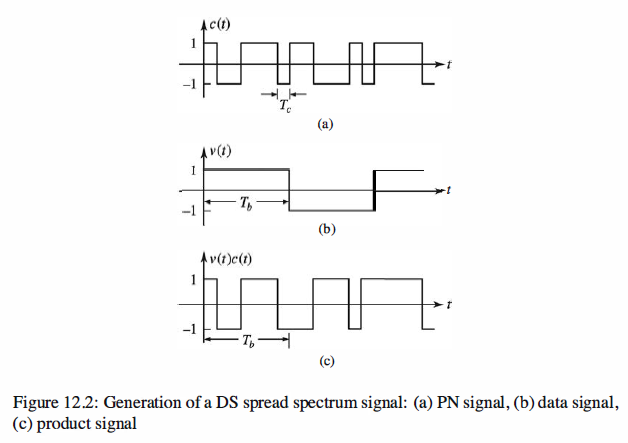
Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum Systems
Let us consider the transmission of a binary information sequence by means of binary
PSK. The information rate is R bits per second, and the bit interval is Tb = 1 / R seconds.
The available channel bandwidth is Be hertz, where Be » R. At the modulator
the bandwidth of the information signal is expanded to W = Be Hz by shifting the
phase of the carrier pseudorandornly at a rate of W times per second according to the
pattern of the PN generator. The resulting modulated signal is called a DS spread spectrum signal.



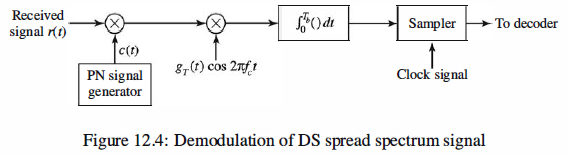
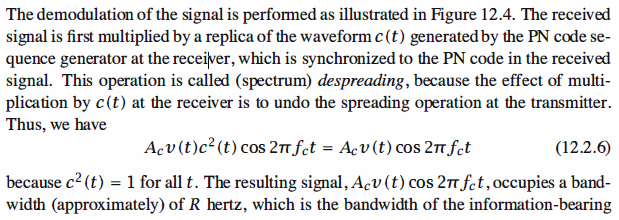
Signal Demodulation

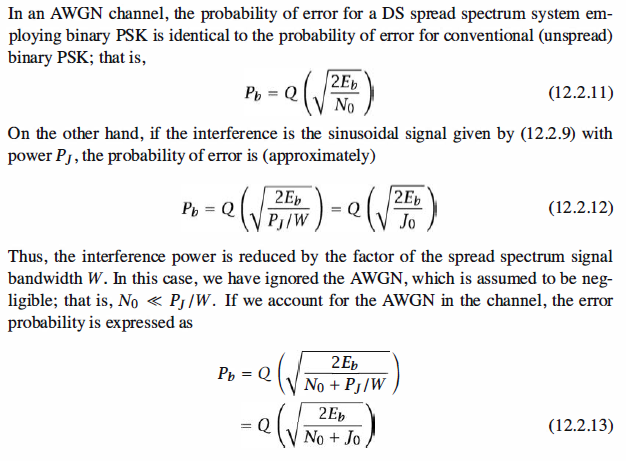
Probability of Error
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis