0x00 内容简介
01 PHP代码执行函数
02 包含函数
03 命令执行函数
04 文件操作函数
05 特殊函数
0x01 PHP代码执行函数
1. eval

2. assert

3. preg_replace


主要是/e修正符使preg_replace()将replacement参数当做PHP代码
4. create_function


它看着很香,但是PHP高版本已经废除了它,从PHP 7.2.0开始,create_function()被废弃
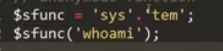
5. call_user_func

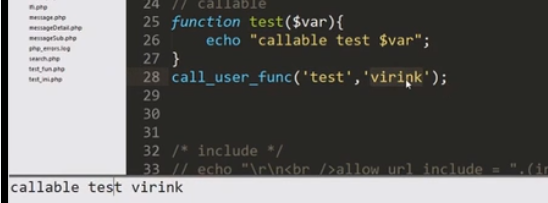
调用test函数,传入virink,输出
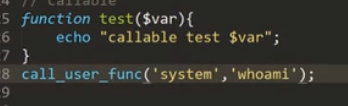
这里就造成了命令执行
0x02 文件包含“函数”
1. include()
语法:include(/path/to/filename)
include()语句将在其被调用的位置处包含一个文件。包含一个文件与在该语句所在位置复制制定文件的数据具有相同内容的效果。
使用include()时可以忽略括号。
可以根据条件来执行include()语句。在条件语句中使用include()有个怪现象,它必须包围在语句块大括号中,或者用其他语句包围符括起来。
2.require()
语法:require(filename)
require()在很大程度上与include相同,都是将一个模板文件包含到require调用坐在的位置。
require和include之间有两点重要的区别。首先,无论require的位置如何,制定文件都将包含到出现require的脚本中。例如,即使require放在计算结果为假的if语句中,依然会包含指定文件。
第二个重要的区别是:require出错时,脚本将停止运行,而在使用include的情况下,脚本将继续执行。
ps:
include和require都是语句结构(并不是函数)
所以,它可以不加圆括号,直接加引号来包含文件。我习惯不加圆括号。
1 include '01_var.php'; 2 或者 3 include('01_var.php'); 4 或者 5 require '01_var.php'; 6 或者 7 require('01_var.php');
3. include_once()
语法:include_once(filename)
include_once() 语句在脚本执行期间包含并运行指定文件。此行为和 include() 语句类似,唯一区别是include_once()会先判断一下这个文件在之前是否已经被包含过,如已经包含,则忽略本次包含。
include_once() 应该用于嵌套包含的情况下,想确保它只被包含一次以避免函数重定义,变量重新赋值等问题。
小结:include_once()函数的作用与include相同,不过它会首先验证是否已经包含了该文件。如果已经包含,则不再执行include_once。否则,则必须包含该文件。除了这一点与include完全相同。
4、require_once()
语法:require_once(filename)
require_once() 语句在脚本执行期间包含并运行指定文件。此行为和 require() 语句类似,唯一区别是require_once()会先判断一下这个文件在之前是否已经被包含过,如已经包含,则忽略本次包含。
require_once() 应该用于嵌套包含的情况下,想确保它只被包含一次以避免函数重定义,变量重新赋值等问题。
0x03 命令执行函数
命令注入(Command Injection),对一些函数的参数没有做过滤或过滤不严导致的,可以执行系统或者应用指令(CMD命令或者 bash 命令)的一种注入攻击手段。
常见的执行系统命令的函数有
1 system() 2 passthru() 3 exec() 4 shell_exec() 5 popen() 6 proc_open() 7 pcntl_exec()
1. system()函数
string system ( string $command [, int &$return_var ] )
$command为执行的命令,&return_var可选,用来存放命令执行后的状态码
system()函数执行有回显,将执行结果输出到页面上
1 <?php 2 system("whoami"); 3 ?>
2. passthru()函数
void passthru ( string $command [, int &$return_var ] )
和system函数类似,$command为执行的命令,&return_var可选,用来存放命令执行后的状态码
执行有回显,将执行结果输出到页面上
1 <?php 2 passthru("whoami"); 3 ?>
3. exec()
string exec ( string $command [, array &$output [, int &$return_var ]] )
$command是要执行的命令
$output是获得执行命令输出的每一行字符串,$return_var用来保存命令执行的状态码(检测成功或失败)
exec()函数执行无回显,默认返回最后一行结果
1 <?php 2 echo exec("whoami"); 3 ?>
1 <?php 2 $test = "ipconfig"; 3 exec($test,$array); 4 print_r($array); 5 ?>
4. shell_exec()函数
string shell_exec( string &command)
&command是要执行的命令
shell_exec()函数默认无回显,通过 echo 可将执行结果输出到页面
1 <?php 2 echo shell_exec("whoami"); 3 ?>
反引号 `
shell_exec() 函数实际上仅是反撇号 (`) 操作符的变体,当禁用shell_exec时,` 也不可执行
在php中称之为执行运算符,PHP 将尝试将反引号中的内容作为 shell 命令来执行,并将其输出信息返回
1 <?php 2 echo `whoami`; 3 ?>
5. popen()函数
resource popen ( string $command , string $mode )
函数需要两个参数,一个是执行的命令command,另外一个是指针文件的连接模式mode,有r和w代表读和写。
函数不会直接返回执行结果,而是返回一个文件指针,但是命令已经执行。
popen()打开一个指向进程的管道,该进程由派生给定的command命令执行而产生。
返回一个和fopen()所返回的相同的文件指针,只不过它是单向的(只能用于读或写)并且必须用pclose()来关闭。
此指针可以用于fgets(),fgetss()和 fwrite()
1 <?php popen( 'whoami >> c:/1.txt', 'r' ); ?>
1 <?php 2 $test = "ls /tmp/test"; 3 $fp = popen($test,"r"); //popen打一个进程通道 4 5 while (!feof($fp)) { //从通道里面取得东西 6 $out = fgets($fp, 4096); 7 echo $out; //打印出来 8 } 9 pclose($fp); 10 ?>
6. proc_open()函数
1 resource proc_open ( 2 string $cmd , 3 array $descriptorspec , 4 array &$pipes [, string $cwd [, array $env [, array $other_options ]]] 5 )
与popen函数类似,但是可以提供双向管道
1 <?php 2 $test = "ipconfig"; 3 $array = array( 4 array("pipe","r"), //标准输入 5 array("pipe","w"), //标准输出内容 6 array("pipe","w") //标准输出错误 7 ); 8 9 $fp = proc_open($test,$array,$pipes); //打开一个进程通道 10 echo stream_get_contents($pipes[1]); //为什么是$pipes[1],因为1是输出内容 11 proc_close($fp); 12 ?>
7. pcntl_exec()函数
void pcntl_exec ( string $path [, array $args [, array $envs ]] )
path是可执行二进制文件路径或一个在文件第一行指定了 一个可执行文件路径标头的脚本
args是一个要传递给程序的参数的字符串数组。
pcntl是linux下的一个扩展,需要额外安装,可以支持 php 的多线程操作。
pcntl_exec函数的作用是在当前进程空间执行指定程序,版本要求:PHP > 4.2.0
1 <?php 2 3 pcntl_exec ( "/bin/bash" , array("whoami")); 4 5 ?>
对这些危险函数,可以在php.ini中禁用,进行安全加固

0x04 文件操作函数
1. fopen() 打开文件或者 URL
fopen ( string $filename , string $mode [, bool $use_include_path = false [, resource $context ]] ) : resource

1 $handle = fopen("/home/rasmus/file.txt", "r"); 2 $handle = fopen("/home/rasmus/file.gif", "wb"); 3 $handle = fopen("http://www.example.com/", "r"); 4 $handle = fopen("ftp://user:password@example.com/somefile.txt", "w");
2. copy()复制文件
copy ( string $source , string $dest [, resource $context ] ) : bool
echo copy("要复制的文件路径/链接.txt","target.txt");//bool(true/false)
3. fclose 关闭一个已打开的文件指针
fclose ( resource $handle ) : bool
$handle = fopen('somefile.txt', 'r'); fclose($handle);
4. feof() 测试文件指针是否到了文件结束的位置
feof ( resource $handle ) : bool
1 $file = fopen("demo.txt", "r"); 2 3 //输出文本中所有的行,直到文件结束为止。 4 while(!feof($file)) 5 { 6 echo fgets($file); 7 } 8 9 fclose($file);
5. fgetc 从文件指针中读取一个字符
fgetc ( resource $handle ) : string
1 $file = fopen("demo.txt", "r"); 2 echo fgetc($file);//t
6. fgets 从文件指针中读取一行
fgets ( resource $handle [, int $length ] ) : string
1 $file = fopen("demo.txt", "r"); 2 echo fgets($file,2048);//this is demo.txt 1
7. file() 把整个文件读入一个数组中
file ( string $filename [, int $flags = 0 [, resource $context ]] ) : array
8. file_get_contents () 将整个文件读入一个字符串
file_get_contents ( string $filename [, bool $use_include_path = false [, resource $context [, int $offset = -1 [, int $maxlen ]]]] ) : string
9. file_put_contents 将一个字符串写入文件
file_put_contents ( string $filename , mixed $data [, int $flags = 0 [, resource $context ]] ) : int 该函数将返回写入到文件内数据的字节数,失败时返回FALSE
10. unlink() 删除文件
若成功,则返回 true,失败则返回 false。
11. rename() 函数重命名文件或目录
12. mkdir() 创建目录
若成功,则返回 true,否则返回 false。

13. move_uploaded_file() 将上传的文件移动到新位置
若成功,则返回 true,否则返回 false。

14. rmdir() 删除空目录
只能删除空的目录 且不能递归删除
15. scandir() 列出指定路径中的文件和目录
scandir ( string $directory [, int $sorting_order [, resource $context ]] ) : array
总结:

0x05 特殊函数
1. phpinfo()
信息泄漏
bool phpinfo ([ int $what = INFO_ALL ] )
输出 PHP 当前状态的大量信息,包含了 PHP 编译选项、启用的扩展、PHP 版本、服务器信息和环境变量(如
果编译为一个模块的话)、PHP环境变量、操作系统版本信息、path 变量、配置选项的本地值和主值、HTTP
头和PHP授权信息(License)。
2. symlink(),symlink()
软连接-读取文件内容
bool symlink ( string $target , string $link )
symlink() 对于已有的 target 建立一个名为 link 的符号连接。
string readlink ( string $path )
readlink() 和同名的 C 函数做同样的事,返回符号连接的内容。
3. getenv(),putenv()
环境变量
string getenv ( string $varname )
获取一个环境变量的值。
bool putenv ( string $setting )
添加 setting 到服务器环境变量。 环境变量仅存活于当前请求期间。 在请求结束时环境会恢复到初始状态。
4. dl()
加载扩展
bool dl ( string $library )
载入指定参数 library 的 PHP 扩展。
5. 配置相关
string ini_get ( string $varname )
成功时返回配置选项的值。
string ini_set ( string $varname , string $newvalue )
string ini_alter ( string $varname , string $newvalue )
设置指定配置选项的值。这个选项会在脚本运行时保持新的值,并在脚本结束时恢复。
void ini_restore ( string $varname )
恢复指定的配置选项到它的原始值。
6. 数字判断
bool is_numeric ( mixed $var )
如果 var 是数字和数字字符串则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE。
仅用is_numeric判断而不用intval转换就有可能插入16进制的字符串到数据库,进而可能导致sql二次注入。
7. 数组相关
bool in_array ( mixed $needle , array $haystack [, bool $strict = FALSE ] )
在 haystack 中搜索 needle,如果没有设置 strict 则使用宽松的比较。
该函数有一个特性,比较之前会进行自动类型转换。
$a = '1abc';
in_array($a,array(1,2,3))的返回值会是真
8. PHP变量覆盖函数
void parse_str ( string $str [, array &$arr ] )
如果 str 是 URL 传递入的查询字符串(query string),则将它解析为变量并设置到当前作用域。
int extract ( array &$var_array [, int $extract_type = EXTR_OVERWRITE [, string $prefix = NULL ]] )
本函数用来将变量从数组中导入到当前的符号表中。检查每个键名看是否可以作为一个合法的变量名,同时也
检查和符号表中已有的变量名的冲突。
bool mb_parse_str ( string $encoded_string [, array &$result ] )
解析 GET/POST/COOKIE 数据并设置全局变量。 由于 PHP 不提供原始 POST/COOKIE 数据,目前它仅能够
用于 GET 数据。 它解析了 URL 编码过的数据,检测其编码,并转换编码为内部编码,然后设置其值为 array
的 result 或者全局变量。
bool import_request_variables ( string $types [, string $prefix ] )
将 GET/POST/Cookie 变量导入到全局作用域中。如果你禁止了 register_globals,但又想用到一些全局变
量,那么此函数就很有用。
9. 列目录
array glob ( string $pattern [, int $flags = 0 ] )
glob() 函数依照 libc glob() 函数使用的规则寻找所有与 pattern 匹配的文件路径,类似于一般 shells 所用的
规则一样。不进行缩写扩展或参数替代。
10. 无参数获取信息
array get_defined_vars ( void )
返回一个包含所有已定义变量列表的多维数组,这些变量包括环境变量、服务器变量和用户定义的变量。
array get_defined_constants ([ bool $categorize = false ] )
返回当前所有已定义的常量名和值。 这包含 define() 函数所创建的,也包含了所有扩展所创建的。
array get_defined_functions ( void )
返回一个包含所有已定义函数列表的多维数组
array get_included_files ( void )
返回所有被 include、 include_once、 require 和 require_once 的文件名。