实验一 感知器及其应用
【实验目的】
1. 理解感知器算法原理,能实现感知器算法;
2. 掌握机器学习算法的度量指标;
3. 掌握最小二乘法进行参数估计基本原理;
4. 针对特定应用场景及数据,能构建感知器模型并进行预测。
【实验内容】
1. 安装Pycharm,注册学生版。
2. 安装常见的机器学习库,如Scipy、Numpy、Pandas、Matplotlib,sklearn等。
3. 编程实现感知器算法。
4. 熟悉iris数据集,并能使用感知器算法对该数据集构建模型并应用。
【实验报告要求]
1. 按实验内容撰写实验过程;
2. 报告中涉及到的代码,每一行需要有详细的注释;
3. 按自己的理解重新组织,禁止粘贴复制实验内容!
实验结果:
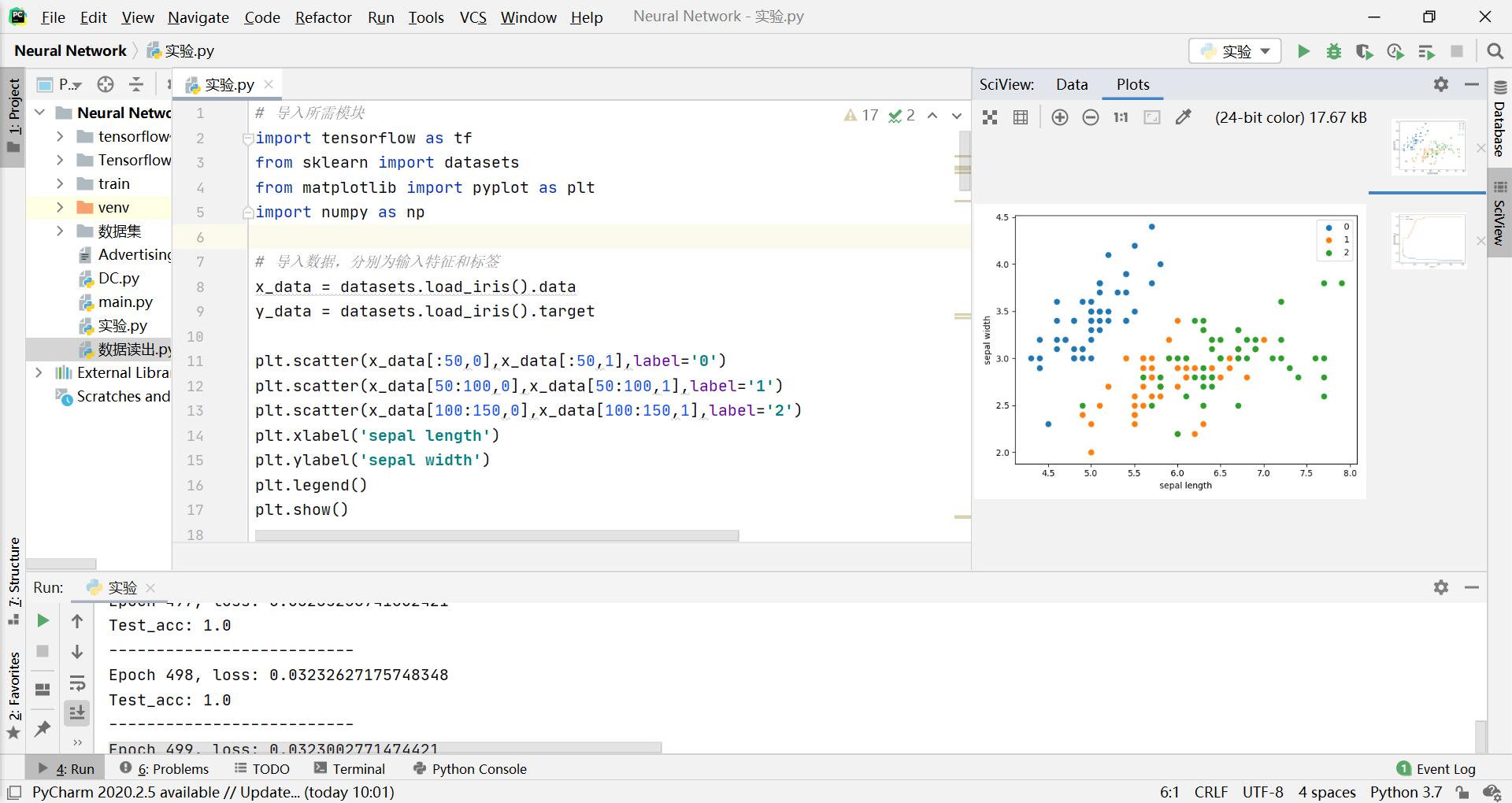
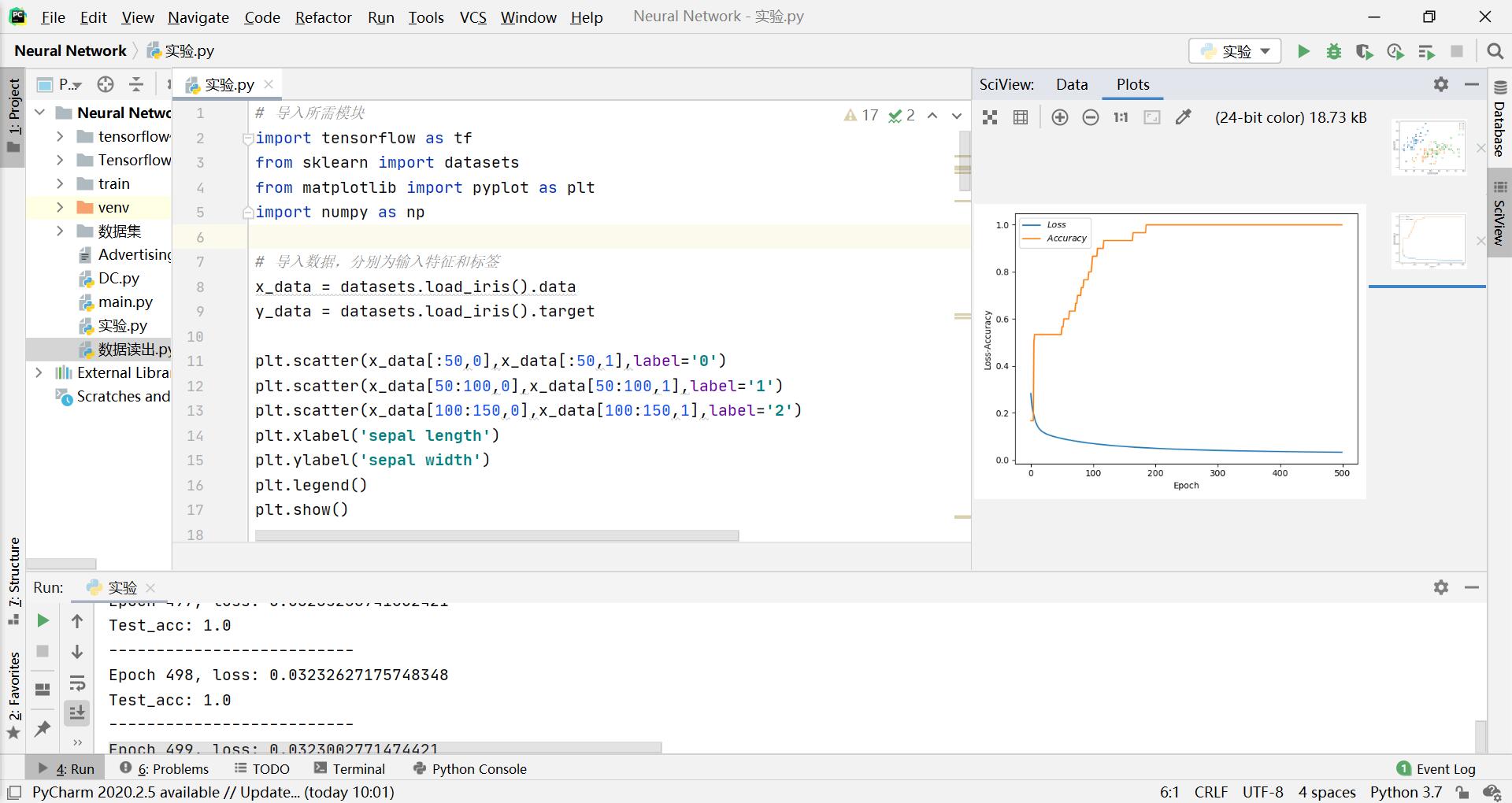
实验代码:
# 导入所需模块 import tensorflow as tf from sklearn import datasets from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import numpy as np # 导入数据,分别为输入特征和标签 x_data = datasets.load_iris().data y_data = datasets.load_iris().target plt.scatter(x_data[:50,0],x_data[:50,1],label='0')#前50个数据组的1、2位置分别为x、y坐标画图,记为类别0 plt.scatter(x_data[50:100,0],x_data[50:100,1],label='1') plt.scatter(x_data[100:150,0],x_data[100:150,1],label='2') plt.xlabel('sepal length') plt.ylabel('sepal width') plt.legend() plt.show() # 随机打乱数据(因为原始数据是顺序的,顺序不打乱会影响准确率) # seed: 随机数种子,是一个整数,当设置之后,每次生成的随机数都一样 np.random.seed(116) # 使用相同的seed,保证输入特征和标签一一对应 np.random.shuffle(x_data) np.random.seed(116) np.random.shuffle(y_data) tf.random.set_seed(116) # 将打乱后的数据集分割为训练集和测试集,训练集为前120行,测试集为后30行 x_train = x_data[:-30] y_train = y_data[:-30] x_test = x_data[-30:] y_test = y_data[-30:] # 转换x的数据类型,否则后面矩阵相乘时会因数据类型不一致报错 x_train = tf.cast(x_train, tf.float32) x_test = tf.cast(x_test, tf.float32) # from_tensor_slices函数使输入特征和标签值一一对应。(把数据集分批次,每个批次batch组数据) train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train)).batch(32) test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(32) # 生成神经网络的参数,4个输入特征故,输入层为4个输入节点;因为3分类,故输出层为3个神经元 # 用tf.Variable()标记参数可训练 # 使用seed使每次生成的随机数相同 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([4, 3], stddev=0.1, seed=1)) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([3], stddev=0.1, seed=1)) lr = 0.1 # 学习率为0.1 train_loss_results = [] # 将每轮的loss记录在此列表中,为后续画loss曲线提供数据 test_acc = [] # 将每轮的acc记录在此列表中,为后续画acc曲线提供数据 epoch = 500 # 循环500轮 loss_all = 0 # 每轮分4个step,loss_all记录四个step生成的4个loss的和 # 训练部分 for epoch in range(epoch): #数据集级别的循环,每个epoch循环一次数据集 for step, (x_train, y_train) in enumerate(train_db): #batch级别的循环 ,每个step循环一个batch with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # with结构记录梯度信息 y = tf.matmul(x_train, w1) + b1 # 神经网络乘加运算 y = tf.nn.softmax(y) # 使输出y符合概率分布(此操作后与独热码同量级,可相减求loss) y_ = tf.one_hot(y_train, depth=3) # 将标签值转换为独热码格式,方便计算loss和accuracy loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_ - y)) # 采用均方误差损失函数mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2) loss_all += loss.numpy() # 将每个step计算出的loss累加,为后续求loss平均值提供数据,这样计算的loss更准确 # 计算loss对各个参数的梯度 grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1]) # 实现梯度更新 w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad b = b - lr * b_grad w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0]) # 参数w1自更新 b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1]) # 参数b自更新 # 每个epoch,打印loss信息 print("Epoch {}, loss: {}".format(epoch, loss_all/4)) train_loss_results.append(loss_all / 4) # 将4个step的loss求平均记录在此变量中 loss_all = 0 # loss_all归零,为记录下一个epoch的loss做准备 # 测试部分 # total_correct为预测对的样本个数, total_number为测试的总样本数,将这两个变量都初始化为0 total_correct, total_number = 0, 0 for x_test, y_test in test_db: # 使用更新后的参数进行预测 y = tf.matmul(x_test, w1) + b1 y = tf.nn.softmax(y) pred = tf.argmax(y, axis=1) # 返回y中最大值的索引,即预测的分类 # 将pred转换为y_test的数据类型 pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=y_test.dtype) # 若分类正确,则correct=1,否则为0,将bool型的结果转换为int型 correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y_test), dtype=tf.int32) # 将每个batch的correct数加起来 correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct) # 将所有batch中的correct数加起来 total_correct += int(correct) # total_number为测试的总样本数,也就是x_test的行数,shape[0]返回变量的行数 total_number += x_test.shape[0] # 总的准确率等于total_correct/total_number acc = total_correct / total_number test_acc.append(acc) print("Test_acc:", acc) print("--------------------------") # 绘制 loss 曲线 plt.xlabel('Epoch') # x轴变量名称 plt.ylabel('Loss-Accuracy') # y轴变量名称 plt.plot(train_loss_results, label="$Loss$") # 逐点画出trian_loss_results值并连线,连线图标是Loss plt.plot(test_acc, label="$Accuracy$") # 逐点画出test_acc值并连线,连线图标是Accuracy plt.legend() # 画出曲线图标 plt.show() # 画出图像