Frequency-Hopped Spread Spectrum
In frequency-hopped (FH) spread spectrum the available channel bandwidth W is subdivided
into a large number of nonoverlapping frequency slots. In any signaling interval
the transmitted signal occupies one or more of the available frequency slots. The selection
of the frequency slot(s) in each signal interval is made pseudorandomly according
to the output from a PN generator.
A block diagram of the transmitter and receiver for a FH spread spectrum system
is shown in Figure 12.10.
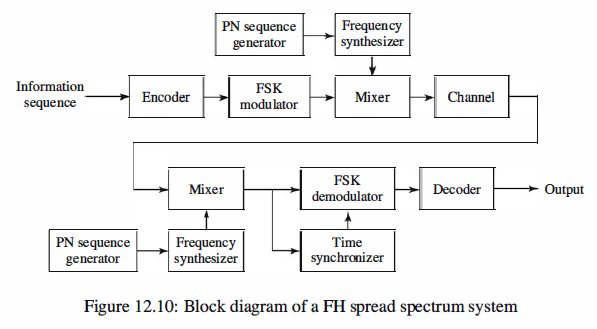
The modulation is either binary or M-ary FSK (MFSK).
For example, if binary FSK is employed, the modulator selects one of two frequencies, say,
f o or Ji , corresponding to the transmission of a 0 or a 1. The resulting binary FSK
signal is translated in frequency by an amount that is determined by the output sequence
from a PN generator, which is used to select a frequency fc that is synthesized by the
frequency synthesizer. This frequency-translated signal is transmitted over the channel.
For example, by taking m bits from the PN generator, we may specify 2m - 1 possible
carrier frequencies.
At the receiver, there is an identical PN sequence generator, synchronized with
the received signal, which is used to control the output of the frequency synthesizer.
Thus, the pseudorandom frequency translation introduced at the transmitter is removed
at the demodulator by mixing the synthesizer output with the received signal. The
resultant signal is then demodulated by means of an FSK demodulator. A signal for
maintaining synchronism of the PN sequence generator with the FH received signal is
usually extracted from the received signal.
The frequency-hopping rate, denoted as Rh, may be selected to be equal to the
symbol rate, lower than the symbol rate, or higher than the symbol rate. If Rh is equal
to or lower than the symbol rate, the FH system is called a slow-hopping system. If Rh
is higher than the symbol rate-that is, there are multiple hops per symbol-the FH
system is called a fast-hopping system. We shall consider only a hopping rate equal to
the symbol rate.
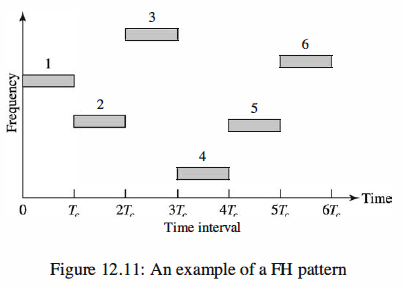
Figure 12.11 illustrates a FH signal pattern.
Probability of Error for FH Signals
Let us consider a FH system in which binary FSK is used to transmit the digital information.
The hop rate is 1 hop per bit. The demodulation and detection are noncoherent.
In an AWGN channel, the probability of error of such a system is

Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis