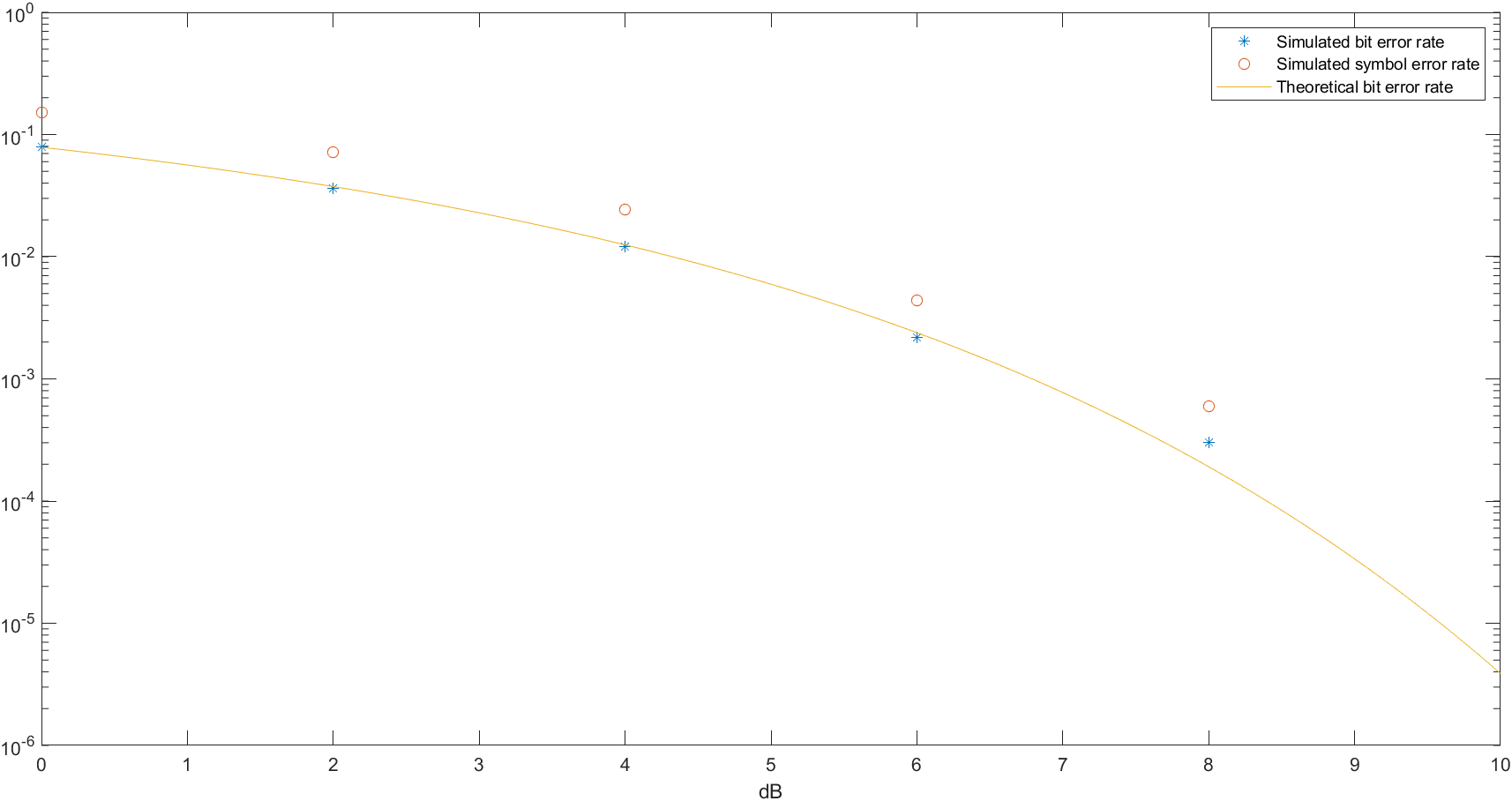
The Optimum Detector and Probability of Error of Binary PSK
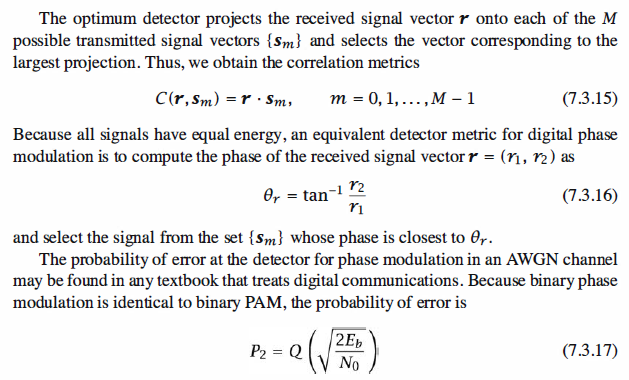
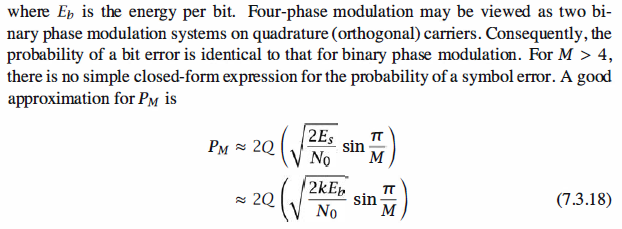
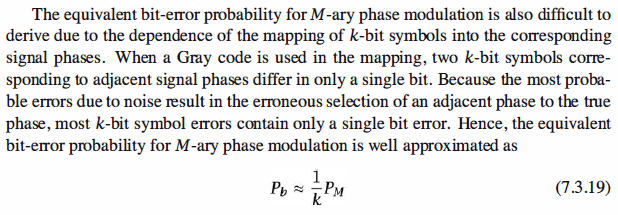
Matlab Coding,

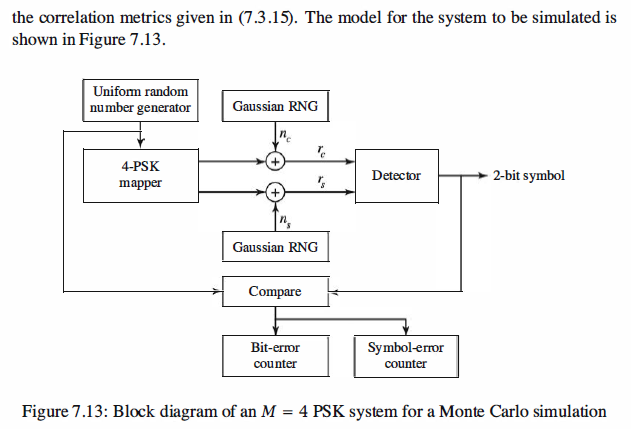
Note, The detector maks a decision which is based on selecting the signal point corresponding in the largest projection.
1 % MATLAB script 2 echo on 3 SNRindB1=0:2:10; 4 SNRindB2=0:0.1:10; 5 for i=1:length(SNRindB1), 6 [pb,ps]=cm_sm32(SNRindB1(i)); % simulated bit and symbol error rates 7 smld_bit_err_prb(i)=pb; 8 smld_symbol_err_prb(i)=ps; 9 echo off ; 10 end; 11 echo on; 12 for i=1:length(SNRindB2), 13 SNR=exp(SNRindB2(i)*log(10)/10); % signal-to-noise ratio 14 theo_err_prb(i)=Qfunct(sqrt(2*SNR)); % theoretical bit-error rate 15 echo off ; 16 end; 17 echo on ; 18 % Plotting commands follow 19 semilogy(SNRindB1,smld_bit_err_prb,'*'); 20 xlabel('dB'); 21 hold 22 semilogy(SNRindB1,smld_symbol_err_prb,'o'); 23 semilogy(SNRindB2,theo_err_prb); 24 25 26 function [pb,ps]=cm_sm32(snr_in_dB) 27 % [pb,ps]=cm_sm32(snr_in_dB) 28 % CM_SM32 finds the probability of bit error and symbol error for the 29 % given value of snr_in_dB, signal-to-noise ratio in dB. 30 N=10000; 31 E=1; % energy per symbol 32 snr=10^(snr_in_dB/10); % signal-to-noise ratio 33 sgma=sqrt(E/snr)/2; % noise variance
34 % the signal mapping 35 s00=[1 0]; 36 s01=[0 1]; 37 s11=[-1 0]; 38 s10=[0 -1];
39 % generation of the data source 40 for i=1:N, 41 temp=rand; % a uniform random variable between 0 and 1 42 if (temp<0.25), % With probability 1/4, source output is "00." 43 dsource1(i)=0; 44 dsource2(i)=0; 45 elseif (temp<0.5), % With probability 1/4, source output is "01." 46 dsource1(i)=0; 47 dsource2(i)=1; 48 elseif (temp<0.75), % With probability 1/4, source output is "10." 49 dsource1(i)=1; 50 dsource2(i)=0; 51 else % With probability 1/4, source output is "11." 52 dsource1(i)=1; 53 dsource2(i)=1; 54 end; 55 end;
56 % detection and the probability of error calculation 57 numofsymbolerror=0; 58 numofbiterror=0; 59 for i=1:N, 60 % The received signal at the detector, for the ith symbol, is: 61 n(1)=gngauss(sgma); 62 n(2)=gngauss(sgma); 63 if ((dsource1(i)==0) & (dsource2(i)==0)), 64 r=s00+n; 65 elseif ((dsource1(i)==0) & (dsource2(i)==1)), 66 r=s01+n; 67 elseif ((dsource1(i)==1) & (dsource2(i)==0)), 68 r=s10+n; 69 else 70 r=s11+n; 71 end;
72 % The correlation metrics are computed below. 73 c00=dot(r,s00); 74 c01=dot(r,s01); 75 c10=dot(r,s10); 76 c11=dot(r,s11);
77 % The decision on the ith symbol is made next. 78 c_max=max([c00 c01 c10 c11]); 79 if (c00==c_max), 80 decis1=0; decis2=0; 81 elseif (c01==c_max), 82 decis1=0; decis2=1; 83 elseif (c10==c_max), 84 decis1=1; decis2=0; 85 else 86 decis1=1; decis2=1; 87 end;
88 % Increment the error counter, if the decision is not correct. 89 symbolerror=0; 90 if (decis1~=dsource1(i)), 91 numofbiterror=numofbiterror+1; 92 symbolerror=1; 93 end; 94 if (decis2~=dsource2(i)), 95 numofbiterror=numofbiterror+1; 96 symbolerror=1; 97 end; 98 if (symbolerror==1), 99 numofsymbolerror = numofsymbolerror+1; 100 end; 101 end;
102 ps=numofsymbolerror/N; % since there are totally N symbols 103 pb=numofbiterror/(2*N); % since 2N bits are transmitted
Simulation result
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis