来源:中国大学MOOC 曹健 《TensorFlow笔记》
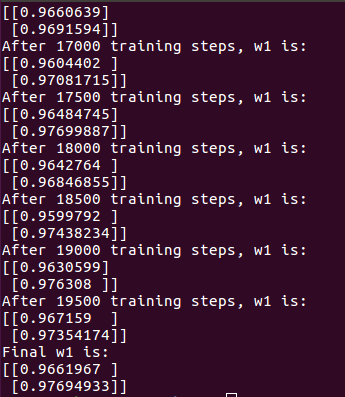
#coding:utf-8 #利润大于成本,希望模型尽可能往多了预测 #0导入模块,生成数据集 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np BATCH_SIZE = 8 SEED = 23455 COST = 1 PROFIT = 9 rdm = np.random.RandomState(SEED) X = rdm.rand(32,2) Y_= [[x1+x2+(rdm.rand()/10.0-0.05)] for (x1,x2) in X] #1定义神经网络的输入、参数和输出,定义前向传播过程 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2)) y_= tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1)) w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,1], stddev=1, seed=1)) y = tf.matmul(x,w1) #2定义损失函数及反向传播方法 #定义损失函数使得预测少了的损失大,于是模型应该偏向多的方向预测 loss_mse = tf.reduce_sum(tf.where(tf.greater(y,y_),(y-y_)*COST,(y_-y)*PROFIT)) train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_mse) #3生成会话,训练STEPS轮 with tf.Session() as sess: init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init_op) STEPS = 20000 for i in range(STEPS): start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 32 end = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 32 + BATCH_SIZE sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x:X[start:end], y_:Y_[start:end]}) if i % 500 == 0: print "After %d training steps, w1 is:" % (i) print sess.run(w1) print "Final w1 is: ",sess.run(w1)
若成本大于利润,则会发现模型会往小的方向预测。
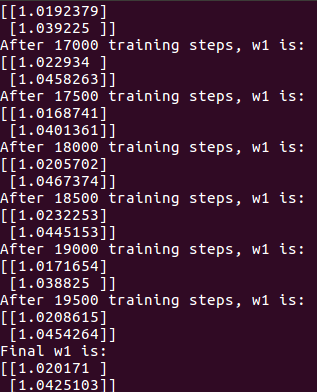
将COST=9,PROFIT=1,结果如下: