一 URL补充
二 Views试图函数
一 URL补充
1 MTV模型
2 django建立流程(用命令版)
(1)django-admin startproject projectname
(2)python manage.py startapp appname
(3)python manage.py runserver IP PORT
3 url配置(urls.py)
功能:建立起URL与视图函数的映射关系。
url:http://127.0.0.1:8080/blog/articles/2003/05?a=1&b=2
url(正则表达式(规则),视图函数) 匹配字符串:用户输入的url对应的路径:“/blog/articles/2003/05”
注意点:
(1) 出现覆盖现象的情况,匹配第一个url
(2) 无名分组 url(r'^articles/(d{4})/(d{2})$', views.year_month), # year(requset,1990,12) 按位置传参数
(3) 有名分组 url(r'^articles/(?P<year>d{4})/(?P<month>d{2})$', views.year_month), # year (requset,year=1990,month=12) 按位置传参数
(4) url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls'))分发
取值:request.POST.get("user")
获取form表单提交的方法:request.method=="POST"
有return 就不往下走 可以去掉else
模板语法两种{{}}
渲染了后再往前端发 render 函数 render函数可以检测模板语法
点击提交 走url 走views 走render函数接着渲染模板(看有无别名) 发往前端
二 视图函数
一定包含两个对象
request------->,请求信息
HttpResponse------->响应内容
render 一个HttpResponse函数也存在render函数里
get 请求的数据放在路径后面
重点 request 里面的哪些信息:
request.GET:GET请求的数据()
request.POST:POST请求的数据()
request.method:请求数据的方式()主要get或者post
request.path:请求路径()与数据无关
根目录 :/(判断根目录)
request.get_full_path()拿到路径后面所有的数据(包括路径)
取一个键下的多个值:request.POST.getlist("hobby")
render 函数 render(request, template_name[, context]) 第三个参数是上下文对象
redirect 函数
对比 render与redirect 的区别:
redirect:发送第二次请求,url更新啦
render: 直接返回一个页面内容但是url没有变化(未发送第二次请求)(涉及页面跳转时不用)
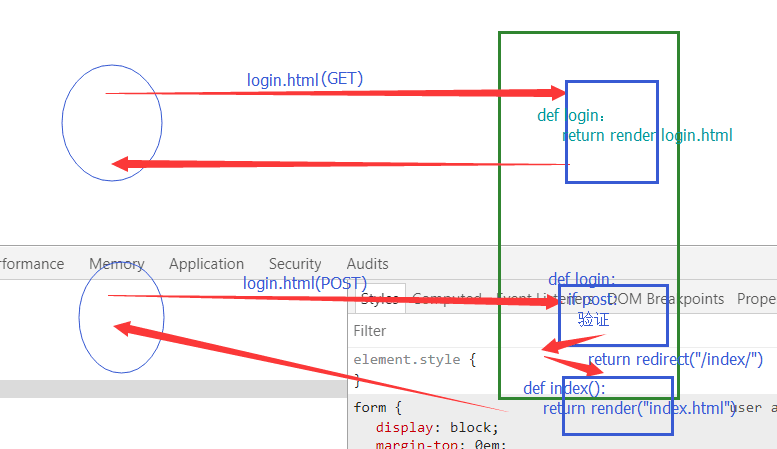
一个小例子:注:跳转是前后都要加/ ,返回时不用加/ 图片用到了分发 例子里没有用到分发
---Model

from django.db import models # Create your models here. import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='day66') cur = conn.cursor() cur.executemany("insert into userinfo values(%s,%s)", [( "yuan", "123"), ( "alex", "456"), ("egon", "789")]) conn.commit() #关闭指针对象 cur.close() #关闭连接对象 conn.close()
---views

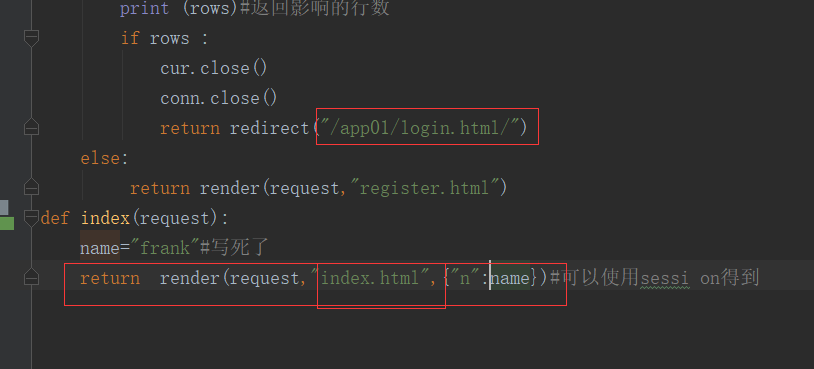
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect # Create your views here. def login(request): print(request.POST) # 这个是获取form表单的提交方法 if request.method=="POST": print(request.POST)#这个是获取form表单的提交方法 username=request.POST.get("user") password=request.POST.get("pwd") if username=="frank" and password=="789": return redirect("/index.html/")#跳转到个人主页 # else:#else 可以去掉啦 # name="frank" return render(request, "login.html") def register(request): if request.method=="POST": username=request.POST.get("user") password=request.POST.get("pwd") # hobby=request.POST.getlist("hobby")#一个键获得多个值时用这种方法 import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='day66') cur = conn.cursor() SQL = "insert into userinfo (name,pwd)values(%s,%s)"; rows = cur.execute(SQL,(username, password)) conn.commit() print (rows)#返回影响的行数 if rows : cur.close() conn.close() return redirect("/login.html/") else: return render(request,"register.html") def index(request): name="frank"#写死了 return render(request,"index.html",{"n":name})#可以使用session得到
Template

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> <style> .cc{ margin-left: 250px; margin-top: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cc"> <h1>注册页面</h1> <form action="{% url 'register' %}" method="post"> <p> 姓名:<input type="text" name="user"></p> <p> 密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"></p> <!--<p> 爱好:--> <!--<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="basketball">篮球--> <!--<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="shuangseqiu ">双色球--> <!--<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" value="football">足球--> <!--</p>--> <p><input type="submit"></p></div> </form> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> <style> .cc{ margin-top: 200px; margin-left: 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cc"> <h1>登陆页面</h1> <form action="{% url "login" %}" method="post"> <p>姓名:<input type="text" name="user"></p> <p>密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"></p> <p><input type="submit"></p> </form> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> <style> .cc{ margin-right: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="cc"> <h1>hello{{ n }} </h1> <h1>欢迎回来</h1> </div> </body> </html>
