2) , and the suffix of length (L) can be divided into two string (s2) and (s1), so that this pair of prefix and suffix is cyclically equivalent. Obviously, (s1) is a border of string (s). Another fact is, if (s1) is of length (len), (s2) is a border of the substring ([len, n - len - 1]). Define (f[len]) as the length of the maximum border of the substring ([len, n - len - 1]) . Let's enumerate the length of (s1) as (len) brutely, and for all legal (len) ("legal" means the prefix of length (len) is a border of (s). We can check it by hashing in (O(1)) time), the answer is (len + f[len]).
Now the problem is how to calculate (f[len]). Brute force takes (O(n^2)) complexity, but the useful fact below can decrease the complexity to (O(n)) :
To make it easy, look at the (beautiful) picture below.
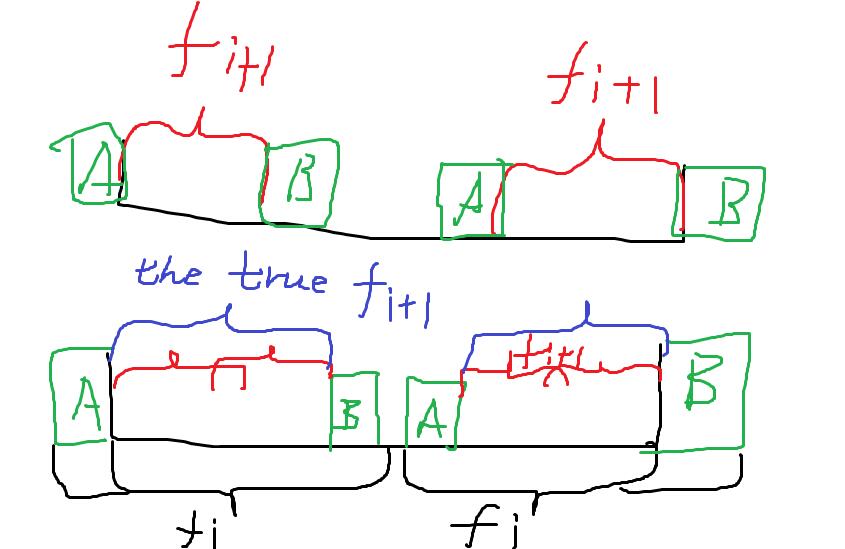
The first picture shows the situation when (f[i]=f[i+1]+2), and the second picture shows if (f[i]) (the black ones) is more than (f[i+1]) (the red ones) plus (2) , the (f[i+1]) must be wrong, for there's a longer border (the blue ones) of substring ([i+1, n-i-2]).
Because of this fact, we can solve (f[len]) in (O(n)) time. We initialize (f[i]) as (f[i+1]+2), and decrease it until the substring ([i, n-i-1]) has a border of length (f[i]). The proof of the complexity is similar to the one of solving (height) array by Suffix Array.
Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
namespace zyt
{
template<typename T>
inline bool read(T &x)
{
char c;
bool f = false;
x = 0;
do
c = getchar();
while (c != EOF && c != '-' && !isdigit(c));
if (c == EOF)
return false;
if (c == '-')
f = true, c = getchar();
do
x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c));
if (f)
x = -x;
return true;
}
inline bool read(char *const s)
{
return ~scanf("%s", s);
}
template<typename T>
inline void write(T x)
{
static char buf[20];
char *pos = buf;
if (x < 0)
putchar('-'), x = -x;
do
*pos++ = x % 10 + '0';
while (x /= 10);
while (pos > buf)
putchar(*--pos);
}
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int f[N], n;
// f[i] is the maximum length of the border of substr[i, n - i - 1]
char str[N];
namespace Hash
{
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pii hash_t;
hash_t h[N], pow[N];
const hash_t seed = hash_t(61, 67), p = hash_t(1e9 + 7, 1e9 + 9);
hash_t operator + (const hash_t &a, const hash_t &b)
{
return hash_t((a.first + b.first) % p.first, (a.second + b.second) % p.second);
}
hash_t operator - (const hash_t &a, const hash_t &b)
{
return hash_t((a.first - b.first + p.first) % p.first,
(a.second - b.second + p.second) % p.second);
}
hash_t operator * (const hash_t &a, const hash_t &b)
{
return hash_t(int((ll)a.first * b.first % p.first),
int((ll)a.second * b.second % p.second));
}
void init()
{
pow[0] = make_pair(1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
pow[i] = pow[i - 1] * seed;
}
inline int ctoi(const char c)
{
return c - 'a';
}
void get(const char *const s)
{
h[0] = make_pair(ctoi(s[0]), ctoi(s[0]));
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
h[i] = h[i - 1] * seed + make_pair(ctoi(s[i]), ctoi(s[i]));
}
hash_t extract(const int l, const int r)
{
return l ? (h[r] - h[l - 1] * pow[r - l + 1]) : h[r];
}
}
using namespace Hash;
void mk_f()
{
f[n >> 1] = 0;
for (int i = (n >> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
f[i] = min(f[i + 1] + 2, (n >> 1) - i);
while (f[i] && extract(i, i + f[i] - 1) != extract(n - i - f[i], n - i - 1))
--f[i];
}
}
int work()
{
read(n), read(str);
init();
get(str);
mk_f();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= (n >> 1); i++)
if (extract(0, i - 1) == extract(n - i, n - 1))
ans = max(ans, i + f[i]);
write(ans);
return 0;
}
}
int main()
{
return zyt::work();
}