20182318 哈夫曼编码测试
1.实验内容
设有字符集:S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n.o.p.q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z}。
给定一个包含26个英文字母的文件,统计每个字符出现的概率,根据计算的概率构造一颗哈夫曼树。
并完成对英文文件的编码和解码。
要求:
- 准备一个包含26个英文字母的英文文件(可以不包含标点符号等),统计各个字符的概率
- 构造哈夫曼树
- 对英文文件进行编码,输出一个编码后的文件
- 对编码文件进行解码,输出一个解码后的文件
2. 实验过程及结果
过程:
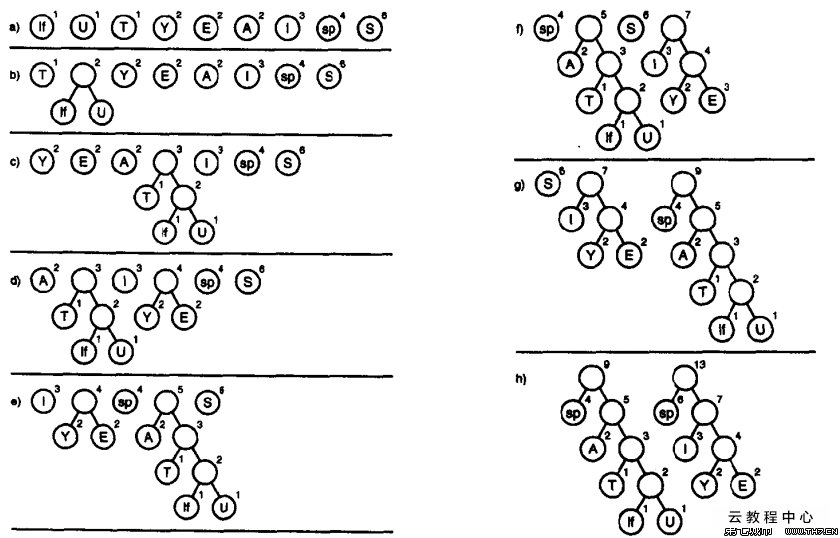
1,哈夫曼树的建立
- 将所有带权值的结点按权值从小到大排列(这里的权值我们用每个字符出现的概率来代替);
- 依次选取权值最小的结点放在树的底部,权值小的在左边(取出的结点相当于从这些结点的集合中剔除);
- 生成一个新节点作为这两个结点的父节点,且父节点的权值等于这两个结点权值之和,然后要把这个新结点放回我们需要构成树的结点中,继续进行排序;
- 重复上述2、3步骤,直至全部节点形成一棵树,此树便是哈夫曼树,最后生成的结点即为根节点。这样构成的哈夫曼树,所有的存储有信息的结点都在叶子结点上。
主要代码
package hafuman;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class harfmain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
char[] S = new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'};
double[] sum = new double[26];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
sum[i] = 0;
}
File file = new File("D:\", "20182318wangzhenao.txt");
Reader reader2 = new FileReader(file);
String result = "";
String result1 = "";
String result2 = "";
while (reader2.ready()) {
result += (char) reader2.read();
}
char[] text = result.toCharArray();
for (int j = 0; j < text.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < S.length; k++) {
if (text[j] == S[k] || text[j] == (S[k] - 32)) {
sum[k]++;
count++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i] / count;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i<sum.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(S[i]+":"+sum[i]);
}
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (int i = 0; i < sum.length; i++) {
nodes.add(new Node(S[i], sum[i]));
}
harf h = new harf();
Node root = h.createTree(nodes);
h.setCode(root);
String s = h.toHufmCode(result, root);
System.out.println(s);
File file1 = new File("D:\", "hello world.txt");
Writer writer2 = new FileWriter(file1);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer2);
bufferedWriter.write("编码后的哈夫曼为"+s, 0, s.length());
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
String a ="哈夫曼解码后"+h.CodeToString(s,root);
File file2 = new File("D:\", "hello world1.txt");
Writer writer3 = new FileWriter(file2);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter1 = new BufferedWriter(writer3);
bufferedWriter1.write(a, 0, a.length());
bufferedWriter1.flush();
bufferedWriter1.close();
Reader reader3 = new FileReader(file1);
Reader reader4 = new FileReader(file2);
while (reader3.ready()) {
result1 += (char) reader3.read();
}
System.out.println(result1);
while (reader4.ready()) {
result2 += (char) reader4.read();
}
System.out.println(result2);
}
}
package hafuman;
public class Node<E> {
E data;
public String code = "";
double weight;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(E data, double weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
package hafuman;
import java.util.List;
public class harf {
Node createTree(List<Node> nodes) {
// ֻҪnodes�����л���2�����ϵĽڵ�
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
quickSort(nodes);
//��ȡȨֵ��С�������ڵ�
Node left = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
Node right = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 2);
//�����½ڵ㣬�½ڵ��ȨֵΪ�����ӽڵ��Ȩֵ֮��
Node parent = new Node(null, left.weight + right.weight);
//���½ڵ���Ϊ����Ȩֵ��С�ڵ�ĸ��ڵ�
parent.leftChild = left;
parent.rightChild = right;
//ɾ��Ȩֵ��С�������ڵ�
nodes.remove(nodes.size() - 1);
nodes.remove(nodes.size() - 1);
//���½ڵ���뵽������
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
private static void subSort(List<Node> nodes, int start, int end) {
if (start < end) {
// �Ե�һ��Ԫ����Ϊ�ֽ�ֵ
Node base = nodes.get(start);
// i������������������ڷֽ�ֵ��Ԫ�ص�����
int i = start;
// j���ұ߿�ʼ����������С�ڷֽ�ֵ��Ԫ�ص�����
int j = end + 1;
while (true) {
// �ҵ����ڷֽ�ֵ��Ԫ�ص�����������i�Ѿ�����end��
while (i < end && nodes.get(++i).weight >= base.weight)
;
// �ҵ�С�ڷֽ�ֵ��Ԫ�ص�����������j�Ѿ�����start��
while (j > start && nodes.get(--j).weight <= base.weight)
;
if (i < j) {
swap(nodes, i, j);
} else {
break;
}
}
swap(nodes, start, j);
//�ݹ����������
subSort(nodes, start, j - 1);
//�ݹ��ұ�������
subSort(nodes, j + 1, end);
}
}
public static void quickSort(List<Node> nodes) {
subSort(nodes, 0, nodes.size() - 1);
}
private static void swap(List<Node> nodes, int i, int j) {
Node tmp;
tmp = nodes.get(i);
nodes.set(i, nodes.get(j));
nodes.set(j, tmp);
}
public void setCode(Node root) {
if (root.leftChild != null) {
root.leftChild.code = root.code + "0";
setCode(root.leftChild);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
root.rightChild.code = root.code + "1";
setCode(root.rightChild);
}
}
public void output(Node root) {
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
System.out.println(root.data + ": " +root.code);
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
output(root.leftChild);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
output(root.rightChild);
}
}
private String hfmCodeStr = "";// �������������ӳɵ��ַ���
/**
* ����
*/
public String toHufmCode(String str,Node root) {
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i) ;
search(root, c);
}
return hfmCodeStr;
}
private void search(Node root, char c) {
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
if (c == (char)root.data) {
hfmCodeStr += root.code; // �ҵ��ַ����������������ƴ�ӵ����շ��ض������ַ����ĺ���
}
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
search(root.leftChild, c);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
search(root.rightChild, c);
}
}
String result="";
boolean target = false; // ������
public String CodeToString(String codeStr,Node root) {
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
while(end <= codeStr.length()){
target = false;
String s = codeStr.substring(start, end);
matchCode(root, s); // ����
// ÿ����һ���ַ���start�����
if(target){
start = end;
}
end++;
}
return result;
}
private void matchCode(Node root, String code){
if (root.leftChild == null && root.rightChild == null) {
if (code.equals(root.code)) {
result += root.data; // �ҵ���Ӧ���ַ���ƴ�ӵ������ַ�����
target = true; // ��־��Ϊtrue
}
}
if (root.leftChild != null) {
matchCode(root.leftChild, code);
}
if (root.rightChild != null) {
matchCode(root.rightChild, code);
}
}
}
运行结果
