Clock Synchronization
In this chapter we have seen that a popular implementation of the
optimal receiver makes use of matched filters and samplers at the matched filter output.
In all these cases we assumed that the receiver has complete knowledge of the
sampling instant and can sample perfectly at this time. Systems that achieve this type
of synchronization between the transmitter and the receiver are called timing recovery,
clock-synchronization, or symbol-synchronization systems.
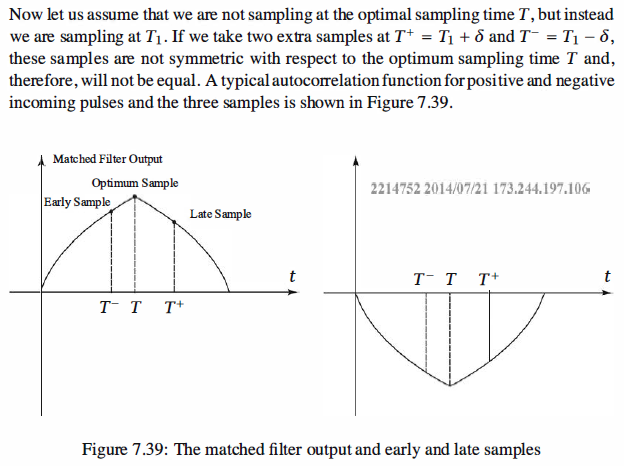
A simple implementation of clock synchronization employs an early-late gate.


Summary

Matlab Coding

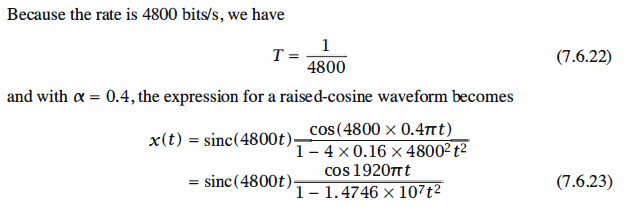
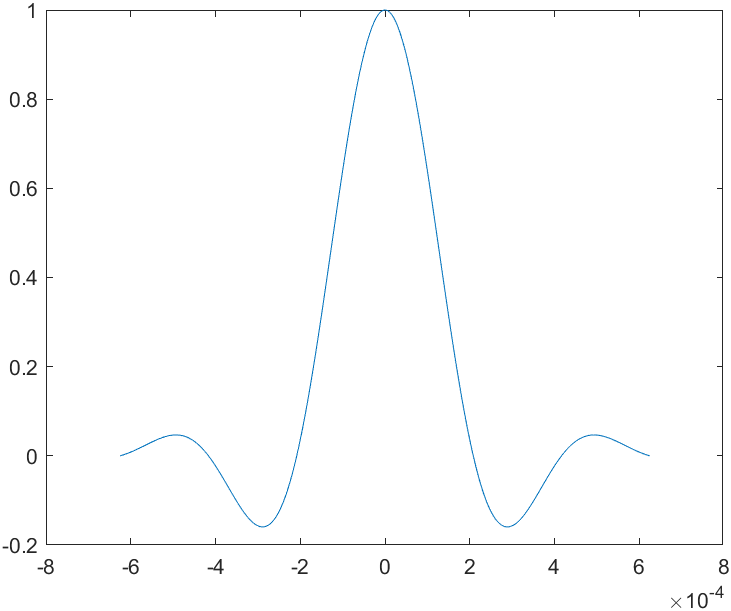
1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 7.14. 2 echo on 3 alpha=0.4; 4 T=1/4800; 5 t=[-3*T:1.001*T/100:3*T]; 6 x=sinc(t./T).*(cos(pi*alpha*t./T)./(1-4*alpha^2*t.^2/T^2)); 7 pause % Press any key to see a plot of x(t). 8 plot(t,x)
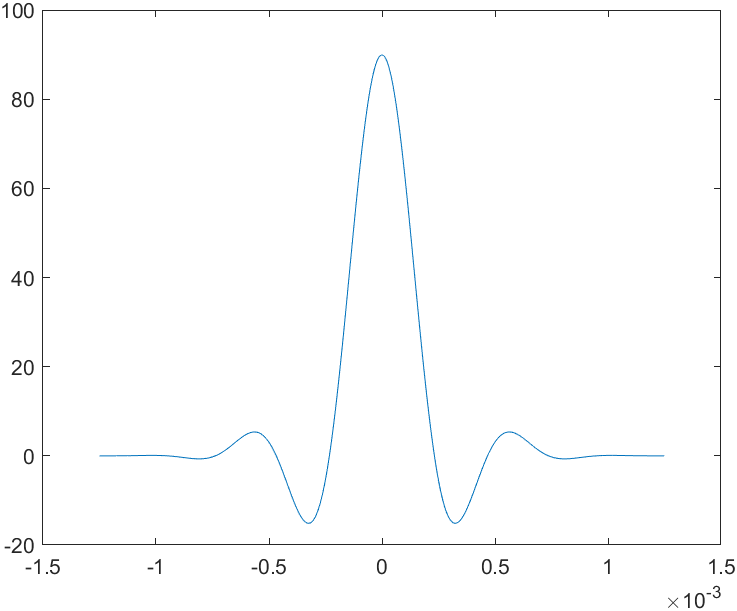
9 y=xcorr(x); 10 ty=[t-3*T,t(2:length(t))+3*T]; 11 pause % Press any key to see a plot of the autocorrelation of x(t). 12 plot(ty,y);
13 d=60; % Early and late advance and delay 14 ee=0.01; % Precision 15 e=1; % Step size 16 n=700; % The incorrect sampling time 17 while abs(abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d)))>=ee 18 if abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d))>0 19 n=n+e; 20 elseif abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d))<0 21 n=n-e; 22 end 23 echo off ; 24 end 25 echo on ; 26 pause % Press any key to see the corrected sampling time 27 n
n =
600

28 n=500; % Another incorrect sampling time 29 while abs(abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d)))>=ee 30 if abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d))>0 31 n=n+e; 32 elseif abs(y(n+d))-abs(y(n-d))<0 33 n=n-e; 34 end 35 echo off ; 36 end 37 echo on ; 38 pause % Press any key to see the corrected sampling time 39 n
n =
600
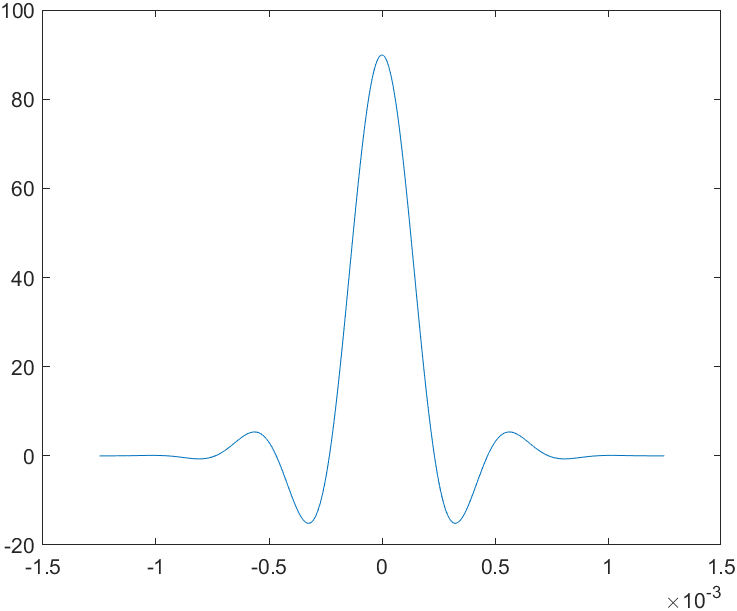
In both cases the early-late gate corrects the sampling time to the optimum 600.
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis