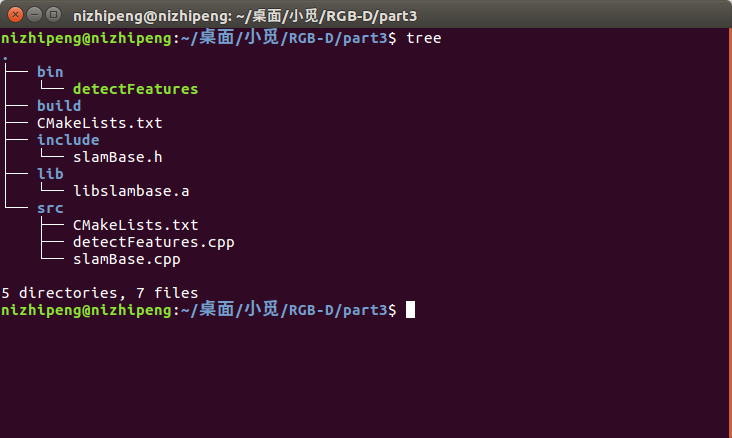
include头文件中有slamBase.h
# pragma once // 各种头文件 // C++标准库 #include <fstream> #include <vector> using namespace std; // OpenCV #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> //PCL #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> // 类型定义 typedef pcl::PointXYZRGBA PointT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud; // 相机内参结构 struct CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS { double cx, cy, fx, fy, scale; }; // 函数接口 // image2PonitCloud 将rgb图和深度图转换为点云 PointCloud::Ptr image2PointCloud( cv::Mat& rgb, cv::Mat& depth, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ); // point2dTo3d 将单个点从图像坐标转换为空间坐标 // input: 3维点Point3f (u,v,d) cv::Point3f point2dTo3d( cv::Point3f& point, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera );
其中有三个部分,相机内参结构,rgb图和深度图转点云,2维像素点转3维空间点坐标(头文件中函数原型)。
src中源程序slamBase.cpp
#include "slamBase.h"
//传入rgb, depth, 和相机内参 PointCloud::Ptr image2PointCloud( cv::Mat& rgb, cv::Mat& depth, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { PointCloud::Ptr cloud ( new PointCloud ); for (int m = 0; m < depth.rows; m++) for (int n=0; n < depth.cols; n++) { // 获取深度图中(m,n)处的值 ushort d = depth.ptr<ushort>(m)[n]; // d 可能没有值,若如此,跳过此点 if (d == 0) continue; // d 存在值,则向点云增加一个点 PointT p; // 计算这个点的空间坐标 p.z = double(d) / camera.scale; p.x = (n - camera.cx) * p.z / camera.fx; p.y = (m - camera.cy) * p.z / camera.fy; // 从rgb图像中获取它的颜色 // rgb是三通道的BGR格式图,所以按下面的顺序获取颜色 p.b = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3]; p.g = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+1]; p.r = rgb.ptr<uchar>(m)[n*3+2]; // 把p加入到点云中 cloud->points.push_back( p ); } // 设置并保存点云 cloud->height = 1; cloud->width = cloud->points.size(); cloud->is_dense = false; return cloud; } //像素坐标转为3维点 cv::Point3f point2dTo3d( cv::Point3f& point, CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS& camera ) { cv::Point3f p; // 3D 点 p.z = double( point.z ) / camera.scale; //point.z d p.x = ( point.x - camera.cx) * p.z / camera.fx; //point.x u p.y = ( point.y - camera.cy) * p.z / camera.fy; //point.y v return p; }
和实现程序slamBase.cpp在同一文件夹下的CMakeLists.txt
# 增加PCL库的依赖 FIND_PACKAGE( PCL REQUIRED COMPONENTS common io ) list(REMOVE_ITEM PCL_LIBRARIES "vtkproj4") # use this in Ubuntu 16.04 # 增加opencv的依赖 FIND_PACKAGE( OpenCV REQUIRED ) INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} ) # 添加头文件和库文件 ADD_DEFINITIONS( ${PCL_DEFINITIONS} ) INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES( ${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS} ) LINK_LIBRARIES( ${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS} ) #把slamBase.cpp编译成 slamBase 库,并把该库里调到的OpenCV和PCL的部分,和相应的库链接起来 ADD_LIBRARY( slambase slamBase.cpp ) # 实现文件 slamBase.cpp TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES( slambase ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} ) ADD_EXECUTABLE( detectFeatures detectFeatures.cpp ) # 可执行程序 detectFeatures.cpp TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES( detectFeatures slambase ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} )
库函数:ADD_LIBRARY( slambase slamBase.cpp ) TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES( slambase ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} )
可执行程序:ADD_EXECUTABLE( detectFeatures detectFeatures.cpp ) TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES( detectFeatures slambase ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} ) 使用到上诉的库
#include<iostream> #include "slamBase.h" // using namespace std; // OpenCV 特征检测模块 #include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp> // #include <opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp> // use this if you want to use SIFT or SURF #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> int main( int argc, char** argv ) { // 声明并从data文件夹里读取两个rgb与深度图 cv::Mat rgb1 = cv::imread( "./data/rgb20.png"); cv::Mat rgb2 = cv::imread( "./data/rgb21.png"); cv::Mat depth1 = cv::imread( "./data/depth20.png", -1); cv::Mat depth2 = cv::imread( "./data/depth21.png", -1); // 声明特征提取器与描述子提取器 cv::Ptr<cv::FeatureDetector> detector; cv::Ptr<cv::DescriptorExtractor> descriptor; // 构建提取器,默认两者都为 ORB // 如果使用 sift, surf ,之前要初始化nonfree模块 // cv::initModule_nonfree(); // _detector = cv::FeatureDetector::create( "SIFT" ); // _descriptor = cv::DescriptorExtractor::create( "SIFT" ); detector = cv::ORB::create(); descriptor = cv::ORB::create(); vector< cv::KeyPoint > kp1, kp2; //关键点 detector->detect( rgb1, kp1 ); //提取关键点 detector->detect( rgb2, kp2 ); cout<<"Key points of two images: "<<kp1.size()<<", "<<kp2.size()<<endl; // 可视化, 显示关键点 cv::Mat imgShow; cv::drawKeypoints( rgb1, kp1, imgShow, cv::Scalar::all(-1), cv::DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS ); cv::namedWindow("Keypoints",0); cv::imshow( "keypoints", imgShow ); cv::imwrite( "./data/keypoints.png", imgShow ); cv::waitKey(0); //暂停等待一个按键 // 计算描述子 cv::Mat desp1, desp2; descriptor->compute( rgb1, kp1, desp1 ); descriptor->compute( rgb2, kp2, desp2 ); // 匹配描述子 vector< cv::DMatch > matches; cv::BFMatcher matcher; matcher.match( desp1, desp2, matches ); cout<<"Find total "<<matches.size()<<" matches."<<endl; // 可视化:显示匹配的特征 cv::Mat imgMatches; cv::drawMatches( rgb1, kp1, rgb2, kp2, matches, imgMatches ); cv::namedWindow("matches",0); cv::imshow( "matches", imgMatches ); cv::imwrite( "./data/matches.png", imgMatches ); cv::waitKey( 0 ); // 筛选匹配,把距离太大的去掉 // 这里使用的准则是去掉大于四倍最小距离的匹配 vector< cv::DMatch > goodMatches; double minDis = 9999; for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { if ( matches[i].distance < minDis ) minDis = matches[i].distance; } cout<<"min dis = "<<minDis<<endl; for ( size_t i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ ) { if (matches[i].distance < 10*minDis) goodMatches.push_back( matches[i] ); } // 显示 good matches cout<<"good matches="<<goodMatches.size()<<endl; cv::drawMatches( rgb1, kp1, rgb2, kp2, goodMatches, imgMatches ); cv::namedWindow("good matches",0); cv::imshow( "good matches", imgMatches ); cv::imwrite( "./data/good_matches.png", imgMatches ); cv::waitKey(0); // 计算图像间的运动关系 // 关键函数:cv::solvePnPRansac() // 为调用此函数准备必要的参数 // 第一个帧的三维点 vector<cv::Point3f> pts_obj; // 第二个帧的图像点 vector< cv::Point2f > pts_img; // 相机内参,使用到结构 CAMERA_INTRINSIC_PARAMETERS C; C.cx = 682.3; C.cy = 254.9; C.fx = 979.8; C.fy = 942.8; C.scale = 1000.0; for (size_t i=0; i<goodMatches.size(); i++) { // query 是第一个, train 是第二个 cv::Point2f p = kp1[goodMatches[i].queryIdx].pt; // 获取d是要小心!x是向右的,y是向下的,所以y才是行,x是列! ushort d = depth1.ptr<ushort>( int(p.y) )[ int(p.x) ]; if (d == 0) continue; pts_img.push_back( cv::Point2f( kp2[goodMatches[i].trainIdx].pt ) ); // 将(u,v,d)转成(x,y,z) cv::Point3f pt ( p.x, p.y, d ); // 深度值/scale = z cv::Point3f pd = point2dTo3d( pt, C ); pts_obj.push_back( pd ); } //使用到结构 double camera_matrix_data[3][3] = { {C.fx, 0, C.cx}, {0, C.fy, C.cy}, {0, 0, 1} }; // 构建相机矩阵 cv::Mat cameraMatrix( 3, 3, CV_64F, camera_matrix_data ); cv::Mat rvec, tvec, inliers; // 求解pnp cv::solvePnPRansac( pts_obj, pts_img, cameraMatrix, cv::Mat(), rvec, tvec, false, 100, 1.0, 0.95, inliers ,cv::SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE); // 求旋转向量和平移向量,旋转矩阵 cout<<"inliers: "<<inliers.rows<<endl; cout<<"R="<<rvec<<endl; cout<<"t="<<tvec<<endl;
//旋转矩阵
cv::Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues(rvec,R);
cout<<"R_matrix="<<R<<endl;
// 画出inliers匹配 vector< cv::DMatch > matchesShow; for (size_t i=0; i<inliers.rows; i++) { matchesShow.push_back( goodMatches[inliers.ptr<int>(i)[0]] ); } cv::drawMatches( rgb1, kp1, rgb2, kp2, matchesShow, imgMatches ); cv::namedWindow("inlier matches",0); cv::imshow( "inlier matches", imgMatches ); cv::imwrite( "./data/inliers.png", imgMatches ); cv::waitKey( 0 ); return 0; }
使用到结构,和将旋转向量转为旋转矩阵的函数cv::Rodrigues()
OpenCV会利用一种“随机采样一致性”(Random Sample Consensus)的思路(见https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RANSAC)
cv::solvePnPRansac()函数 https://blog.csdn.net/jay463261929/article/details/53818611
和src,include文件同一文件夹下的CMakeLists.txt
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED( VERSION 2.8 ) PROJECT( slam ) SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++") SET( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug ) SET(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/bin) #可执行文件输出的文件夹 SET(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib) #库函数编译输出位置 INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES( ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include ) #头文件 LINK_DIRECTORIES( ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib) #使用编译好的库文件libslamBase.a ADD_SUBDIRECTORY( ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/src ) #可执行程序

注意:当lib 文件下已经有编译好的库库文件libslamBase.a,可以将第一个CMakeLists.txt中ADD_LIBRARY( slambase slamBase.cpp ) TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES( slambase ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${PCL_LIBRARIES} )去掉,因为slamBase.cpp已经被编译。
将第二个CMakeLists.txt中SET(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib) 去掉。
