ADI:ARM Debug Interface,出到现在共有五代:
1)version1 and version 2:只针对ARM7TDMI和ARM9的processor;
2)version 3:只针对ARM10的processor family;
3)ADIv4:使用与所有的ARMv6 architecture;
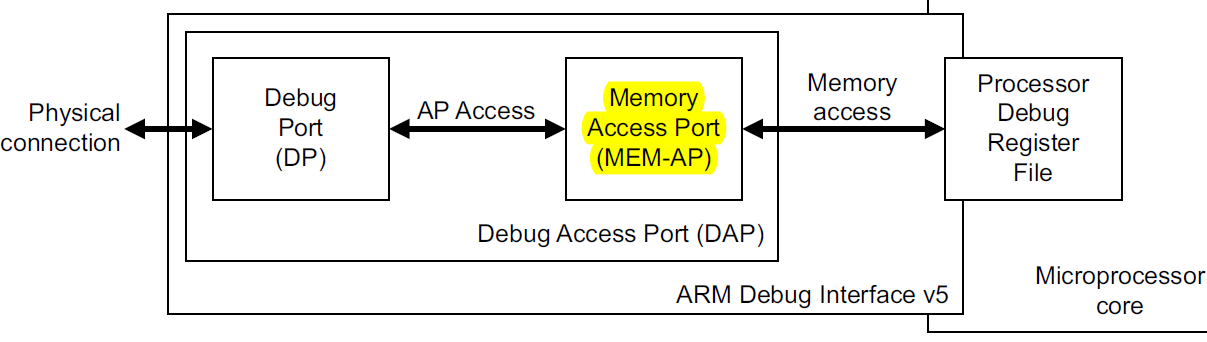
4)ADIv5.2:针对ARMv7-A和ARMv8-A的processor;分为了Access Port(AP) architecture和Debug Port(DP) architecture
DP包括三类:1)JTAG-DP; 满足IEEE 1149.1的接口;
2)SW-DP; 基于packet-based protocol(host-target req, target-host ack, data transfer)
3)SWJ-DP; can switch between SWD and JTAG
AP包括两类:1)MEM-AP(扩展到AXI/ACE); a memory-mapped resource such as a debug peripheral
2)JTAG-AP; a legacy jtag device
DP来连接外部的host,AP来访问内部的debug component registers
由
ADIv5 DAP
CoreSight components
CoreSIght debug architecture
能提供的功能包括:
1)Embedded core debug functionality,由arm core和ETM这样的module来保证
1)modify the contents of the internal registers and the memory system;
2)read the contents of the internal registers and the memory system;
3)program debug events,在某个event被触发之后,processor可以由外部可控;
4)Force the processor to enter and exit debug state;
5)Trace program flow around programmable events;
2)System debug functionality,系统性的debug
1)Components within an embeded SoC
program trace
cross-triggering mechanisms
2)The interconnection fabric of the system
trace access on the interconnection fabric
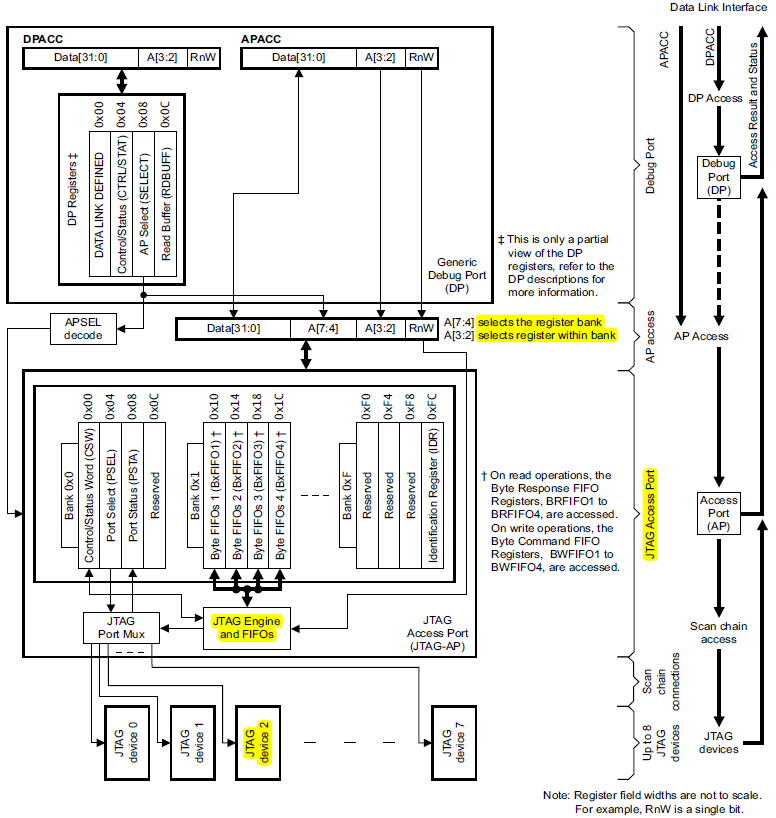
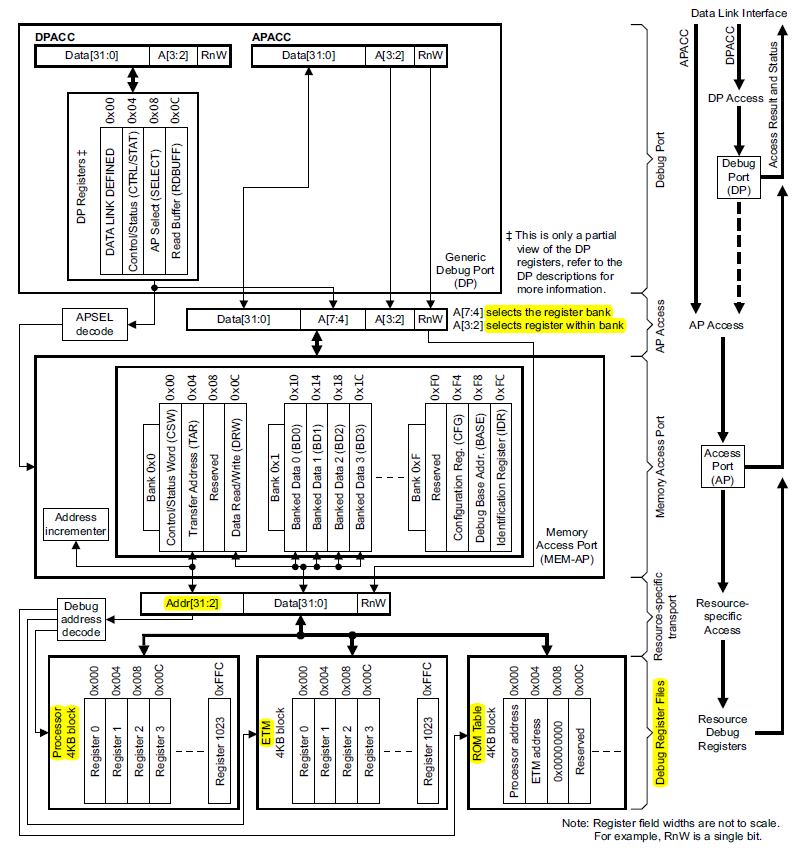
从DP到AP的access:
由AP_Select选择不同的AP,
address的A[7:4]选择不同的bank;
address的A[3:2]选择不同的register;
四个寄存器保存每个ap的一些信息
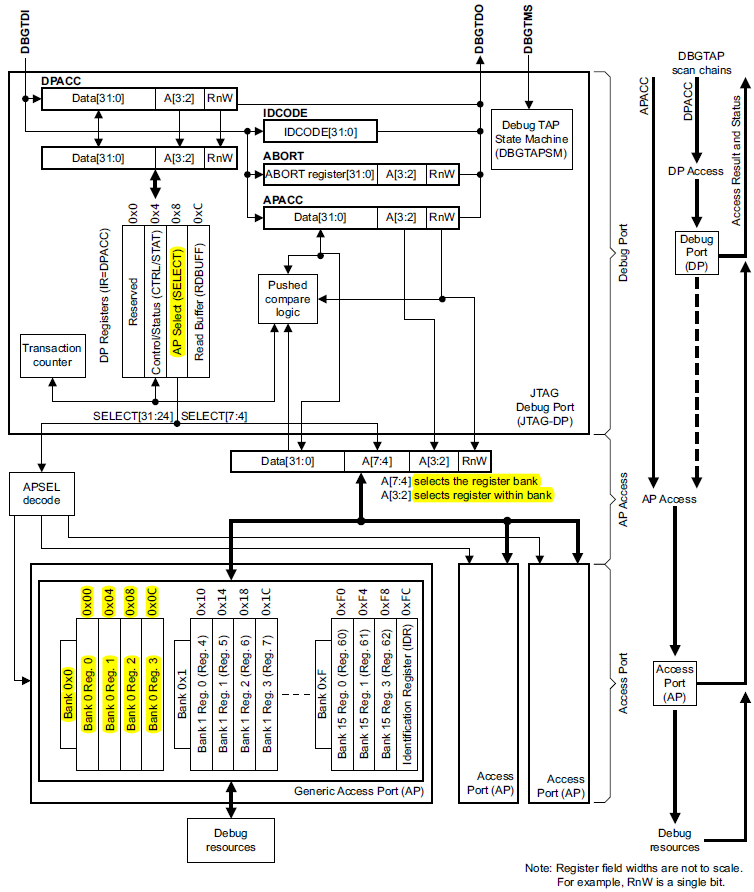
在DP的implement过程中,
首先选择不同的DP接口:

选择每个JTAG-AP的JTAG scan chain的个数;
选择每个scan chain中包含的TAP的个数,主要是为了嵌套扩展;
在AP的implement过程中,
首先选择MEM-AP或者JTAG-AP,
在架构方面。可以选择MEM-AP直接连接到debug register file或者system bus再连接到debug register file,
结合ROM_TABLE进行MEM-AP的address map以及bus width的决定。
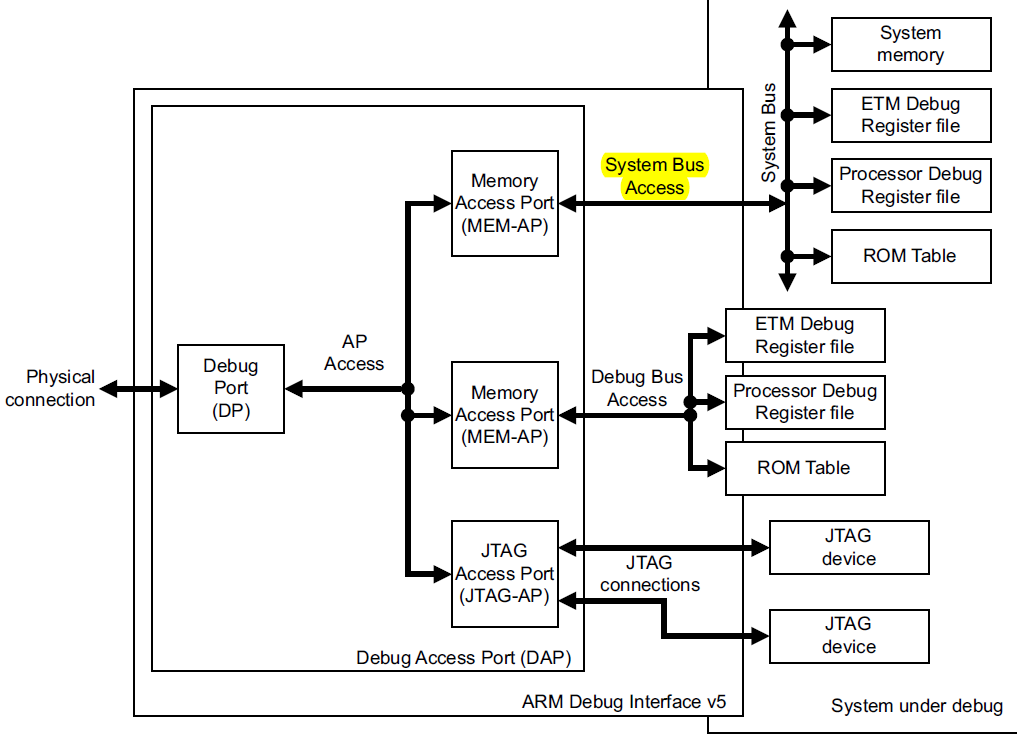
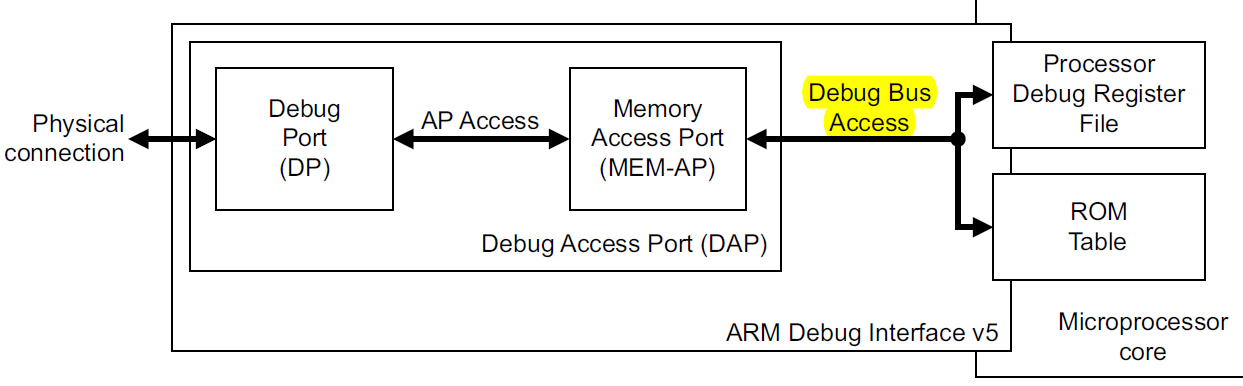

从DP到MEM-AP的access的路径图:
前半部分的memory map与DP到AP的相同,
但是到mem-ap的部分,必须有一个rom table来进行寄存器的访问。
同样的DP到JTAG-AP的路径图:
TDO的信号经过一个mux来回到jtag的接口ap中。