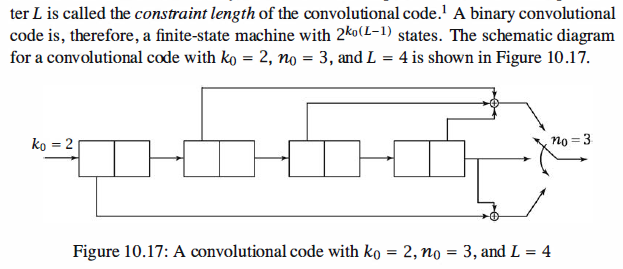
Convolutional Codes
In block codes each sequence of k information bits is mapped into a sequence of n
channel inputs in a fixed way regardless of the previous information bits. In convolutional
codes each sequence of ko information bits is mapped into a channel input
sequence of length no, but the encoder output sequence depends not only on the most
recent ko information bits but also on the last (L - 1) ko inputs of the encoder. Therefore,
the encoder has the structure of a finite-state machine, where at each time instance
the output sequence depends not only on the input sequence but also on the state of the
encoder, which is determined by the last (L - 1) ko inputs of the encoder. The parameter
L is called the constraint length of the convolutional code.


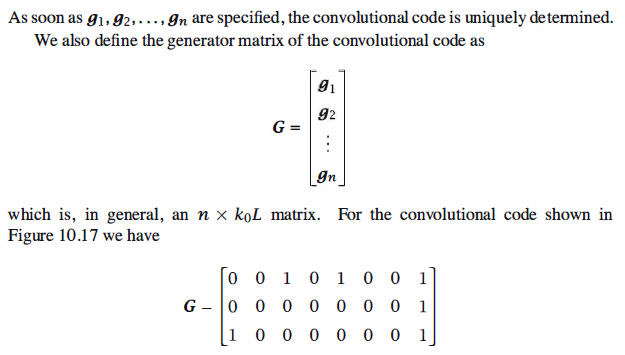
Matlab Coding



1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 10.13. 2 k0=2; 3 g=[0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1;0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1;1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]; 4 input=[1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1]; 5 output=cnv_encd(g,k0,input); 6 7 8 function output=cnv_encd(g,k0,input) 9 % cnv_encd(g,k0,input) 10 % determines the output sequence of a binary convolutional encoder 11 % g is the generator matrix of the convolutional code 12 % with n0 rows and l*k0 columns. Its rows are g1,g2,...,gn. 13 % k0 is the number of bits entering the encoder at each clock cycle. 14 % input is the binary input seq. 15 16 % Check to see if extra zero-padding is necessary. 17 if rem(length(input),k0) > 0 18 input=[input,zeros(size(1:k0-rem(length(input),k0)))]; 19 end 20 n=length(input)/k0; 21 % Check the size of matrix g. 22 if rem(size(g,2),k0) > 0 23 error('Error, g is not of the right size.') 24 end 25 % Determine l and n0. 26 l=size(g,2)/k0; 27 n0=size(g,1); 28 % add extra zeros 29 u=[zeros(size(1:(l-1)*k0)),input,zeros(size(1:(l-1)*k0))]; 30 % Generate uu, a matrix whose columns are the contents of 31 % conv. encoder at various clock cycles. 32 u1=u(l*k0:-1:1); 33 for i=1:n+l-2 34 u1=[u1,u((i+l)*k0:-1:i*k0+1)]; 35 end 36 uu=reshape(u1,l*k0,n+l-1); 37 % Determine the output 38 output=reshape(rem(g*uu,2),1,n0*(l+n-1));
>> output
output =
Columns 1 through 20
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0
Columns 21 through 36
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis