1009,直接贪心,只要让后面的尽量小,第一位和第二位尽量大即可。
1011,直接统计奇数的字母的个数,然后用偶数的个数平均分配到它们上面即可。代码如下:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int T; 9 scanf("%d",&T); 10 while(T--) 11 { 12 int n; 13 int odd = 0, even = 0; 14 scanf("%d",&n); 15 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 16 { 17 int t; 18 scanf("%d",&t); 19 if(t % 2) 20 { 21 odd ++; 22 even += (t - 1) / 2; 23 } 24 else even += t / 2; 25 } 26 if(odd == 0) 27 { 28 printf("%d ",even << 1); 29 } 30 else 31 { 32 printf("%d ",even / odd * 2 + 1); 33 } 34 } 35 }
1001,用二次函数做即可,把阿尔法看做一个未知数。分析过程如下:
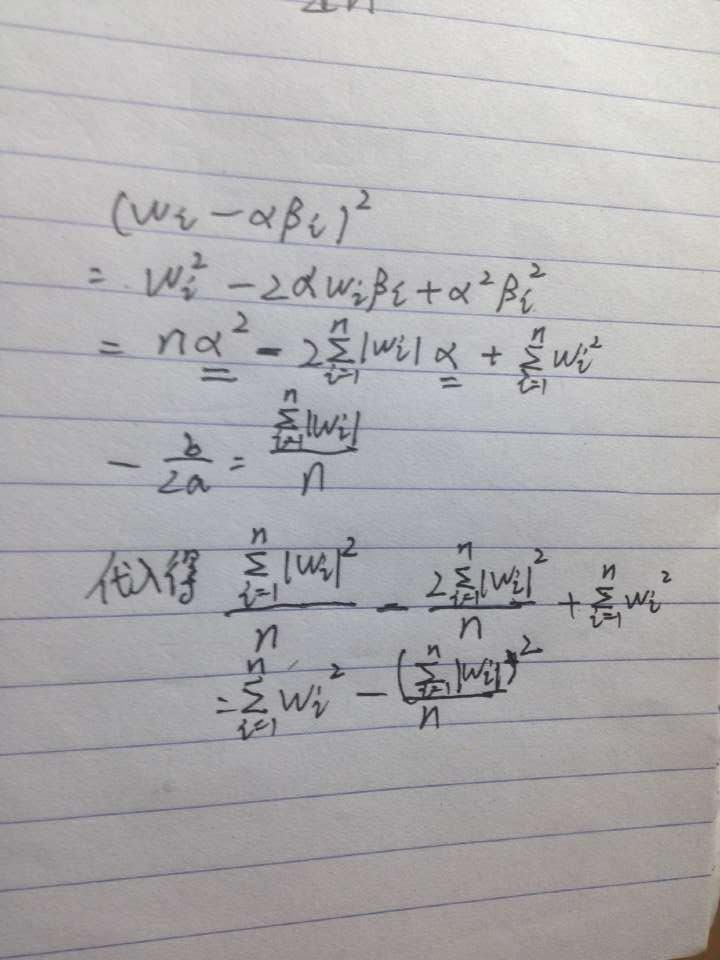
代码如下:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 typedef long long ll; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 int T; 10 scanf("%d",&T); 11 while(T--) 12 { 13 ll sum = 0, sum2 = 0; 14 int n; 15 scanf("%d",&n); 16 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 17 { 18 int t; 19 scanf("%d",&t); 20 if(t<0) t = -t; // 全部值都变正 21 sum += t; 22 sum2 += (ll)t*t; 23 } 24 sum *= sum; 25 if(sum == 0) 26 { 27 printf("I64%d/%d ",sum2,1); 28 continue; 29 } 30 ll gd = __gcd(sum,(ll)n); 31 if(gd > 1) 32 { 33 sum /= gd; 34 n /= gd; 35 } 36 sum2 *= n; 37 sum2 -= sum; 38 if(sum2 == 0) 39 { 40 printf("%d/%d ",0,1); 41 continue; 42 } 43 gd = __gcd(sum2,(ll)n); 44 if(gd > 1) 45 { 46 sum2 /= gd; 47 n /= gd; 48 } 49 printf("%I64d/%d ",sum2,n); 50 } 51 }
1012,题意是匹配串和原串去匹配,原串的相应区间可以对某些位置进行操作。设位置x是可以操作的,那么x和它下一个位置进行交换;同时,两个x之间的间隔必须大于等于1。直接暴力即可,代码如下:

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 char s[(int)1e5+5],t[5000+5]; 5 char ans[(int)1e5+5]; 6 int n,m; 7 8 bool isok(int pos) 9 { 10 int j = 1; 11 for(int i=pos;i<=pos+m-1;) 12 { 13 if(s[i] == t[j]) 14 { 15 i++,j++; 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 20 if(i == pos+m-1) return false; 21 if(s[i] != t[j+1] || s[i+1] != t[j]) return false; 22 else i += 2,j += 2; 23 } 24 } 25 return true; 26 } 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 int T; 31 scanf("%d",&T); 32 while(T--) 33 { 34 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 35 scanf("%s",s+1); 36 scanf("%s",t+1); 37 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans[i] = '0'; 38 for(int i=1;i+m-1<=n;i++) 39 { 40 if(isok(i)) ans[i] = '1'; 41 else ans[i] = '0'; 42 } 43 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 44 { 45 printf("%c",ans[i]); 46 } 47 puts(""); 48 } 49 }
1005,找出共线的点的集合(集合内点的个数大于等于2,可以是重点)。最初的做法是,找出所有的直线方程,统计这上面的点的个数,然后这条线上的集合的个数就是C(2,m)+C(3,m)+...+C(m,m) = 2^m - m - 1。但是我们实现用了大量的map,可能是因为这一点,超时了。TLE的代码如下:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include <map> 5 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 6 #define ll long long 7 using namespace std; 8 const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7; 9 //const ll p = 257; 10 11 struct line 12 { 13 ll a,b,c; 14 bool operator <(const line & A) const 15 { 16 return a==A.a? b==A.b?c<A.c:b<A.b :a<A.a; 17 } 18 }; 19 struct point 20 { 21 ll x,y; 22 bool operator < (const point & A) const 23 { 24 return x==A.x ? y<A.y :x<A.x; 25 } 26 27 }p[1000+5]; 28 29 ll qpow(ll x,ll y) 30 { 31 ll ans = 1; 32 while(y) 33 { 34 if(y&1) ans = ans * x % mod; 35 y >>= 1; 36 x = (x*x) % mod; 37 } 38 return ans; 39 } 40 41 map<line,ll> M; 42 map<point,ll> M2; 43 map<line,ll> M3; 44 //set<point> S; 45 46 bool isequel(point a,point b) 47 { 48 if(a.x==b.x && a.y==b.y) return 1; 49 return 0; 50 } 51 52 void get(ll &a,ll &b,ll &c,point p1,point p2) 53 { 54 ll x1 = p1.x,y1 = p1.y; 55 ll x2 = p2.x,y2 = p2.y; 56 c = x1 - x2; 57 a = y1 - y2; 58 b = x1*y2-y1*x2; 59 } 60 61 ll getn(ll now) 62 { 63 for(ll i = 1 ;;i++) 64 { 65 if(i*(i+1)/2 == now) return i+1; 66 } 67 } 68 69 void modify(ll& a , ll & b, ll &c) 70 { 71 if(a==0 && b == 0) {c=1;return;} 72 if(b==0 && c == 0) {a=1;return;} 73 if(a==0 && c == 0) {b=1;return;} 74 if(a && b && c) 75 { 76 int gd = __gcd(a,__gcd(b,c)); 77 a /= gd; 78 b /= gd; 79 c /= gd; 80 } 81 else 82 { 83 if(a==0) 84 { 85 int gd = __gcd(b,c); 86 b /= gd; 87 c /= gd; 88 } 89 else if(b==0) 90 { 91 int gd = __gcd(a,c); 92 a /= gd; 93 c /= gd; 94 } 95 else if(c==0) 96 { 97 int gd = __gcd(a,b); 98 a /= gd; 99 b /= gd; 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 104 int main() 105 { 106 int T; 107 scanf("%d",&T); 108 while(T--) 109 { 110 M.clear(); 111 M2.clear(); 112 M3.clear(); 113 //S.clear(); 114 int n; 115 scanf("%d",&n); 116 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 117 { 118 ll x,y; 119 scanf("%I64d%I64d",&x,&y); 120 p[i] = (point){x,y}; 121 M2[p[i]] ++; 122 } 123 124 for(map<point,ll>::iterator it=M2.begin();it!=M2.end();it++) 125 { 126 map<point,ll>::iterator it2 = it; 127 it2++; 128 for(;it2!=M2.end();it2++) 129 { 130 //if(isequel((*it).first,(*it2).first)) continue; 131 ll a,b,c; 132 get(a,b,c,(*it).first,(*it2).first); 133 modify(a,b,c); 134 M[(line){a,b,c}] += (*it).second + (*it2).second; 135 M3[(line){a,b,c}] ++; 136 //S.insert(p[i]); 137 //printf("%d %d %d !! ",i,j,M[(line){a,b,c}]); 138 } 139 } 140 141 ll ans = 0; 142 143 for(map<line,ll>::iterator it = M.begin();it!=M.end();it++) 144 { 145 ll nownow = (*it).second; 146 //cout << now <<"!!"<<endl; 147 //ll n = now / 2; 148 map<line,ll>::iterator itt = M3.find((*it).first); 149 ll now = ((*itt).second); 150 //ll now = M3.second; 151 ll n = getn(now); 152 ll nn = nownow/(n-1); 153 ans += (qpow(2,nn)-nn-1); 154 ans %= mod; 155 } 156 for(map<point,ll>::iterator it = M2.begin();it!=M2.end();it++) 157 { 158 ll now = (*it).second; 159 if(now<=1) continue; 160 ans += (qpow(2,now)-now-1); 161 } 162 163 cout << ans <<endl; 164 165 } 166 return 0; 167 } 168 169 /* 170 171 5 172 0 1 173 0 0 174 0 0 175 0 1 176 0 2 177 */
看了标程以后觉得他的方法很好。大概是这样子的:先对所有的点按照x,y的大小排序,然后对每一个点,算出包含了这个点的的集合的个数。具体见代码和注释:

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 typedef long long ll; 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N = 1000 + 50; 5 const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7; 6 7 struct point 8 { 9 int x, y; 10 point() {} 11 point(int _x, int _y): x(_x), y(_y) {} 12 point operator - (const point & temp) const 13 { 14 return point(x - temp.x, y - temp.y); 15 } 16 bool operator < (const point & temp) const 17 { 18 return x < temp.x || (x == temp.x && y < temp.y); 19 } 20 bool operator == (const point & temp) const 21 { 22 return x == temp.x && y == temp.y; 23 } 24 void reduce() 25 { 26 int g = __gcd(abs(x), abs(y)); 27 if(g) {x /= g; y /= g;} 28 } 29 } p[N], Q[N]; 30 31 int pw[N]; 32 void init() 33 { 34 pw[0] = 1; 35 for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) pw[i] = pw[i-1] * 2 % mod; 36 } 37 38 void update(int &x, int y) 39 { 40 x += y; 41 if(x >= mod) x -= mod; 42 } 43 44 void run() 45 { 46 int n;scanf("%d", &n); 47 int ans = 0; 48 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d%d",&p[i].x, &p[i].y); 49 // 先要对所有点排序,不然共线向量会有正负的区别 50 sort(p + 1, p + 1 + n); 51 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 52 { 53 int cnt = 0, tot = 0; 54 // cnt 是除了i这个点以外的重点的个数 55 // m是 这个点位置以外的点的个数 56 for(int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) 57 { 58 if(p[i] == p[j]) cnt++; 59 else Q[++tot] = p[j] - p[i]; // Q 放的是向量 60 } 61 update(ans, pw[cnt] - 1); // 这里是对重点们形成集合的贡献 62 // 计算方式是选出i这个点,之后从剩下的cnt这么多个点中选出至少一个的种类数 63 // 那么,贡献就是C(1,cnt)+C(2,cnt)+...+C(cnt,cnt) = 2^cnt - 1 64 65 for(int j = 1; j <= tot; j++) Q[j].reduce(); 66 sort(Q + 1, Q + 1 + tot); 67 for(int x = 1, y; x <= tot; x = y) 68 { 69 for(y = x; y <= tot && Q[x] == Q[y]; y++) ; 70 // y 出来的时候已经是 Q[x] != Q[y] 了,因此 y-x 正好是这一个角度上其他的点的个数 71 // 这时候,对答案的贡献是,从除了i这个点以外的重点中选出任意个数的点的种类数 72 // 和从这个角度上的其他点中选出至少1个点的种类数的乘积 73 update(ans, 1LL * pw[cnt] * (pw[y - x] - 1) % mod); 74 } 75 } 76 printf("%d ", ans); 77 } 78 79 int main() 80 { 81 init(); 82 int T;scanf("%d", &T); 83 while(T--) run(); 84 return 0; 85 }
