不想写。我想睡觉。
向生活低头。我写。QWQ
一、
面向对象的程序设计的重要特性之一就是代码重用,可以提高程序开发效率。
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名 { 派生类成员的声明 } ;
继承方式有三种 private public protected.默认情况下是private。
类的继承方式决定了派生类成员以及类外对象对从基类继承来的成员的访问权限。
class Person { public: Person(const char *Name,int Age,char Sex); char* getName(); int getAge(); char GetSex(); void Display(); private: char name[11]; char sex; int age; }; class Student::public Person { public: Student(char*pName,int Age,char Sex,char *pId,float score):Person(pName,Age,Sex); char *GetId(char *pId); float GetScore(); void Display(); private: char sid[9]; float score; } ; class Teacher:public Person { public: Teacher(char *pName,int Age,char Sex,char *pId,char *pprof,float Salary): Person(pName,Age,Sex); char *GetId(char *pId); char *Getprof(char *pprof); float GetSalary(); void Display(); private: char id[9]; char prof[12]; float salary; };
基类的构造函数和析构函数派生类不继承
派生类可以通过继承方式来控制派生类类内和类外对基类成员的访问。
尽管派生类继承了基类的全部成员。但其对基类成员的访问却受到基类成员自身访问权限和派生类继承方式的共同制约。
①基类的私有成员在派生类中以及派生类外均不可访问,只能由基类的成员函数访问。
②公用继承。基类中的公用成员和保护成员在派生类中访问属性不变,派生类外仅能访问公用成员。
③保护继承。基类中的公用成员和保护成员在派生类中均为保护成员,在派生类外不能访问从基类继承的任何成员。
④私有继承。基类中的公用成员和保护成员在派生类中均为私有成员,派生类外不能访问基类继承的任何成员。
(一)公用继承
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class Person { public: Person(const char *Name,int Age,char Sex) { strcpy(name,Name); age=Age;sex=Sex; } char *GetName() { return name; } int GetAge(){return age;} char GetSex(){return sex;} void Display() { cout<<"name:"<<name<<' '; cout<<"age:"<<age<<' '; cout<<"sex:"<<sex<<endl; } private: char name[11]; char sex; protected: int age; }; class Student:public Person { public://调用基类的构造函数初始化基类的数据成员。 Student(char *pName,int Age,char Sex,char *pId,float Score):Person(pName,Age,Sex) { strcpy(id,pId); score=Score; } char *GetId(){ return id;} float GetScore() {return score;} void Display() { cout<<"id:"<<id<<' '; cout<<"age:"<<age<<' '; cout<<"score:"<<score<<endl; } private: char id[9]; float score; }; int main() { char name[11]; cout<<"Enter a person's name:"; cin>>name; Person p1(name,29,'m'); p1.Display(); char pId[9]; cout<<"Enter a student's name:"; cin>>name; Student s1(name,19,'f',"03410101",95); cout<<"name:"<<s1.GetName()<<' '; cout<<"id:"<<s1.GetId()<<' '; cout<<"age:"<<s1.GetAge()<<' '; cout<<"sex:"<<s1.GetSex()<<' '; cout<<"score:"<<s1.GetScore()<<endl; return 0; }
(二)私有继承
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class Person { private: char name[11]; char sex; protected: int age; public: Person(const char *Name,int Age,char Sex) { strcpy(name,Name); age=Age;sex=Sex; } char *GetName(){return name;} int GetAge(){return age;} char GetSex(){return sex;} void Display() { cout<<"name:"<<name<<' '; cout<<"age:"<<age<<' '; cout<<"sex:"<<sex<<endl; } }; class Student:private Person { public: Student(char *pName,int Age,char Sex,char *pId,float Score):Person(pName,Age,Sex) { strcpy(id,pId); score=Score; } char *GetId(){return id;} float GetScore(){return score;} void Display() { cout<<"name:"<<GetName()<<' ';//************ cout<<"id:"<<id<<' '; cout<<"age:"<<GetAge()<<' ';//************ cout<<"sex:"<<GetSex()<<' ';//************ cout<<"score:"<<score<<' '; //************ } private: char id[11]; float score; }; int main() { Student s2("wang min",20,'m',"03410102",80); s2.Display(); return 0; }
二、派生类的构造函数
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class A { private: int a; public: A(int x):a(x) { cout<<"construct A"<<a<<endl; } }; class B:public A { private: int b,c; const int d; A x,y; public: B(int v):y(v+2),x(v+1),d(v+3),A(v) { b=v;c=v; cout<<"construct B"<<b<<" "<<c<<" "<<d<<endl; } }; int main() { B b1(10); return 0; }
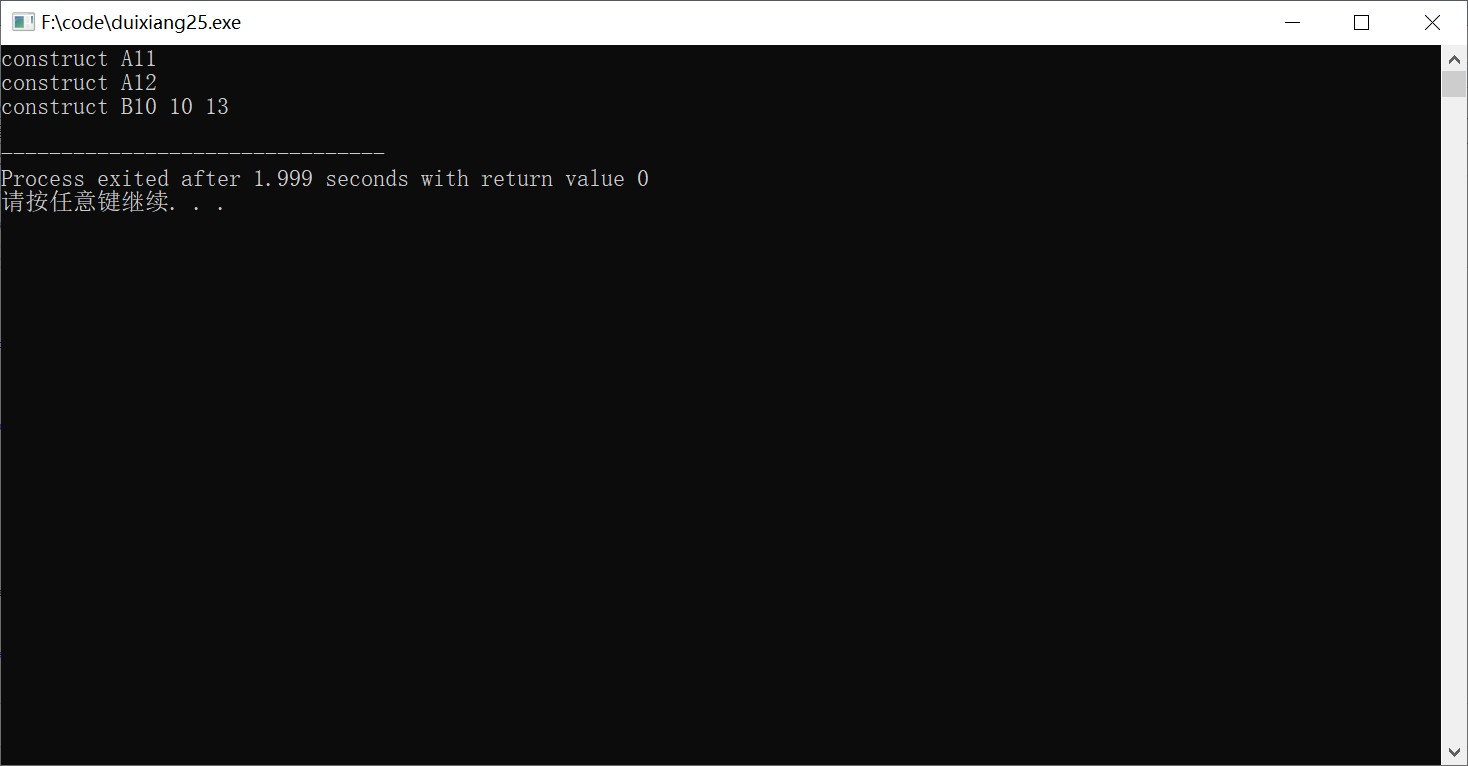
顺序:先祖先(先调用基类的构造函数) 再客人(对象x和y的初始化)后自己(派生类普通数据成员 b c d 的初始化)
三、派生类的析构函数
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class A { private: int a; public: A(int x):a(x) { cout<<"construct A"<<a<<endl; } ~A() { cout<<"destruct A"<<a<<endl; } }; class B:public A { private: int b,c; const int d; A x,y; public: B(int v):b(v),y(b+2),x(b+1),d(b),A(v) { c=v; cout<<"construct B"<<b<<" "<<c<<" "<<d<<endl; } ~B() { cout<<"destruct B"<<b<<" "<<c<<" "<<d<<endl; } }; int main() { B b1(10); return 0; }
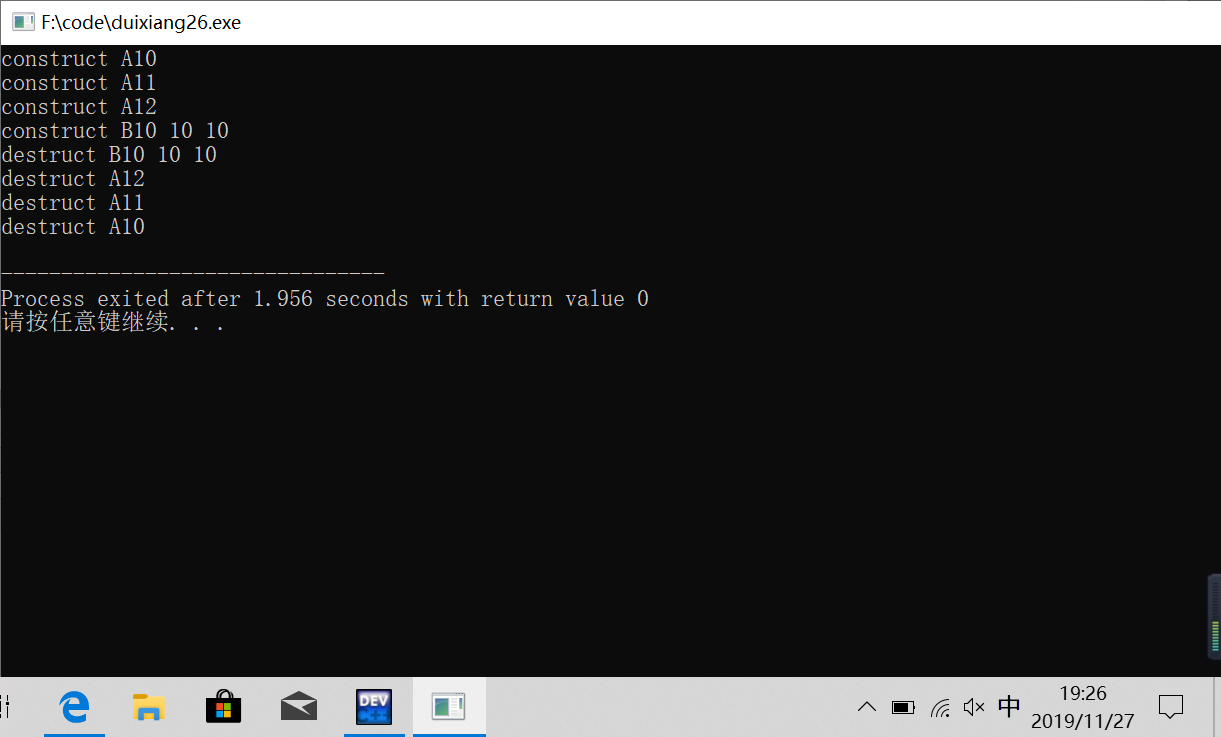
调用顺序:先自己 再客人(x,y)后祖先(基类)
四、多重继承
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名1,继承方式 基类名2,。。。继承方式 基类名n
{定义派生类自己的成员};
派生类继承其全部基类的所有成员(构造函数和析构函数除外)
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class CBase1 { protected: int b; public: CBase1(int x=0) { b=x; cout<<"Construct CBase1! "<<b<<endl; } ~CBase1() { cout<<"Destruct CBase1! "<<b<<endl; } }; class CBase2 { protected: int b; public: CBase2(int x=0) { b=x; cout<<"Construct CBase2! "<<b<<endl; } ~CBase2() { cout<<"Destruct CBase2! "<<b<<endl; } }; class CDerived:public CBase1,private CBase2 { protected: CBase1 b1; CBase2 b2; int d; public: CDerived(int x,int y,int z):b1(y),CBase2(y),b2(z),CBase1(x) { d=z; cout<<"Construct CDerived! "<<d<<endl; } ~CDerived() { cout<<"Destruct CDerived! "<<d<<endl; } }; int main() { CDerived d1(1,2,3); return 0; }
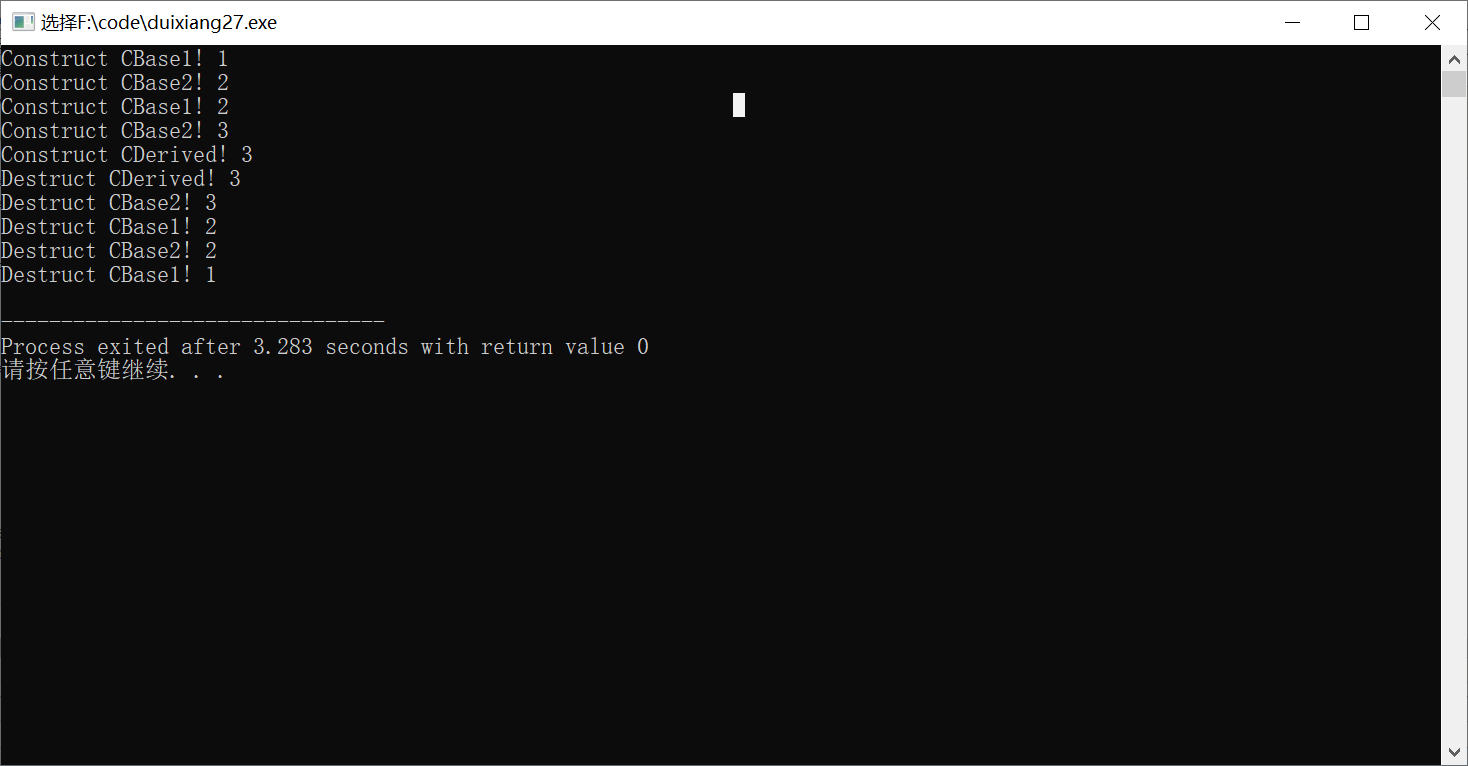
五、多重继承的二义性
(1)同不同基类继承同名成员时产生二义性。
由于派生类继承了基类的多个数据成员,会出现重名的现象。
如 C继承A和B,而A和B中都有数据成员b,那么在C中输出b,到底会输出哪个b,会出现错误。
这个是正确的代码,不正确的一行被注释掉了。
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class CBase1 { protected: int b; public: CBase1(int x=0) { b=x; } int GetB() { return b; } }; class CBase2 { protected: int b; public: CBase2(int x=0) { b=x; } int GetB() { return b; } }; class CDerived:public CBase1,private CBase2 { protected: int d; public: CDerived(int x,int y,int z):CBase1(x),CBase2(y) { d=z; } void Output() { //cout<<d<<" "<<b<<endl; cout<<d<<","<<CBase1::b<<","<<CBase2::b<<endl; } }; int main() { CDerived d1(1,2,3); d1.Output(); int x=d1.CBase1::GetB(); cout<<x<<endl; return 0; }
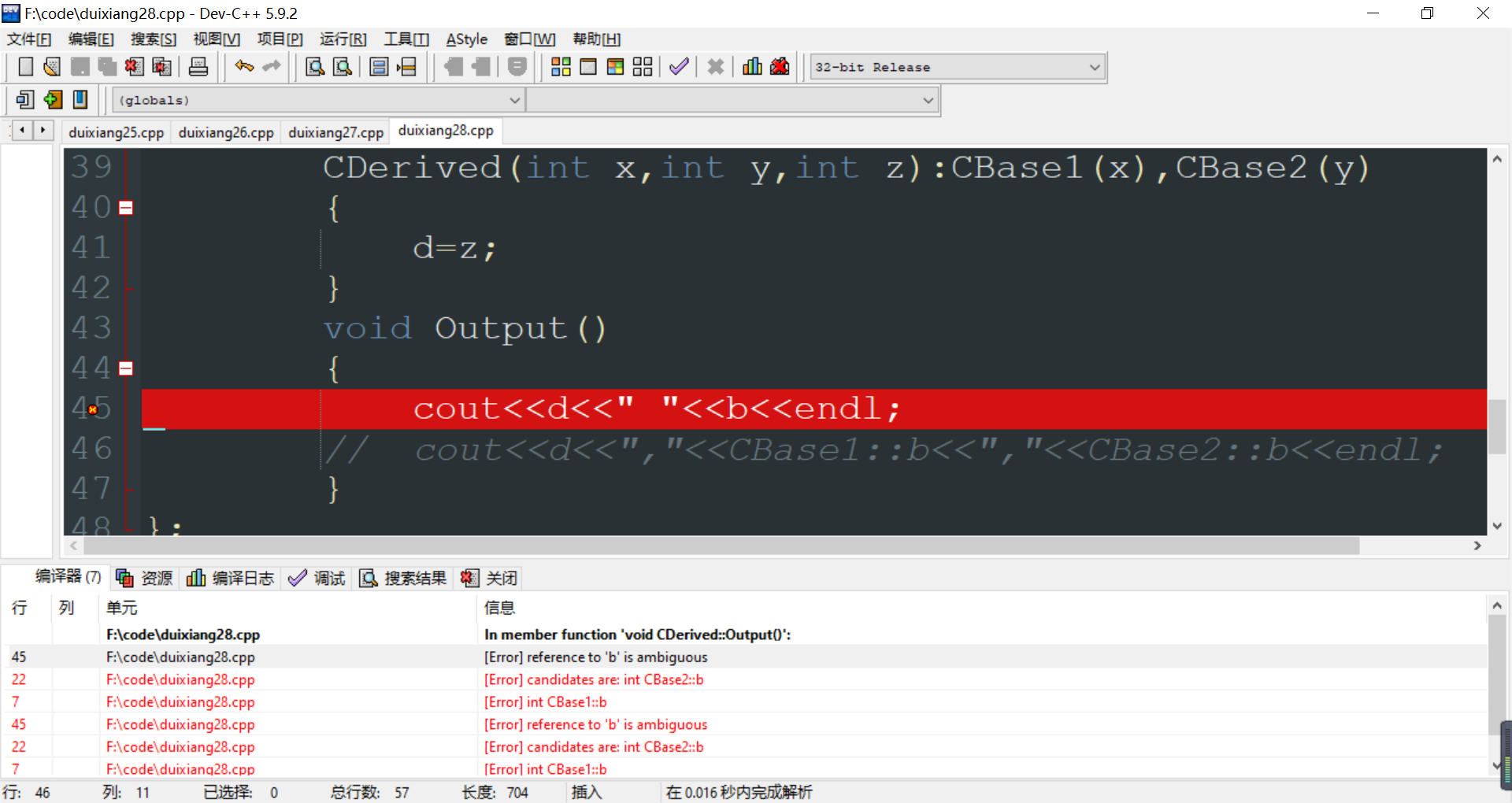
如果output函数这样改就会出错----b是模棱两可的。
(2)当底层派生类从不同路径上多次继承同一个基类时也会产生二义性。
这个是正确代码,不正确的被注释掉了。
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class CBase0 { protected: int b0; public: CBase0(int x=0) { b0=x; } int GetB0() { return b0; } }; class CBase1:public CBase0 { public: CBase1(int x=0):CBase0(x){} }; class CBase2:public CBase0 { public: CBase2(int x=0):CBase0(x){} }; class CDerived:public CBase1,public CBase2 { public: CDerived(int x,int y):CBase1(x),CBase2(y){} }; int main() { CDerived d1(1,2); // cout<<d1.GetB0()<<endl; cout<<d1.CBase1::GetB0(); return 0; }
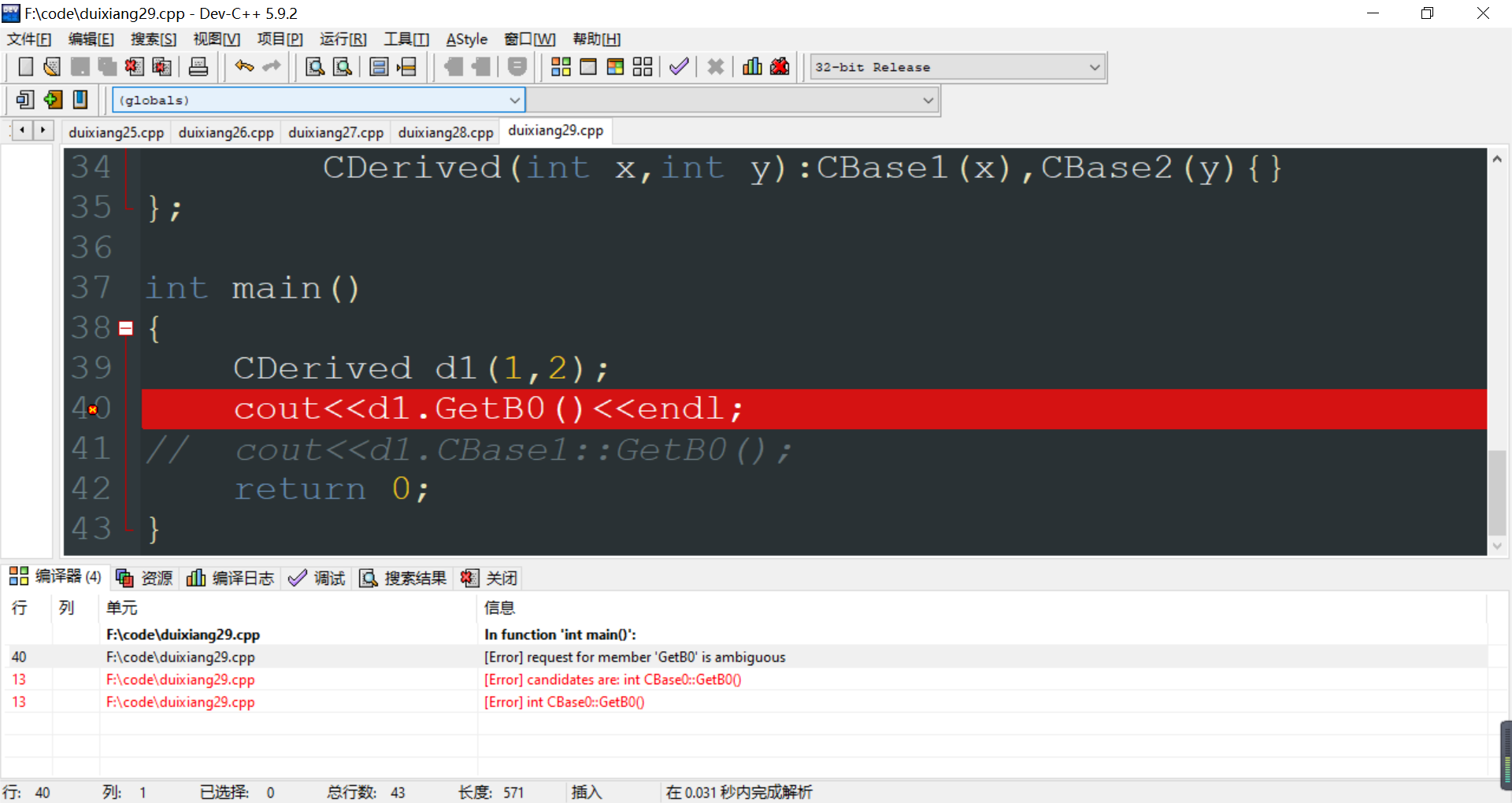
编译系统不知道调用从哪个基类继承而来的成员函数。
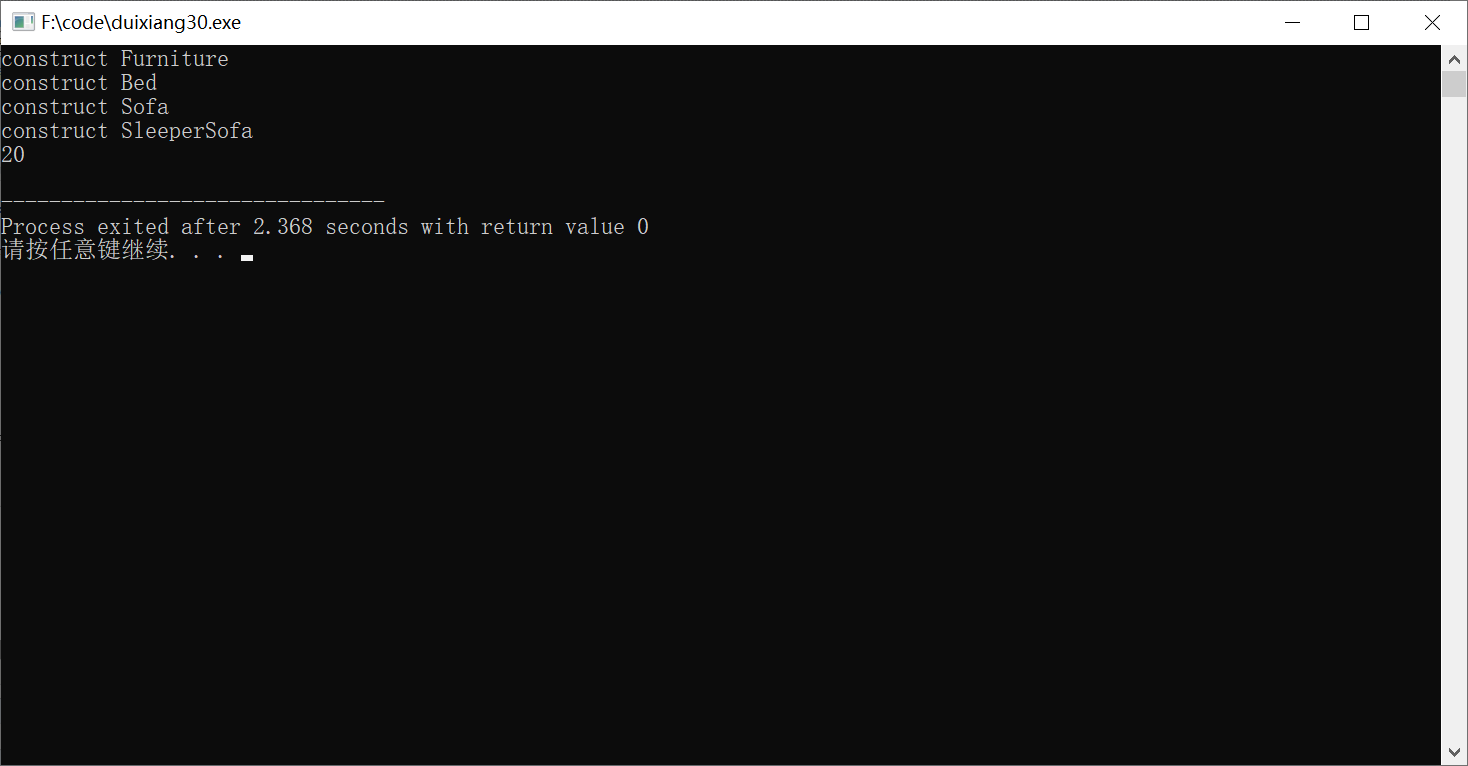
六、虚基类
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; class Furniture { public: Furniture() { cout<<"construct Furniture "<<endl; } void SetWeight(int i){weight=i;} int GetWeight(){return weight;} protected: int weight; }; class Bed:virtual public Furniture { public: Bed() { cout<<"construct Bed"<<endl; } void Sleep() { cout<<"Sleeping... "; } }; class Sofa:virtual public Furniture { public: Sofa() { cout<<"construct Sofa"<<endl; } void WatchTV(){cout<<"Watching TV. ";} }; class SleeperSofa:public Bed,public Sofa { public: SleeperSofa():Sofa(),Bed() { cout<<"construct SleeperSofa"<<endl; } void FoldOut(){cout<<"Fold out the sofa. ";} }; int main() { SleeperSofa ss; ss.SetWeight(20); cout<<ss.GetWeight()<<endl; return 0; }