There are three types of relationships in database. They are:
- One-to-Many
- One-to-One
- Many-to-Many
The One-to-Many relationship
Write some codes first:
class Company
{
public int CompanyId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string CompanyName { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
class Employee
{
public int EmployeeId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string EmployeeName { get; set; }
public virtual int CompanyId { get; set; }
}
class MyContext:DbContext
{
public MyContext():base("name=Test")
{
}
public DbSet<Company> Companies { get; set; }
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
}
We use the virtual keyword when define the navigation property. This keyword can enable us to use lazy loading. It' means Entity Framework will load the data to Employees property of Company automatic only when we attempt to access it.
After execute command Update-Database in Nuget command line, take a look at database:

The column Companyid is created as the foreign key automatic.
Let's have a test:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Company company1 = new Company
{
CompanyName = "Baidu",
Employees = new List<Employee>()
{
new Employee
{
EmployeeName = "Joey",
},
new Employee
{
EmployeeName = "Ross",
}
}
};
AddCompany(company1);
}
private static void AddCompany(Company company)
{
using (MyContext db = new MyContext())
{
db.Companies.Add(company);
db.SaveChanges();
}
}
After Run the program, there have been some data:
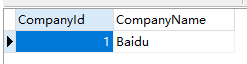
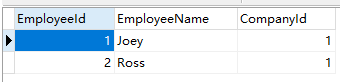
Now, Let's try to delete the company:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DeleteCompany(1);
}
private static void DeleteCompany(int companyId)
{
using (MyContext db = new MyContext())
{
Company company = db.Companies.Find(companyId);
if (company != null)
{
db.Companies.Remove(company);
db.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
After run the program, you'll find the employee data is deleted also. Cascade deletion is the default way. if you don't want Cascade deletion, you can configurate it by The DbModelBuilder API or Configuration Classes:
class CompanyMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<Company>
{
public CompanyMap()
{
HasMany(c => c.Employees)
.WithRequired()
.HasForeignKey(c=>c.CompanyId)
.WillCascadeOnDelete(false);
}
}
If you don't need to access proerty CompanyId in class Employee, you'd better remove it from the class Employee. Then Entity Framework will create a foreign key named Company_CompanyId automatic. Of cause, you can define it flexible by using The DbModelBuilder API or Configuration Classes.
The Many-to-Many relationship
Write some codes first:
class Company
{
public int CompanyId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string CompanyName { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Person> Employees { get; set; }
}
class Person
{
public int PersonId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string PersonName { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Company> companies { get; set; }
}
class MyContext:DbContext
{
public MyContext():base("name=Test")
{
}
public DbSet<Company> Companies { get; set; }
public DbSet<Person> People { get; set; }
}
After execute the command Upate-Database, take a look at the database:
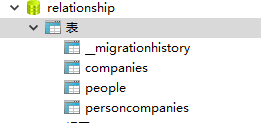
Entity Framework has created a junction table named personcompanies. it's contains two columns: personId and companyId.
Of cause, you also can define the columns's name by coding, for example:
class PersonMap:EntityTypeConfiguration<Person>
{
public PersonMap()
{
HasMany(p => p.companies)
.WithMany(c => c.Employees)
.Map(m =>
{
m.MapLeftKey("PersonId");
m.MapRightKey("CompanyId");
});
}
}
Add it to Configurations of modelBuilder:
// OnModelCreating is a fucntion of DbContext
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new PersonMap());
}
The One-to-One relationship
Coding first:
class Person
{
public int PersonId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(50)]
public string PersonName { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Company> companies { get; set; }
public virtual Student Student{ get; set; }
}
class Student
{
[Key]
public int PersonId { get; set; }
[MaxLength(200)]
public string SchoolName { get; set; }
public virtual Person Person { get; set; }
}
class StudentMap:EntityTypeConfiguration<Student>
{
public StudentMap()
{
HasRequired(s => s.Person)
.WithOptional(s => s.Student);
}
}
A student must be a person, but a person dosn't must be student, so, the codes like this:
HasRequired(s => s.Person).WithOptional(s => s.Student);
There is another way to create One-to-One relationship. Please see: Lerning Entity Framework 6 ------ Introduction to TPT.
That's all.