1. 引言
在实际的项目中,树还是用的比较多的一种,尤其是对于具有层次结构的数据。相信很多人都学过树的遍历,比如先序遍历,后序遍历等,利用递归还是很容易理解的。
今天给大家介绍下二叉树的几种遍历算法,包括递归和非递归的实现。
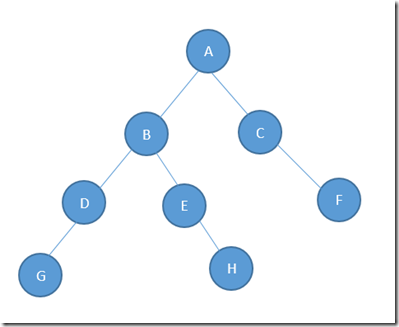
首先建立一棵二叉树 如:
[DebuggerDisplay("Value={Value}")] public class Tree { public string Value; public Tree Left; public Tree Right; } public static Tree CreatFakeTree() { Tree tree = new Tree() {Value = "A"}; tree.Left = new Tree() { Value = "B", Left = new Tree() {Value = "D", Left = new Tree() {Value = "G"}}, Right = new Tree() {Value = "E", Right = new Tree() {Value = "H"}} }; tree.Right = new Tree() {Value = "C", Right = new Tree() {Value = "F"}}; return tree; }
一棵简单的二叉树
2. 先序遍历
先序遍历还是很好理解的,一次遍历根节点,左子树,右子数
递归实现
public static void PreOrder(Tree tree) { if (tree == null) return; System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value); PreOrder(tree.Left); PreOrder(tree.Right); }
非递归实现
public static void PreOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree) { if(tree == null) return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>(); Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any()) { if (node != null) { stack.Push(node); System.Console.WriteLine(node.Value); node = node.Left; } else { var item = stack.Pop(); node = item.Right; } } }
3. 中序遍历
递归实现
public static void InOrder(Tree tree) { if(tree == null) return; InOrder(tree.Left); System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value); InOrder(tree.Right); }
非递归实现
public static void InOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree) { if (tree == null) return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>(); Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any()) { if (node != null) { stack.Push(node); node = node.Left; } else { var item = stack.Pop(); System.Console.WriteLine(item.Value); node = item.Right; } } }
4. 后序遍历
递归实现
public static void PostOrder(Tree tree) { if (tree == null) return; PostOrder(tree.Left); PostOrder(tree.Right); System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value); }
非递归实现 比前两种稍微复杂一点。要保证左右节点都被访问后,才能访问根节点。这里给出两种形式。
public static void PostOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree) { if (tree == null) return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>(); Tree node = tree; Tree pre = null; stack.Push(node); while (stack.Any()) { node = stack.Peek(); if ((node.Left == null && node.Right == null) || (pre != null && (pre == node.Left || pre == node.Right))) { System.Console.WriteLine(node.Value); pre = node; stack.Pop(); } else { if(node.Right != null) stack.Push(node.Right); if(node.Left != null) stack.Push(node.Left); } } } public static void PostOrderNoRecursion2(Tree tree) { HashSet<Tree> visited = new HashSet<Tree>(); System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>(); Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any()) { if (node != null) { stack.Push(node); node = node.Left; } else { var item = stack.Peek(); if (item.Right != null && !visited.Contains(item.Right)) { node = item.Right; } else { System.Console.WriteLine(item.Value); visited.Add(item); stack.Pop(); } } } }
5. 层序遍历
层序遍历就是按照层次由左向右输出
public static void LevelOrder(Tree tree) { if(tree == null) return; Queue<Tree> queue = new Queue<Tree>(); queue.Enqueue(tree); while (queue.Any()) { var item = queue.Dequeue(); System.Console.Write(item.Value); if (item.Left != null) { queue.Enqueue(item.Left); } if (item.Right != null) { queue.Enqueue(item.Right); } } }
6. Z-型层序遍历
Z-层序遍历就是奇数层按照由左向右输出,偶数层按照由右向左输出,这里定义了几个辅助函数,比如计算节点所在的层次。算法思想是按照层次保存树形节点,应该是有更加优化的算法,希望大家指出。
public static int GetDepth(Tree tree, Tree node) { if (tree == null) return 0; if (tree == node) return 1; if (tree.Left == node || tree.Right == node) return 2; int lDepth = GetDepth(tree.Left, node); lDepth = lDepth == 0 ? 0 : lDepth + 1; int rDepth = GetDepth(tree.Right, node); rDepth = rDepth == 0 ? 0 : rDepth + 1; return lDepth >= rDepth ? lDepth : rDepth; } public static void Z_LevelOrder(Tree tree, Dictionary<int, List<Tree>> dictionary) { if (tree == null) return; Queue<Tree> queue = new Queue<Tree>(); queue.Enqueue(tree); while (queue.Any()) { var item = queue.Dequeue(); var depth = GetDepth(tree, item); List<Tree> list; if (!dictionary.TryGetValue(depth, out list)) { list = new List<Tree>(); dictionary.Add(depth, list); } list.Add(item); if (item.Left != null) { queue.Enqueue(item.Left); } if (item.Right != null) { queue.Enqueue(item.Right); } } } public static void Z_LevelOrder(Tree tree) { if (tree == null) return; Dictionary<int, List<Tree>> dictionary = new Dictionary<int, List<Tree>>(); Z_LevelOrder(tree, dictionary); foreach (KeyValuePair<int, List<Tree>> pair in dictionary) { if (pair.Key%2 == 0) { pair.Value.Reverse(); } pair.Value.ForEach(t=> { System.Console.Write(t.Value); }); } }