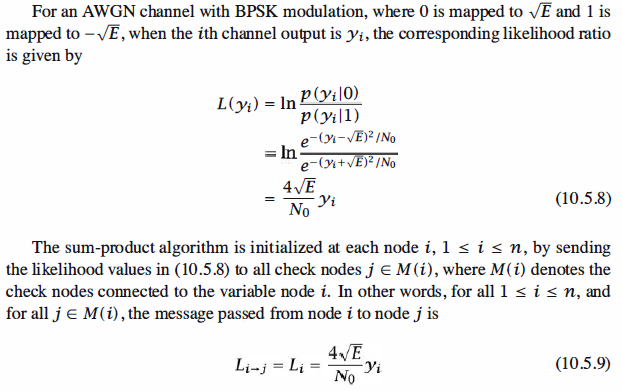
The Sum-Product Algorithm
The sum-product algorithm, which belongs to the class of message-passing algorithms,
is an iterative decoding algorithm for LDPC codes that is based on passing likelihood
ratios between variable and check nodes. The variable nodes receive the outputs of the
channel and pass the likelihoods of codeword components to the check nodes. Each
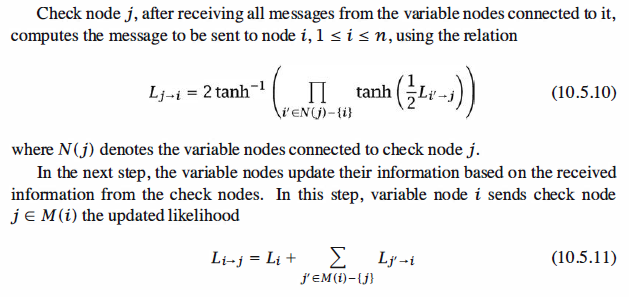
check node updates the received likelihoods using the information it has gathered from
all variable nodes that are connected to it and sends the updated likelihoods back to
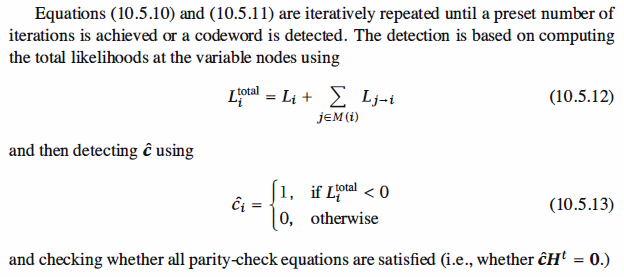
the check nodes. This process is repeated until a predetermined maximum number
of iterations is achieved or until a codeword is decoded (i.e., all check equations are satisfied).
Matlab Coding
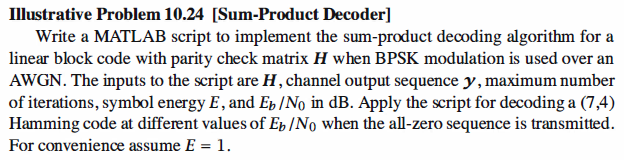
1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 10.24 2 3 H = [1 0 1 1 1 0 0 4 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 5 0 1 1 1 0 0 1]; % Code parity-check matrix 6 E = 1; % Symbol energy 7 n = size(H,2); % Codeword length 8 f = size(H,1); % Number of parity check bits 9 R = (n-f)/n; % Code rate 10 EbN0_dB = 2; 11 EbN0 = 10^(EbN0_dB/10); 12 noise_variance = E/(2*R*EbN0); 13 noise = sqrt(noise_variance)*randn(1,n); 14 y = ones(1,n) + noise; % Assuming the all-zero codeword is transmitted 15 max_it = 50; 16 [c check] = sp_decoder(H,y,max_it,E,EbN0_dB); 17 18 19 20 function [c check] = sp_decoder(H,y,max_it,E,EbN0_dB) 21 %SP_DECODER is the Sum-Product decoder for a linear block code code with BPSK modulation 22 % [c check] = sp_decoder(H,y,max_it,N0) 23 % y channel output 24 % H parity-check matrix of the code 25 % max_it maximum number of iterations 26 % E symbol energy 27 % EbN0_dB SNR/bit (in dB) 28 % c decoder output 29 % check is 0 if c is a codeword and is 1 otherwise 30 31 n = size(H,2); % Length of the code 32 f = size(H,1); % Number of parity checks 33 R = (n-f)/n; % Rate 34 Eb = E/R; % Energy/bit 35 N0 = Eb*10^(-EbN0_dB/10); % one-sided noise PSD 36 L_i = 4*sqrt(E)*y/N0; 37 [j i] = find(H); 38 nz = length(find(H)); 39 L_j2i = zeros(f,n); 40 L_i2j = repmat(L_i,f,1) .* H; 41 L_i2j_vec = L_i + sum(L_j2i,1); 42 % Decision making: 43 L_i_total = L_i2j_vec; 44 for l = 1:n 45 if L_i_total(l) <= 0 46 c_h(l) = 1; 47 else 48 c_h(l) = 0; 49 end 50 end 51 s = mod(c_h*H',2); 52 if nnz(s) == 0 53 c = c_h; 54 else 55 it = 1; 56 while ((it <= max_it) && (nnz(s)~=0)) 57 % Variable node updates: 58 for idx = 1:nz 59 L_i2j(j(idx),i(idx)) = L_i2j_vec(i(idx)) - L_j2i(j(idx),i(idx)); 60 end 61 % Check node updates: 62 for q = 1:f 63 F = find(H(q,:)); 64 L_j2i_vec(q) = prod(tanh(0.5*L_i2j(q,F(:))),2); 65 end 66 for idx = 1:nz 67 L_j2i(j(idx),i(idx)) = 2*atanh(L_j2i_vec(j(idx)) /... 68 tanh(0.5*L_i2j(j(idx),i(idx)))); 69 end 70 L_i2j_vec = L_i + sum(L_j2i,1); 71 % Decision making: 72 L_i_total = L_i2j_vec; 73 for l = 1:n 74 if L_i_total(l) <= 0 75 c_h(l) = 1; 76 else 77 c_h(l) = 0; 78 end 79 end 80 s = mod(c_h*H',2); 81 it = it + 1; 82 end 83 end 84 c = c_h; 85 check = nnz(s); 86 if (check > 0) 87 check = 1; 88 end
>> EbN0_dB
EbN0_dB =
2
>> c
c =
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
>> check
check =
0
>> EbN0_dB
EbN0_dB =
-4
>> c
c =
0 0 0 0 1 0 0
>> check
check =
1
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis