概念
G=(V,E)
V={v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7,v8,v9,v10,v11}
E={(v1,v2),(v2,v3),(v2,v6),(v3,v7)...}
|V|=11
|E|=11

Walk: close walk x=y otherwise open walk
Trail: x - y trail is a walk with no repeated edge,没有重复走边
Path: x - y path is a walk with no repeated Vertex,没有走重复的点
Cycle: x - x path is a cycle
Circuit: x - x trail is a circuit
Degree:点有多少个边连出去,度
Regular graph:每个点有相同的度
Complete graph:图像任意两个点都有边
Simple graph:一个图没有self-loop的点
Multigraph: A graph with multiple edges
Pseudograph:有self-loop也有multiple edges
Hypergraph: Allow an edge connected to multiple vertcies

三类任务:
1 节点层面任务:比如文章最开始提到的引文网络中,节点论文的分类,社交网络中用户标签的分类等。此时,主要关注节点和边层面的特征。
2 边层面任务:比如社交网络中,将用户作为节点,用户之间的关注关系建模为边,通过边预测实现社交用户的推荐。此时,主要关注节点和边的特征。
3 图层面的任务:比如对药物分子的分类。此时,任务不依赖于某个节点或某条边的属性,而是,需要考虑整个图的信息。
图嵌入、图神经网络、图卷积的关系:
查看图神经网络的资料,最常见图嵌入(Graph Embedding)、图神经网络(GNN)、图卷积(GCN)这三个词,同时,也很容易迷惑:到底这三个说的是三个东西还是一个东西?大家平时说的图网络指的是哪一个?这三个有什么联系?图神经网络是一个很宽泛的概念,图神经网络=图+神经网络。我们通俗讲的图神经网络主要指GNN和GCN(类似于深度学习网络中的前馈全连接DNN和CNN)。
图嵌入发展较早,在早期是一个相对独立的领域,关注的问题大致分为4类:
1、节点分类
2、链接预测
3、聚类
4、可视化
方法主要分为三类:
基于因子分解的方法
基于随机游走的方法
基于深度学习的方法

GNN的分类:
Graph convolution networks
Graph attention networks
Graph autoencoders
Graph generative networks
Graph spatial-temporal networks
GCN分类:
Spectral-based GCN————基于频谱域的GCN
Spatial-based GCN————基于空域的GCN
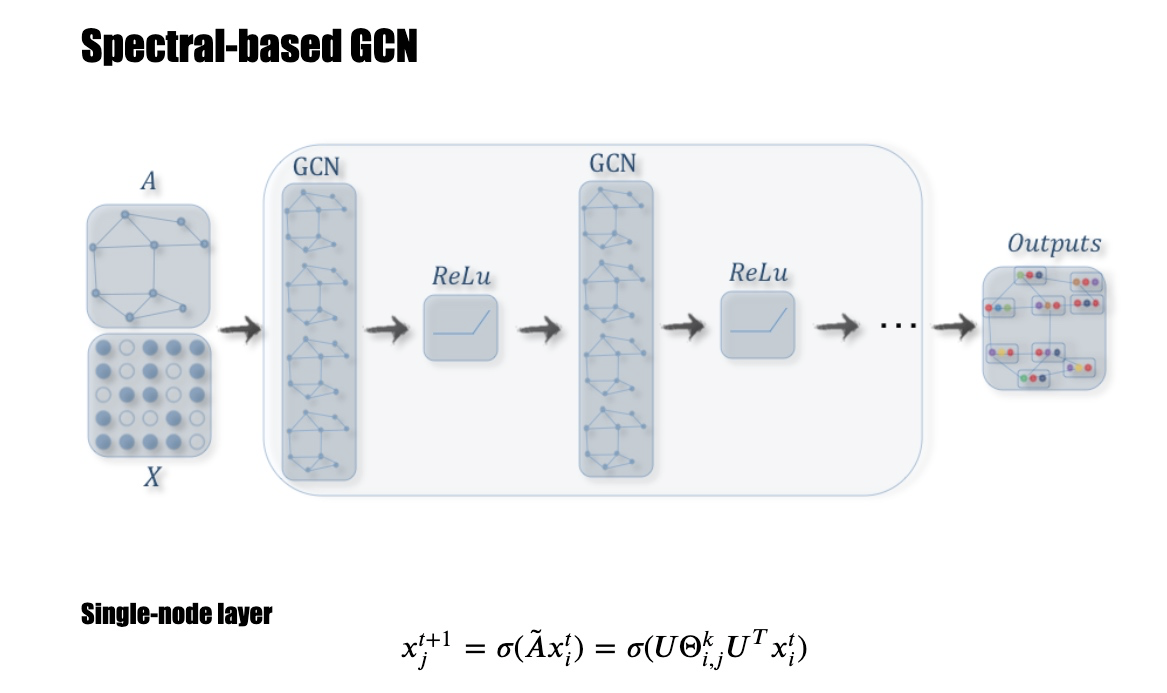
x是feature
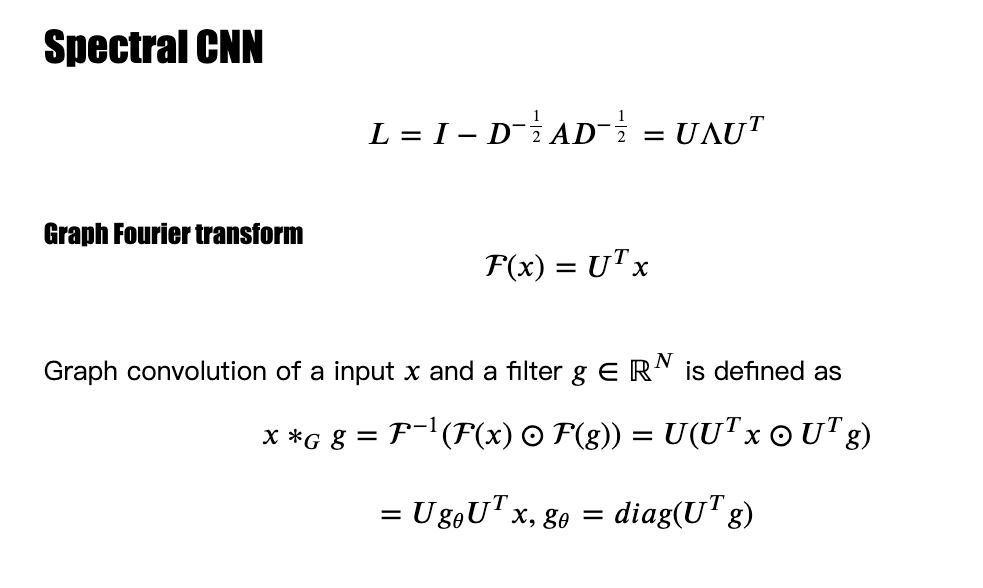
把A做特征分解

先拉普拉斯在做特征分解
傅里叶变换
ChebNet MPNN
节点并缩
GAT (Graph attention networks)
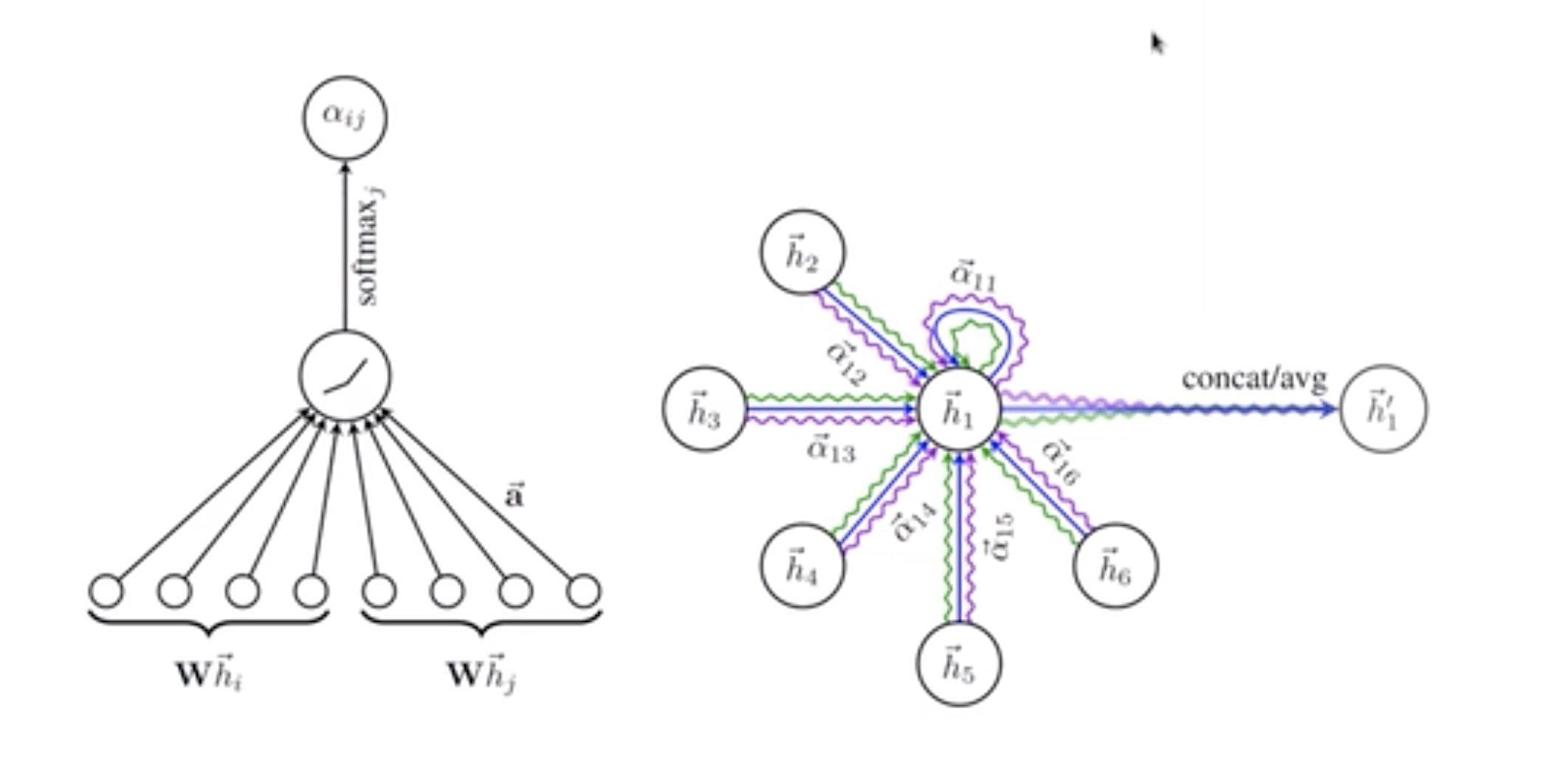
attention:key和一个query 比较和哪些key相似,得到一个weight
拿中间的点当query---i 和周围的key---j比较
比较像的话α就比较大

transformer --- Multi-head attention
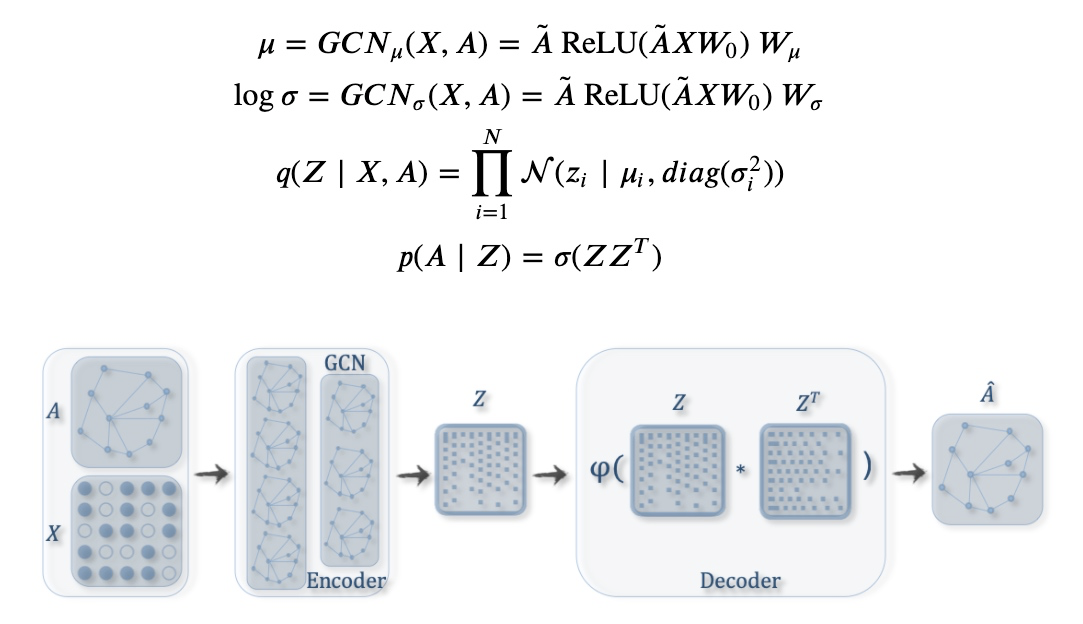
Graph autoencoder(GAE)

Variational graph autoencoder(VGAE)
CVPR/KDD/ECCV/ICML2020的关于图卷积网络的论文:
[CVPR 2020] Point-GNN: Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
[CVPR 2020] Geometrically Principled Connections in Graph Neural Networks [CVPR 2020] SuperGlue: Learning Feature Matching With Graph Neural Networks
[CVPR 2020] Learning Multi-View Camera Relocalization With Graph Neural Networks
[CVPR 2020] Multi-Modal Graph Neural Network for Joint Reasoning on Vision and Scene Text
[CVPR 2020] Social-STGCNN: A Social Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network for Human Trajectory
[CVPR 2020] Dynamic Multiscale Graph Neural Networks for 3D Skeleton Based Human Motion Prediction
[CVPR 2020] Dynamic Graph Message Passing Networks
[ECCV 2020] Graph convolutional networks for learning with few clean and many noisy labels
[ICML 2020] When Spectral Domain Meets Spatial Domain in Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Graph Structural-topic Neural Network
[KDD 2020] Towards Deeper Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Redundancy-Free Computation for Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] TinyGNN: Learning Efficient Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] PolicyGNN: Aggregation Optimization for Graph Neural Networks [KDD 2020] Residual Correlation in Graph Neural Network Regression
[KDD 2020] Spotlight: Non-IID Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] XGNN: Towards Model-Level Explanations of Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network for Real-time Event Prediction
[KDD 2020] Handling Information Loss of Graph Neural Networks for Session-based Recommendation
[KDD 2020] Connecting the Dots: Multivariate Time Series Forecasting with Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] GPT-GNN: Generative Pre-Training of Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Graph Structure Learning for Robust Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Minimal Variance Sampling with Provable Guarantees for Fast Training of Graph Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] A Framework for Recommending Accurate and Diverse Items Using Bayesian Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
[KDD 2020] Competitive Analysis for Points of Interest
[KDD 2020] Knowing your FATE: Explanations for User Engagement Prediction on Social Apps
[KDD 2020] GHashing: Semantic Graph Hashing for Approximate Similarity Search in Graph Databases
[KDD 2020] Comprehensive Information Integration Modeling Framework for Video Titling`
相关paper
1.A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks
2.Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and graph networks
3.Geometric deep learning: going beyond Euclidean data
4.The Graph Neural Network Model
5.Variational Graph Auto-encoders
6.Neural Message Passing for Quantum Chemistry
7.DIFFUSION CONVOLUTIONAL RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK: DATA DRIVEN TRAFFIC FORECASTING
8.GRAPH ATTENTION NETWORKS
9.MOLGAN: An implicit generative model for small molecular graphs
论文综述目前较推荐的有这三篇:
《Graph Neural Networks: A Review of Methods and Applications》
《Deep Learning on Graphs: A Survey》
《A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks》
机器之心对这三篇综述还有专门的报道,《图神经网络概述第三弹:来自IEEE Fellow的GNN综述》
北师大的集智学园
中科院的人工智能前沿讲习
这两个主页上有不少图网络相关的视频,视频质量也不错。
参考文献
《图嵌入(Graph embedding)综述》
《【论文笔记】DeepWalk》
《The Graph Neural Network Model》
《GNN 简介和入门资料》
《Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs》
《Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs-PPT》
《论文笔记:Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs》
《Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks》
《Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks阅读笔记》
《Abusive Language Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks》
《Spam Review Detection with Graph Convolutional Networks》
《Graph Neural Networks: A Review of Methods and Applications》
《Deep Learning on Graphs: A Survey》
《A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks》
图神经网络概述第三弹:来自IEEE Fellow的GNN综述》
哔哩哔哩上有视频
《唐杰-图神经网络及认知推理-图神经网络学习班》
《图神经网络介绍-Introduction to GNN》
Dataset
➢ KarateClub:数据为无向图,来源于论文An Information Flow Model for Conflict and Fission in Small Groups;
➢ TUDataset:包括58个基础的分类数据集集合,数据都为无向图,如“IMDB-BINARY”, “PROTEINS”等,来源于TU Dortmund University
➢ Planetoid:引用网络数据集,包括“Cora”, “CiteSeer” and “PubMed”,数据都为无向图,来源 于论文Revisiting Semi-Supervised Learning with Graph Embeddings。节点代表文档,边代表引 用关系。
➢ CoraFull:完整的“Cora”引用网络数据集,数据为无向图,来源于论文Deep Gaussian Embedding of Graphs: Unsupervised Inductive Learning via Ranking。节点代表文档,边代表引 用关系。
➢ Coauthor:共同作者网络数据集,包括“CS”和“Physics”,数据都为无向图,来源于论文Pitfalls of Graph Neural Network Evaluation。节点代表作者,若是共同作者则被边相连。学习任务是将作者映射到 各自的研究领域中。
➢ Amazon:亚马逊网络数据集,包括“Computers”和“Photo”,数据都为无向图,来源于论文Pitfalls of Graph Neural Network Evaluation。节点代表货物,边代表两种货物经常被同时购买。学习任务是将货物 映射到各自的种类里。
➢ PPI:蛋白质-蛋白质反应网络,数据为无向图,来源于论文Predicting multicellular function through multi- layer tissue networks
➢Entities:关系实体网络,包括“AIFB”, “MUTAG”, “BGS” 和“AM”,数据都为无向图,来源 于论文Modeling Relational Data with Graph Convolutional Networks
➢ BitcoinOTC:数据为有向图,包括138个“who-trusts-whom”网络,来源于论文EvolveGCN: Evolving Graph Convolutional Networks for Dynamic Graphs,数据链接为Bitcoin OTC trust weighted signed network